示意图:
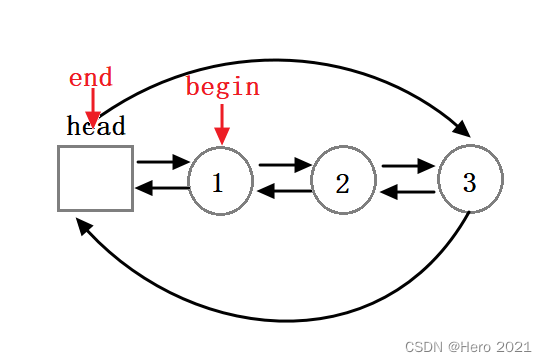
迭代器
正向迭代器类
我们之前所理解的是:迭代器理解为像指针一样的东西,但是在list中有些不同
// 迭代器逻辑
while(it!=l.end())
{
*it; // 解引用取数据
++it;// 自加到达下一个位置
}
我们可以来观察一下STL源码中大佬是怎么封装的:
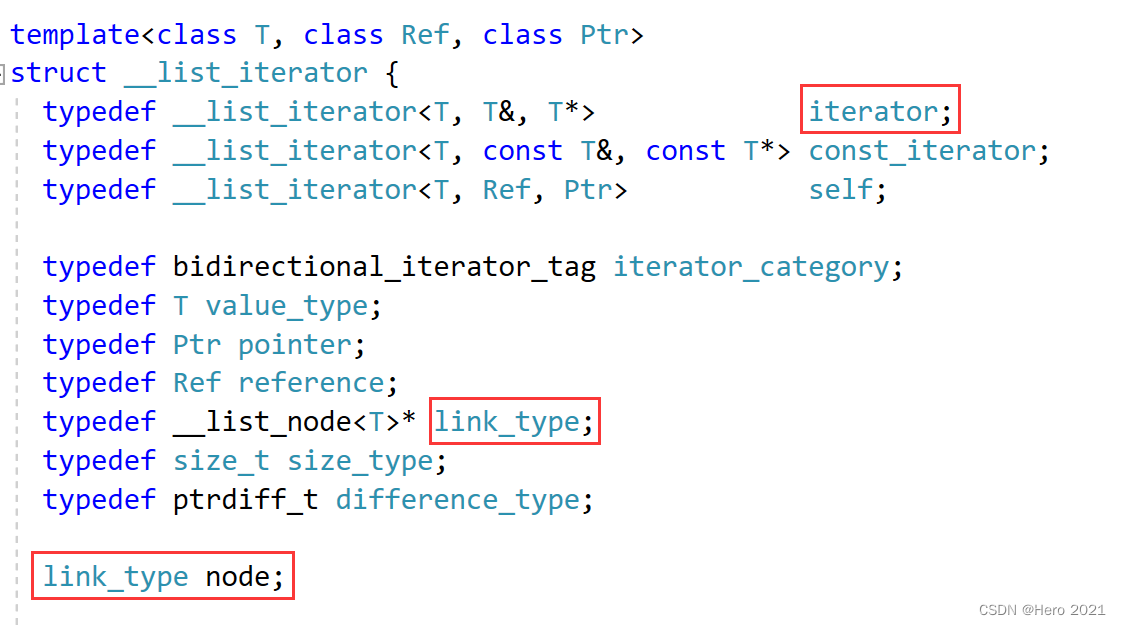
我们可以看到,只有一个成员,那就是一个结点的指针node,link_type又是一个自定义类型的指针,我们原生类型的指针在vector或者string中是可以直接typedef成为迭代器的,但是list底层是双链表,数据结构并非连续的,所以直接*it或者++it是不能够完成迭代器的任务的,但是C++中支持对于自定义类型的运算符重载,我们可以对解引用和自加两个运算符重载。
++it:就是当前指针存放下一个结点的地址
*it:解引用当前节点,取出值来
迭代器中,拷贝构造、运算符赋值重载、析构都不需要自己实现,使用默认生成的即可(即浅拷贝),因为迭代器是用自定义类型的指针封装的,访问修改链表,节点属于链表,不属于迭代器,所以不用管它。
我们在传入const版本的list时,list是const对象,需要的是const_iterator,这里会出现错误,不能将const的list的迭代器传给普通迭代器。如下所示例子:
void print_list(const list<int>& lt)
{
// lt.begin()是const迭代器(只可读)
// it是普通迭代器(可读可写)
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
}
现在我们如何实现一个const的迭代器呢?
意思就是只可以读不能够写。可以++,- -,*解引用,但是解引用时不能修改数据。
可以想到这种写法:
const T& operator*()const
{
return _node->_data;
}
T& operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
但是并不是迭代器是const的,而是我们传入的list容器是const版本的。
我们可以将写一个const_iterator 的类版本,这样普通迭代器和const迭代器就不是一个类型了,是两个不同的类型了,这样会造成代码冗余。
template<class T>
struct __const_list_iterator
{
//...
// __list_iterator全部替换为__const_list_iterator
};
优化:
增加一个模板参数class Ref
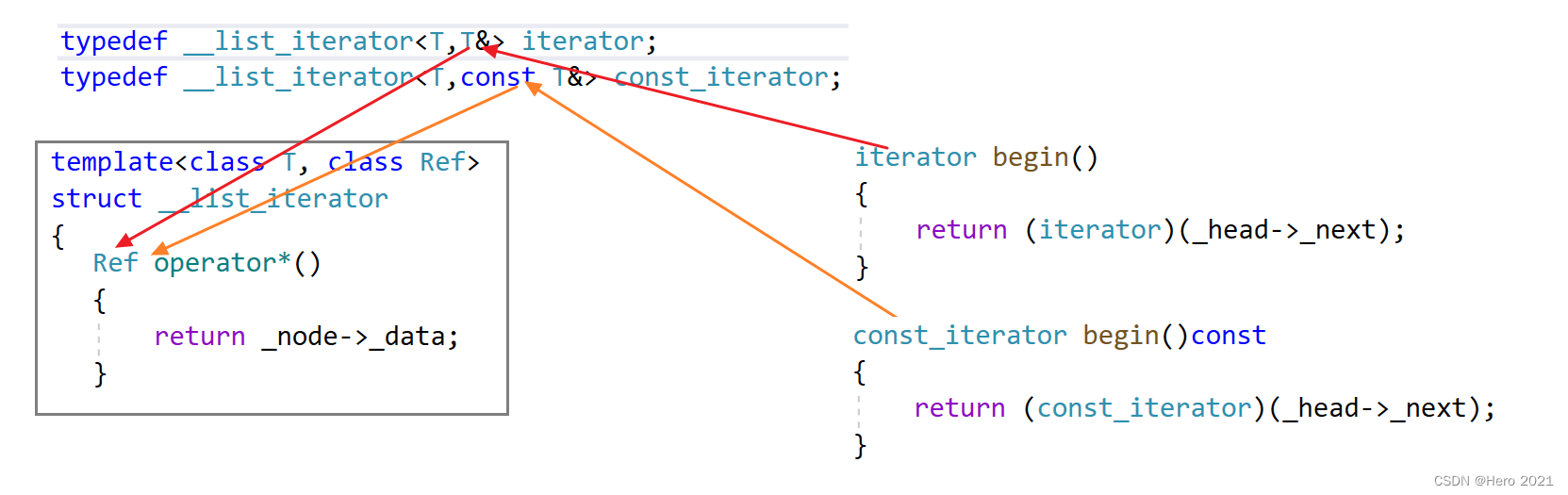
这样第一个模板参数都是T,我们可以根据传入的第二个参数来推出时T&还是const T&,本来我们是要实现两个类的,现在只需要增加一个模板参数即可,这里体现出了C++泛型的优势!
迭代器我们说,它是像指针一样的东西,如果它是指向的一个结构体,需要用它的成员变量,我们还需要重载->箭头
struct Date {
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
Date(int year = 0, int month = 0, int day = 0)
//这里要给默认参数,因为需要构建一个哨兵位头结点
:_year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
};
void test_list2()
{
list<Date> lt;
lt.push_back(Date(2022, 1, 1));
lt.push_back(Date(2022, 1, 2));
lt.push_back(Date(2022, 1, 3));
lt.push_back(Date(2022, 1, 4));
// 现在来遍历日期类
list<Date>::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
cout << (*it)._year << "/" << (*it)._month << "/" << (*it)._day << endl;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
这里的*解引用然后再去.,我们可以重载->,让他可以去调用结构体的成员,这样更加快捷高效方便。
T* operator->()
{
return &(_node->_data);
}
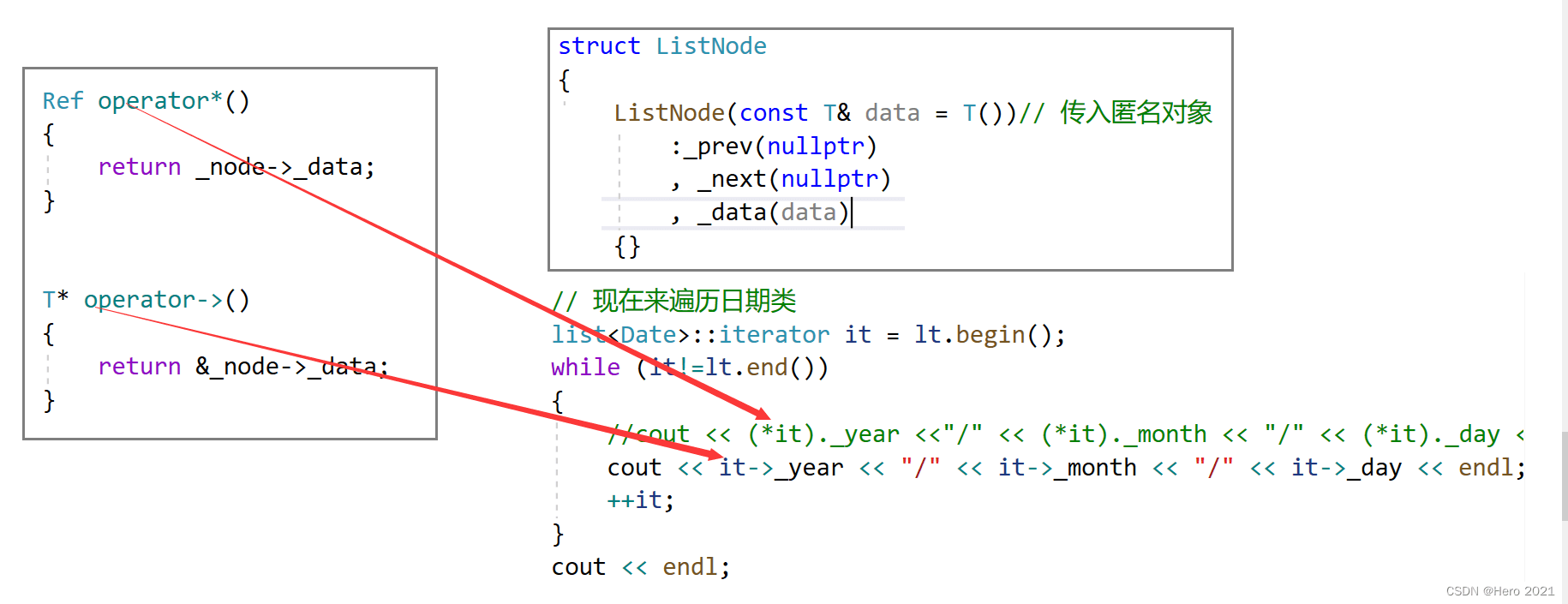
进一步解释:
*it调用operator*,返回一个结点对象,对象再.操作,拿到数据
it->调用operator->,返回对象的指针,(这里返回的是原生指针)再通过->调用用结构体成员,这里实际上应该是it->->_year,但是这样写,可读性很差,所以编译器做了一个优化,省略了一个->,所以所有的类型只要想要重载->,都会这样优化省略一个->
这里又会衍生出一个问题,那就是如果使用const_iterator,使用->也会修改数据,所以再增加一个模板参数
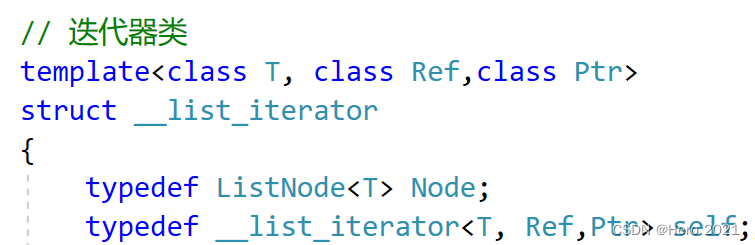
// 正向迭代器类
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __list_iterator
{
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;// 再次typedef,方便后续的修改
Node* _node;
__list_iterator(Node* x)// 迭代器的实质,就是自定义类型的指针
:_node(x)
{}
// ++it 返回++之后的引用对象
self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
// it++ 返回++之前的对象
self operator++(int)
{
self tmp(this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
// --it
self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
// it--
self operator--(int)
{
self tmp(this);
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}
// 返回引用,可读可写
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
// 返回对象的指针
Ptr operator->()
{
return &(_node->_data);
}
bool operator!=(const self& it)const
{
return _node != it._node;
}
bool operator==(const self& it)const
{
return _node == it._node;
}
};
反向迭代器类
实质:对于正向迭代器的一种封装
反向迭代器跟正想迭代器区别就是++,- -的方向是相反的
所以反向迭代器封装正向迭代器即可,重载控制++,- -的方向
#pragma once
// reverse_iterator.h
namespace sjj
{
template <class Iterator, class Ref, class Ptr>
class reverse_iterator
{
typedef reverse_iterator<Iterator,Ref,Ptr> self;
public:
reverse_iterator(Iterator it)
:_it(it)
{}
// 比较巧妙,解引用取的是当前位置的前一个位置的数据
// operator*取前一个位置, 主要就是为了让反向迭代器开始和结束跟正向迭代器对称
Ref operator *()
{
Iterator tmp = _it;
return *--tmp;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &(operator*());
}
self& operator++()
{
--_it;
return *this;
}
self operator++(int)
{
self tmp = *this;
--_it;
return tmp;
}
self& operator--()
{
++_it;
return *this;
}
self operator--(int)
{
self tmp = *this;
++_it;
return tmp;
}
bool operator!=(const self& rit)
{
return _it != rit._it;
}
bool operator==(const self& rit)
{
return _it == rit._it;
}
private:
Iterator _it;
};
}
push_back尾插函数
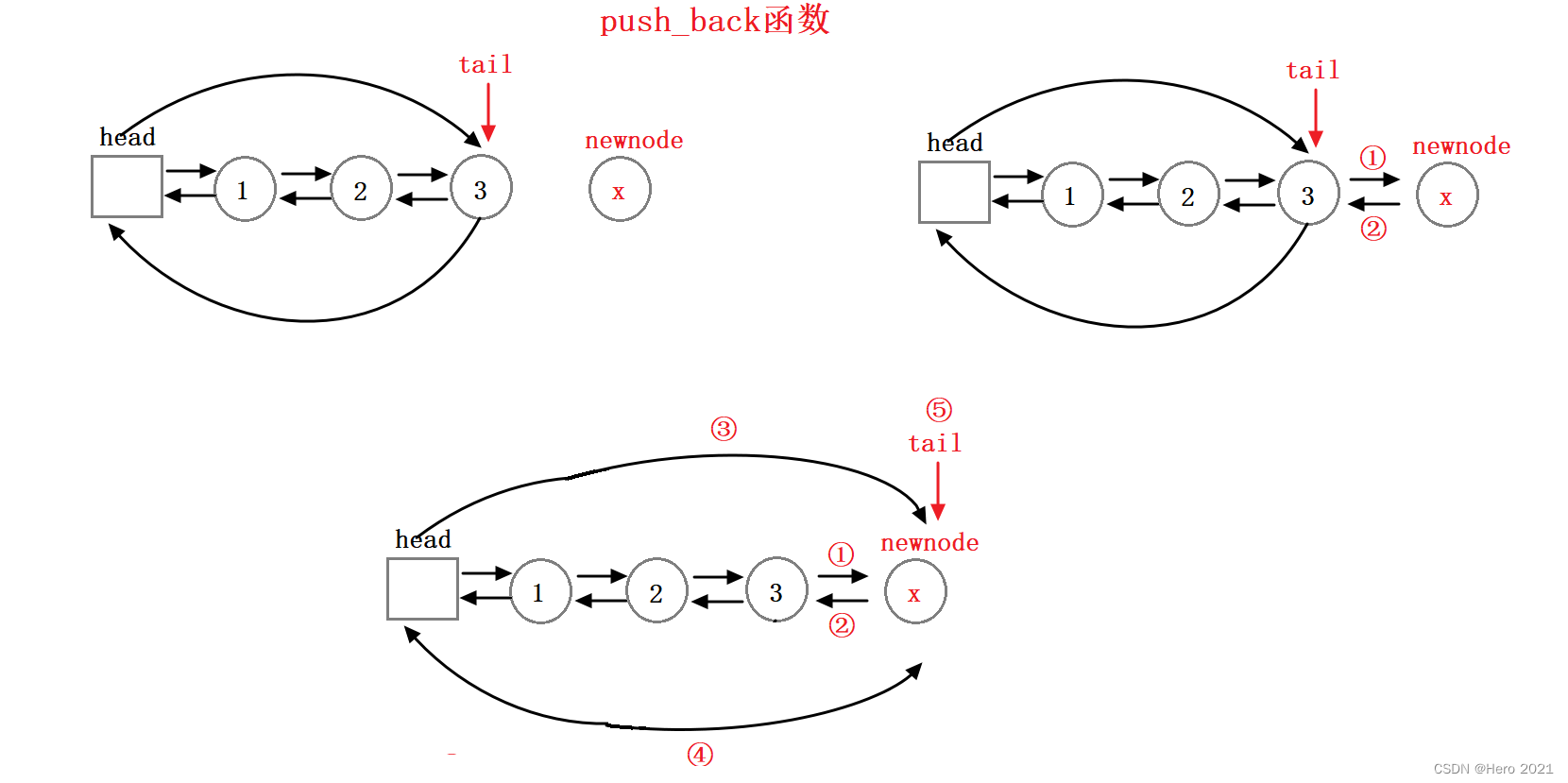
void push_back(const T& x)
{
// 先找尾记录
/*Node* tail = _head->_prev;
Node* newnode = new Node(x);
tail->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = tail;
_head->_prev = newnode;
newnode->_next = _head;
tail = tail->_next;*/
// 复用insert函数
insert(end(), x);
}
push_front头插函数
// 头插
void push_front(const T& x)
{
// 复用insert函数
insert(begin(), x);
}
insert插入函数
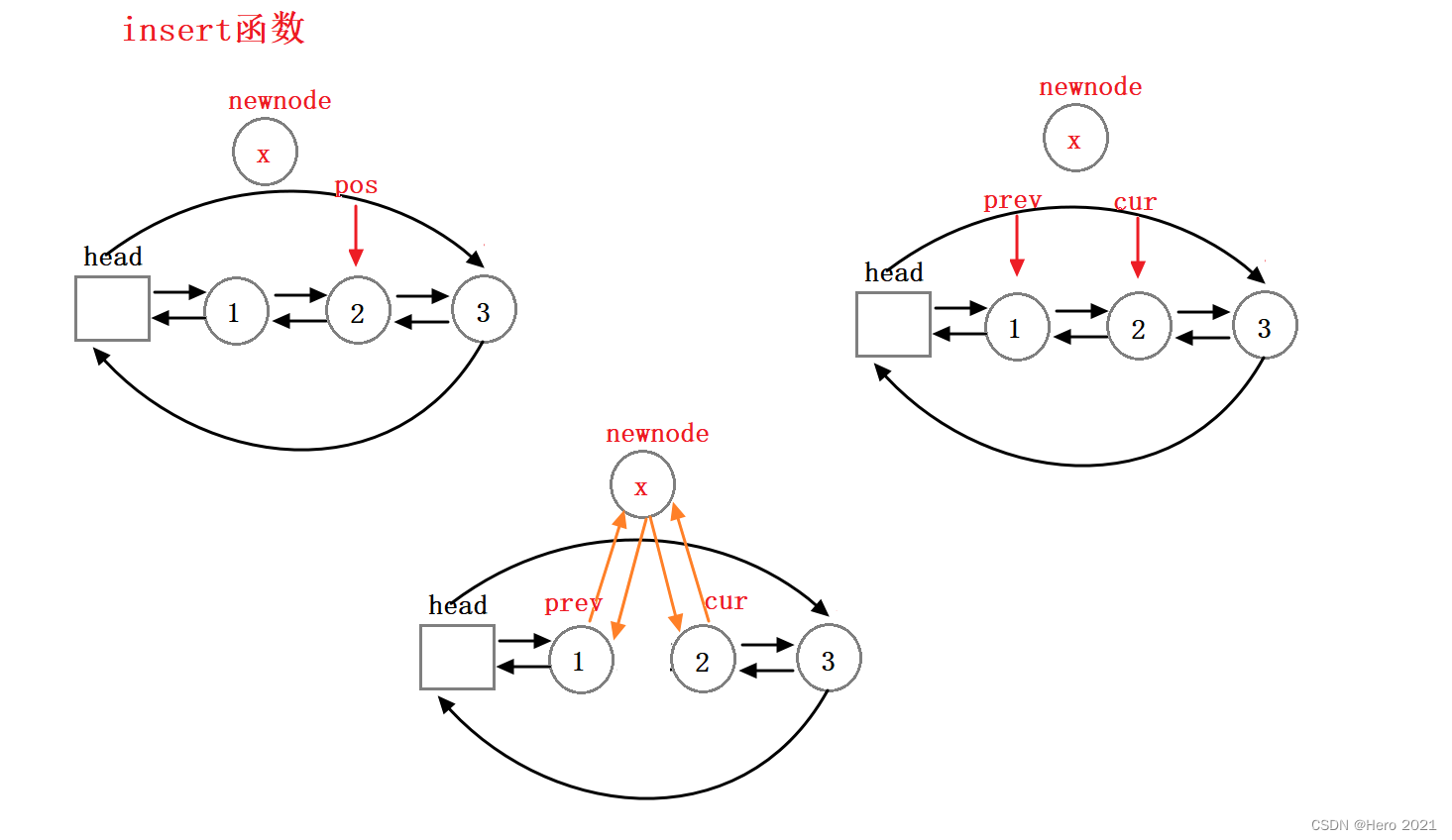
// 在pos位置前插入
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
Node* newnode = new Node(x);
prev->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = prev;
newnode->_next = cur;
cur->_prev = newnode;
return iterator(newnode);// 返回新插入结点位置的迭代器
}
注意:这里list的insert函数,pos位置的迭代器不会失效,因为pos指向的位置不会改变,vector中迭代器失效的原因是因为挪动数据,导致指向的位置的数据发生变化。
erase删除函数
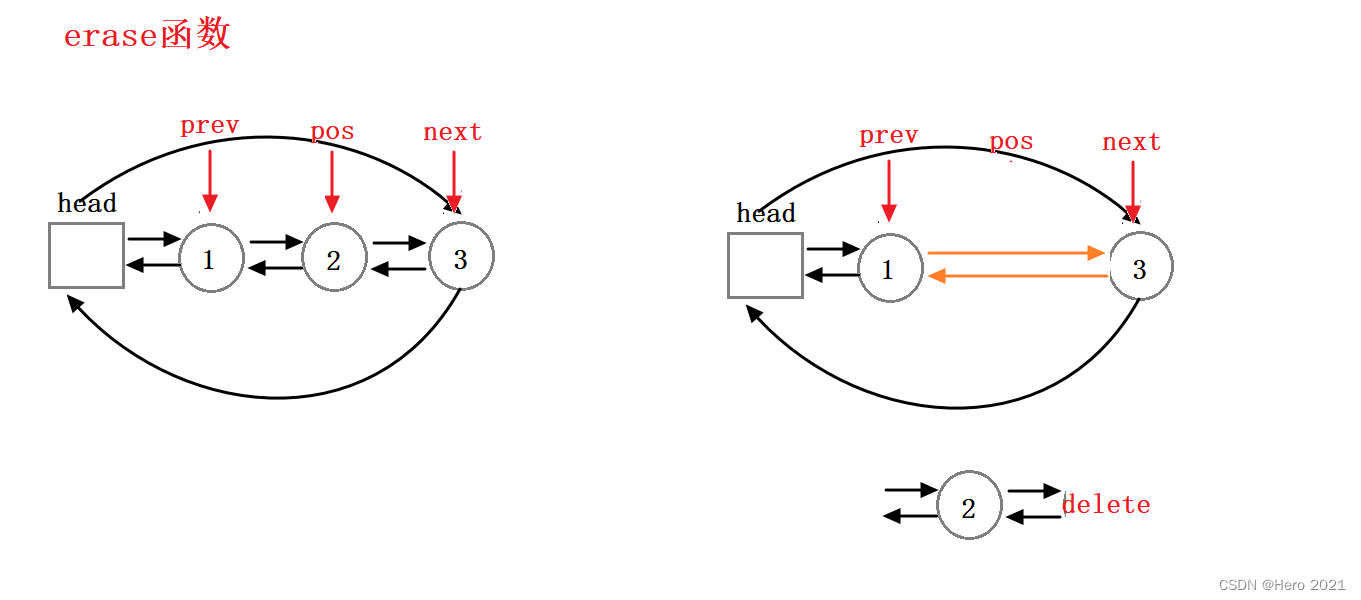
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos != end());//不能将哨兵位的头结点给删除了
Node* prev = pos._node->_prev;
Node* next = pos._node->_next;
delete pos._node;
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
return iterator(next);// 返回pos位置的下一个位置的迭代器
}
注意:这里的pos位置的迭代器一定会失效,因为都已经将结点给删除了。
pop_front函数
// 复用erase函数
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}
pop_back函数
// 复用erase函数
void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());
}
构造函数
list()
{
_head = new Node();
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
}
// 函数模板,用迭代器区间进行初始化
template<class InputIterator>
list(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
_head = new Node();
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
++first;
}
}
list(size_t n, const T& val = T())
{
_head = new Node();
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
push_back(val);
}
}
注意:

这两个构造函数一起使用可能会存在问题,填充版本和构造器版本可能会存在冲突,如下例子:
struct Date {
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
Date(int year = 0, int month = 0, int day = 0)//这里要给默认参数,因为有一个哨兵位头结点需要初始化
:_year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
};
void test_list4()
{
list<Date> lt1(5, Date(2022, 9, 9));
for (auto e : lt1)
{
cout << e._year << "/" << e._month << "/" << e._day << endl;
}
cout << endl;
list<int> lt2(5, 1);
for (auto e : lt2)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
对于这两个:在实例化时会调用更加匹配的构造函数初始化
list lt1(5, Date(2022, 9, 9))它会正常调用list(size_t n, const T& val = T())
list lt2(5, 1)而它会将5和1推演成两个int,进而去匹配这个迭代器版本的构造函数
template < class InputIterator> list(InputIterator first, InputIterator last),但是与我们的本意,用n个val初始化原意相背,而其中有个*first,这里int去解引用必会报错
改进:再多提供第一个参数是int重载版本的list(int n, const T& val = T())构造函数
list(int n, const T& val = T())
{
_head = new Node();
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
push_back(val);
}
}
析构函数
~list()
{
clear();
// 析构与clear不同,要将哨兵位头结点给删除了
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}
list拷贝构造函数
浅拷贝会崩溃的原因是,同一块空间被析构了两次,所以我们要完成深拷贝
传统写法
// 传统写法
// lt2(lt1)
list(const list<T>& lt)
{
_head = new Node();
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
for (auto e : lt)
{
push_back(e);
}
}
注意: 因为要调用push_back函数,push_back的前提是这个链表(lt2)已经被初始化了,所以必须要先搞一个哨兵位头结点,不然会崩溃
现代写法
// 函数模板
template<class InputIterator>
list(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
_head = new Node();
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
++first;
}
}
// lt2(lt1)
list(const list<T>& lt)
{
_head = new Node();
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
list<T> tmp(lt.begin(), lt.end());
std::swap(_head, tmp._head);
}
注意:lt2需要一个哨兵位头结点
list赋值重载函数
传统写法
// lt2=lt1
list<T>& operator=(const list<T>& lt)
{
if (this != lt)
{
clear(); // 将lt2清空
for (auto e : lt)// 再将值全部拷贝过去
{
push_back(e);
}
}
return *this;
}
现代写法
// 现代写法
list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt)
{
std::swap(_head, lt._head);
return *this;
}
其他函数
// 清空
void clear()
{
/*
iterator it = begin();
while (it!=end())
{
iterator del = it++;// 利用后置++,返回加加前的迭代器
delete del._node;
}
// 最后剩下哨兵位头结点
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
*/
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
erase(it++); // 也可以复用erase,it++返回加加之前的值
}
}
到此这篇关于C++深入探究list的模拟实现的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C++ list模拟实现内容请搜索服务器之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持服务器之家!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_57675461/article/details/125339737