前言:dp/dip代表独立像素,dpi代表屏幕每英寸像素点的个数,px与dp的转换公式为: px = dp *(dpi / 160)
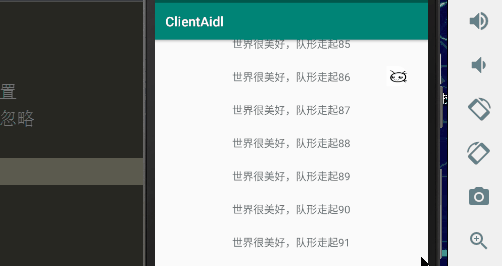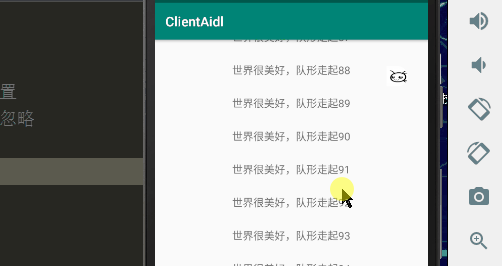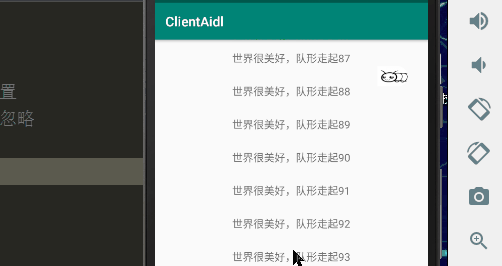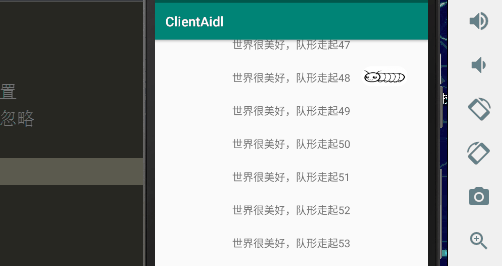
一、效果图
二、源代码
AnimationActivity:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
|
package com.example.duoyi.clientaidl; import android.animation.Animator;import android.animation.ObjectAnimator;import android.support.annotation.NonNull;import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;import android.os.Bundle;import android.support.v7.widget.CardView;import android.support.v7.widget.LinearLayoutManager;import android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView;import android.util.Log;import android.view.View;import android.widget.ImageView; import com.example.duoyi.AnimationAdapter; import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List; public class AnimationActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private static final int MAX_COUNT = 100; private static final String TAG = "AnimationActivity"; RecyclerView rv; CardView cv; ImageView image; ObjectAnimator animator; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_animation); rv = findViewById(R.id.itemRv); cv = findViewById(R.id.expand); image = findViewById(R.id.insect); List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < MAX_COUNT; i++) { list.add("世界很美好,队形走起" + i); } LinearLayoutManager manager = new LinearLayoutManager(this); manager.setOrientation(RecyclerView.VERTICAL); AnimationAdapter adapter = new AnimationAdapter(list, this); rv.setLayoutManager(manager); rv.setAdapter(adapter); rv.scrollToPosition(list.size() - 1); image.setTranslationX(dp2px(50)); //监听recyclerview的滑动事件 rv.addOnScrollListener(new RecyclerView.OnScrollListener() { @Override public void onScrollStateChanged(RecyclerView recyclerView, int newState) { super.onScrollStateChanged(recyclerView, newState); Log.i(TAG, "current scroll state = " + newState); image.setTranslationX(dp2px(-1)); if (newState == RecyclerView.SCROLL_STATE_IDLE) { //第一种动画方式// image.animate()// .translationX(dp2px(50))// .setDuration(1500)// .start(); //第二种动画方式 animator = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(image, "translationX", dp2px(50)); animator.setDuration(1500); animator.addListener(new Animator.AnimatorListener() { @Override public void onAnimationStart(Animator animation) { } @Override public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) { //当图片发生点击时可以通过下面代码将图片复位到原来位置 //否则响应点击事件的图片可能会显示不全,不响应点击的忽略 //image.setTranslationX(dp2px(-1)); } @Override public void onAnimationCancel(Animator animation) { } @Override public void onAnimationRepeat(Animator animation) { } }); animator.start(); } } }); image.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { if (animator != null && animator.isRunning()) { animator.cancel(); } image.setImageResource(R.drawable.insect); } }); } public int dp2px(int dip) { int dpi = getResources().getDisplayMetrics().densityDpi; return dip * (dpi / 160); }} |
activity_animator.xml:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".AnimationActivity"> <android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView android:id="@+id/itemRv" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" /> <android.support.v7.widget.CardView android:id="@+id/expand" android:layout_width="70dp" android:layout_height="30dp" android:layout_alignParentEnd="true" android:layout_marginTop="40dp" android:layout_marginEnd="30dp" app:cardBackgroundColor="#00000000" app:cardCornerRadius="15dp" app:cardElevation="0dp"> <ImageView android:id="@+id/insect" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_gravity="end" android:scaleType="fitXY" android:src="@drawable/insect" /> </android.support.v7.widget.CardView> </RelativeLayout> |
item_anim.xml:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="50dp" tools:context=".AnimationActivity"> <TextView android:textSize="16sp" android:id="@+id/content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerInParent="true" android:text="hello World" /> </RelativeLayout> |
AnimatorAdapter.java:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
|
package com.example.duoyi; import android.content.Context;import android.support.annotation.NonNull;import android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView;import android.view.LayoutInflater;import android.view.View;import android.view.ViewGroup;import android.widget.TextView; import com.example.duoyi.clientaidl.AnimationActivity;import com.example.duoyi.clientaidl.R; import java.util.List; public class AnimationAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<AnimationAdapter.AnimationViewHolder> { private List<String> list; private AnimationActivity context; public AnimationAdapter(List<String> list, AnimationActivity context) { this.list = list; this.context = context; } @Override public AnimationViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(ViewGroup viewGroup, int i) { View view = LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.item_anim, viewGroup, false); return new AnimationViewHolder(view); } @Override public void onBindViewHolder(AnimationViewHolder holder, int position) { String content = list.get(position); holder.content.setText(content); } @Override public int getItemCount() { return list.size(); } static class AnimationViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder { TextView content; AnimationViewHolder(View view) { super(view); content = view.findViewById(R.id.content); } }} |
三、逻辑分析
首先实现的效果是图片从做到右显示,那我们就使用平移动画,让图片从左到右移动消失,所以就在需要显示ImageView嵌套一层父容器,这样图片不断移出容器的范围内就会造成一种图片从左到右消失的效果
需求:父容器需设置为圆角显示
如果需要实现ImageView的父容器为圆角布局的话,那就采用CardView,通过改变其属性
app:cardCornerRadius="15dp"
实现,不要使用其他诸如LinearLayout的父容器,设置其backgroud为一个圆角的drawable方式实现,这样的话内部的图片如果是矩形,即时你设置了父容器为圆角的,但是内部图片的显示还是会超出圆角的范围显示
需求:图片消失的动画中响应点击事件,完整显示另一张图片
这个实现我们首先需要在图片的点击事件中判断当前动画是否还是运行isRunning(),如果运行的话调用animator的cancel()方法取消动画,然后进行图片的位置的复位;如果我们不进行复位操作,此时ImageView的位置由于平移动画发生改变,当我们显示另一张图片可能会发生显示不全情况
当动画终止(可能自然终止,也可能调用了动画的cance()方法),会响应其结束的监听方法,然后我们在该方法复位图片的位置即可:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
animator.addListener(new Animator.AnimatorListener() { @Override public void onAnimationStart(Animator animation) { } @Override public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) { //当图片发生点击时可以通过下面代码将图片复位到原来位置 //否则响应点击事件的图片可能会显示不全,不响应点击的忽略 //image.setTranslationX(dp2px(-1)); } @Override public void onAnimationCancel(Animator animation) { } @Override public void onAnimationRepeat(Animator animation) { } }); |
动画实现的两种方式:
直接通过组件的animator()方式可以实现动画的链式调用,并且可以通过其withEndAction()或者withStartAction()方法在动画启动和结束的时候执行一些逻辑,该方式可以不需要调用其start()就能执行,因为其会在屏幕刷新的时候会自动执行
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
//第一种动画方式image.animate() .translationX(dp2px(50)) .setDuration(1500) .start(); |
下面这种方式就是比较老实的方式,但是我们可以通过将其赋值给一个全局变量进行动画的操控(pause() cancel())
|
1
2
3
4
|
animator = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(image, "translationX", dp2px(50));animator.setDuration(1500);animato.start(); |
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/ssAfterHard/article/details/103218531