前言#
我们都知道泛型在C#的重要性,泛型是OOP语言中三大特征的多态的最重要的体现,几乎泛型撑起了整个.NET框架,在讲泛型之前,我们可以抛出一个问题,我们现在需要一个可扩容的数组类,且满足所有类型,不管是值类型还是引用类型,那么在没有用泛型方法实现,如何实现?
一.泛型之前的故事#
我们肯定会想到用object来作为类型参数,因为在C#中,所有类型都是基于Object类型的。因此Object是所有类型的最基类,那么我们的可扩容数组类如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
|
public class ArrayExpandable{private object?[] _items = null;private int _defaultCapacity = 4;private int _size;public object? this[int index]{get{if (index < 0 || index >= _size) throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(nameof(index));return _items[index];}set{if (index < 0 || index >= _size) throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(nameof(index));_items[index] = value;}}public int Capacity{get => _items.Length;set{if (value < _size){ throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(nameof(value));}if (value != _items.Length){ if (value > 0) { object[] newItems = new object[value]; if (_size > 0) { Array.Copy(_items, newItems, _size); } _items = newItems; } else { _items = new object[_defaultCapacity]; }}}}public int Count => _size;public ArrayExpandable(){_items = new object?[0];}public ArrayExpandable(int capacity){_items = new object?[capacity];}public void Add(object? value){//数组元素为0或者数组元素容量满if (_size == _items.Length) EnsuresCapacity(_size + 1);_items[_size] = value;_size++;}private void EnsuresCapacity(int size){if (_items.Length < size){int newCapacity = _items.Length == 0 ? _defaultCapacity : _items.Length * 2;if (newCapacity < size) newCapacity = size;Capacity = newCapacity;}} |
然后我们来验证下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
var arrayStr = new ArrayExpandable();var strs = new string[] { "ryzen", "reed", "wymen" };for (int i = 0; i < strs.Length; i++){ arrayStr.Add(strs[i]); string value = (string)arrayStr[i];//改为int value = (int)arrayStr[i] 运行时报错 Console.WriteLine(value);}Console.WriteLine($"Now {nameof(arrayStr)} Capacity:{arrayStr.Capacity}");var array = new ArrayExpandable();for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ array.Add(i); int value = (int)array[i]; Console.WriteLine(value);}Console.WriteLine($"Now {nameof(array)} Capacity:{array.Capacity}"); |
输出:
Copy
ryzen
reed
wymen
gavin
Now arrayStr Capacity:4
0
1
2
3
4
Now array Capacity:8
貌似输出结果是正确的,能够动态进行扩容,同样的支持值类型Struct的int32和引用类型的字符串,但是其实这里会发现一些问题,那就是
- 引用类型string进行了类型转换的验证
- 值类型int32进行了装箱和拆箱操作,同时进行类型转换类型的检验
- 发生的这一切都是在运行时的,假如类型转换错误,得在运行时才能报错
大致执行模型如下:
引用类型:
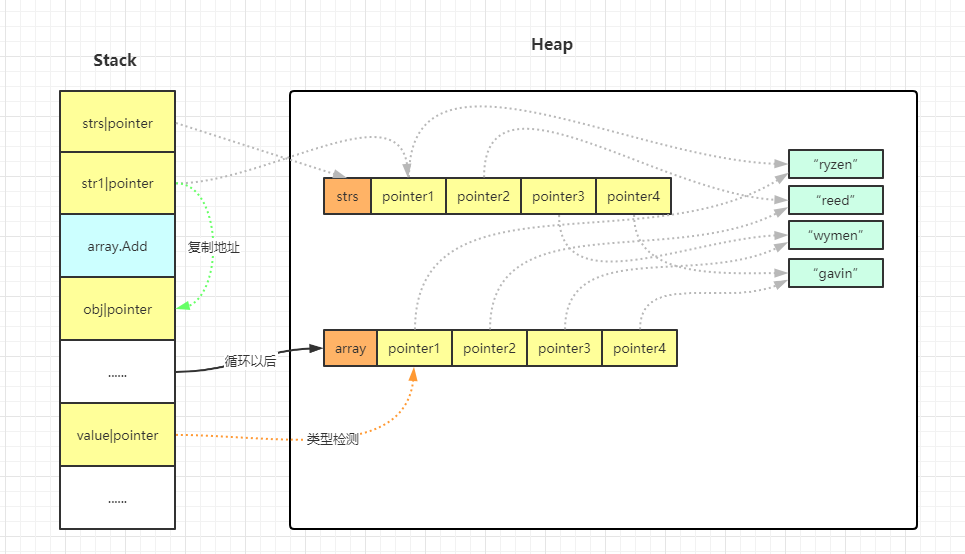
值类型:
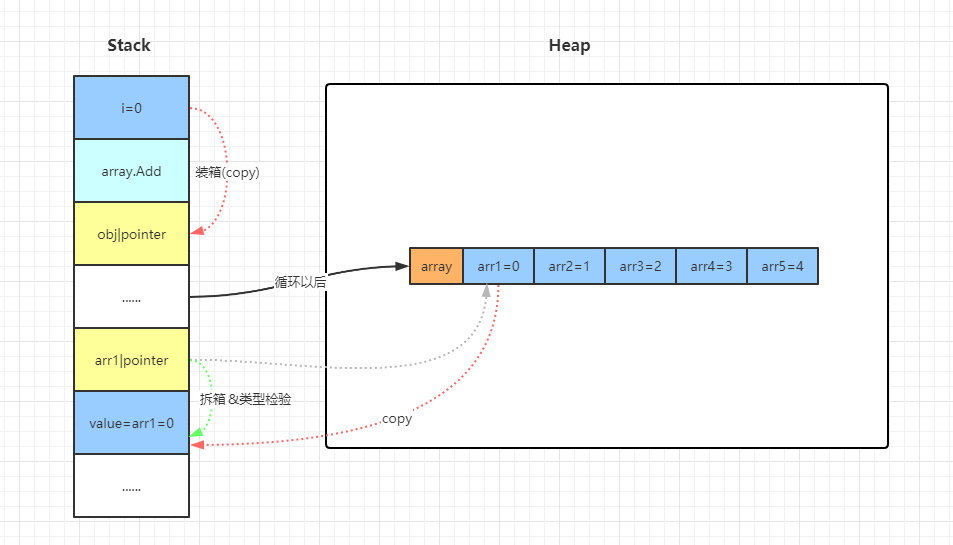
那么有没有一种方法能够避免上面遇到的三种问题呢?在借鉴了cpp的模板和java的泛型经验,在C#2.0的时候推出了更适合.NET体系下的泛型
二.用泛型实现#
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
|
public class ArrayExpandable<T>{ private T[] _items; private int _defaultCapacity = 4; private int _size; public T this[int index] { get { if (index < 0 || index >= _size) throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(nameof(index)); return _items[index]; } set { if (index < 0 || index >= _size) throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(nameof(index)); _items[index] = value; } } public int Capacity { get => _items.Length; set { if (value < _size) { throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException(nameof(value)); } if (value != _items.Length) { if (value > 0) { T[] newItems = new T[value]; if (_size > 0) { Array.Copy(_items, newItems, _size); } _items = newItems; } else { _items = new T[_defaultCapacity]; } } } } public int Count => _size; public ArrayExpandable() { _items = new T[0]; } public ArrayExpandable(int capacity) { _items = new T[capacity]; } public void Add(T value) { //数组元素为0或者数组元素容量满 if (_size == _items.Length) EnsuresCapacity(_size + 1); _items[_size] = value; _size++; } private void EnsuresCapacity(int size) { if (_items.Length < size) { int newCapacity = _items.Length == 0 ? _defaultCapacity : _items.Length * 2; if (newCapacity < size) newCapacity = size; Capacity = newCapacity; } } } |
那么测试代码则改写为如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
var arrayStr = new ArrayExpandable<string>();var strs = new string[] { "ryzen", "reed", "wymen", "gavin" };for (int i = 0; i < strs.Length; i++){ arrayStr.Add(strs[i]); string value = arrayStr[i];//改为int value = arrayStr[i] 编译报错 Console.WriteLine(value);}Console.WriteLine($"Now {nameof(arrayStr)} Capacity:{arrayStr.Capacity}");var array = new ArrayExpandable<int>();for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){ array.Add(i); int value = array[i]; Console.WriteLine(value);}Console.WriteLine($"Now {nameof(array)} Capacity:{array.Capacity}"); |
输出:
Copy
ryzen
reed
wymen
gavin
Now arrayStr Capacity:4
0
1
2
3
4
Now array Capacity:8
我们通过截取部分ArrayExpandable<T>的IL查看其本质是个啥:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
|
//声明类.class public auto ansi beforefieldinit MetaTest.ArrayExpandable`1<T> extends [System.Runtime]System.Object{ .custom instance void [System.Runtime]System.Reflection.DefaultMemberAttribute::.ctor(string) = ( 01 00 04 49 74 65 6D 00 00 ) } //Add方法.method public hidebysig instance void Add(!T 'value') cil managed{ // 代码大小 69 (0x45) .maxstack 3 .locals init (bool V_0) IL_0000: nop IL_0001: ldarg.0 IL_0002: ldfld int32 class MetaTest.ArrayExpandable`1<!T>::_size IL_0007: ldarg.0 IL_0008: ldfld !0[] class MetaTest.ArrayExpandable`1<!T>::_items IL_000d: ldlen IL_000e: conv.i4 IL_000f: ceq IL_0011: stloc.0 IL_0012: ldloc.0 IL_0013: brfalse.s IL_0024 IL_0015: ldarg.0 IL_0016: ldarg.0 IL_0017: ldfld int32 class MetaTest.ArrayExpandable`1<!T>::_size IL_001c: ldc.i4.1 IL_001d: add IL_001e: call instance void class MetaTest.ArrayExpandable`1<!T>::EnsuresCapacity(int32) IL_0023: nop IL_0024: ldarg.0 IL_0025: ldfld !0[] class MetaTest.ArrayExpandable`1<!T>::_items IL_002a: ldarg.0 IL_002b: ldfld int32 class MetaTest.ArrayExpandable`1<!T>::_size IL_0030: ldarg.1 IL_0031: stelem !T IL_0036: ldarg.0 IL_0037: ldarg.0 IL_0038: ldfld int32 class MetaTest.ArrayExpandable`1<!T>::_size IL_003d: ldc.i4.1 IL_003e: add IL_003f: stfld int32 class MetaTest.ArrayExpandable`1<!T>::_size IL_0044: ret} // end of method ArrayExpandable`1::Add |
原来定义的时候就是用了个T作为占位符,起一个模板的作用,我们对其实例化类型参数的时候,补足那个占位符,我们可以在编译期就知道了其类型,且不用在运行时进行类型检测,而我们也可以对比ArrayExpandable和ArrayExpandable<T>在类型为值类型中的IL,查看是否进行拆箱和装箱操作,以下为IL截取部分:
ArrayExpandable:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
IL_0084: newobj instance void GenericSample.ArrayExpandable::.ctor()IL_0089: stloc.2IL_008a: ldc.i4.0IL_008b: stloc.s V_6IL_008d: br.s IL_00bcIL_008f: nopIL_0090: ldloc.2IL_0091: ldloc.s V_6IL_0093: box [System.Runtime]System.Int32 //box为装箱操作IL_0098: callvirt instance void GenericSample.ArrayExpandable::Add(object)IL_009d: nopIL_009e: ldloc.2IL_009f: ldloc.s V_6IL_00a1: callvirt instance object GenericSample.ArrayExpandable::get_Item(int32)IL_00a6: unbox.any [System.Runtime]System.Int32 //unbox为拆箱操作 |
ArrayExpandable:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
IL_007f: newobj instance void class GenericSample.ArrayExpandable`1<int32>::.ctor()IL_0084: stloc.2IL_0085: ldc.i4.0IL_0086: stloc.s V_6IL_0088: br.s IL_00adIL_008a: nopIL_008b: ldloc.2IL_008c: ldloc.s V_6IL_008e: callvirt instance void class GenericSample.ArrayExpandable`1<int32>::Add(!0)IL_0093: nopIL_0094: ldloc.2IL_0095: ldloc.s V_6IL_0097: callvirt instance !0 class GenericSample.ArrayExpandable`1<int32>::get_Item(int32) |
我们从IL也能看的出来,ArrayExpandable<T>的T作为一个类型参数,在编译后在IL已经确定了其类型,因此当然也就不存在装拆箱的情况,在编译期的时候IDE能够检测类型,因此也就不用在运行时进行类型检测,但并不代表不能通过运行时检测类型(可通过is和as),还能通过反射体现出泛型的灵活性,后面会讲到
其实有了解ArrayList和List的朋友就知道,ArrayExpandable和ArrayExpandable<T>其实现大致就是和它们一样,只是简化了很多的版本,我们这里可以通过 BenchmarkDotNet 来测试其性能对比,代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
|
[SimpleJob(RuntimeMoniker.NetCoreApp31,baseline:true)][SimpleJob(RuntimeMoniker.NetCoreApp50)][MemoryDiagnoser]public class TestClass{[Benchmark]public void EnumAE_ValueType(){ ArrayExpandable array = new ArrayExpandable(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { array.Add(i);//装箱 int value = (int)array[i];//拆箱 } array = null;//确保进行垃圾回收}[Benchmark]public void EnumAE_RefType(){ ArrayExpandable array = new ArrayExpandable(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { array.Add("r"); string value = (string)array[i]; } array = null;//确保进行垃圾回收}[Benchmark]public void EnumAE_Gen_ValueType(){ ArrayExpandable<int> array = new ArrayExpandable<int>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { array.Add(i); int value = array[i]; } array = null;//确保进行垃圾回收;}[Benchmark]public void EnumAE_Gen_RefType(){ ArrayExpandable<string> array = new ArrayExpandable<string>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { array.Add("r"); string value = array[i]; } array = null;//确保进行垃圾回收;}[Benchmark]public void EnumList_ValueType(){ List<int> array = new List<int>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { array.Add(i); int value = array[i]; } array = null;//确保进行垃圾回收;}[Benchmark]public void EnumList_RefType(){ List<string> array = new List<string>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { array.Add("r"); string value = array[i]; } array = null;//确保进行垃圾回收;}[Benchmark(Baseline =true)]public void EnumAraayList_valueType(){ ArrayList array = new ArrayList(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { array.Add(i); int value = (int)array[i]; } array = null;//确保进行垃圾回收;}[Benchmark]public void EnumAraayList_RefType(){ ArrayList array = new ArrayList(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { array.Add("r"); string value = (string)array[i]; } array = null;//确保进行垃圾回收;}} |
我还加入了.NETCore3.1和.NET5的对比,且以.NETCore3.1的EnumAraayList_valueType方法为基准,性能测试结果如下:
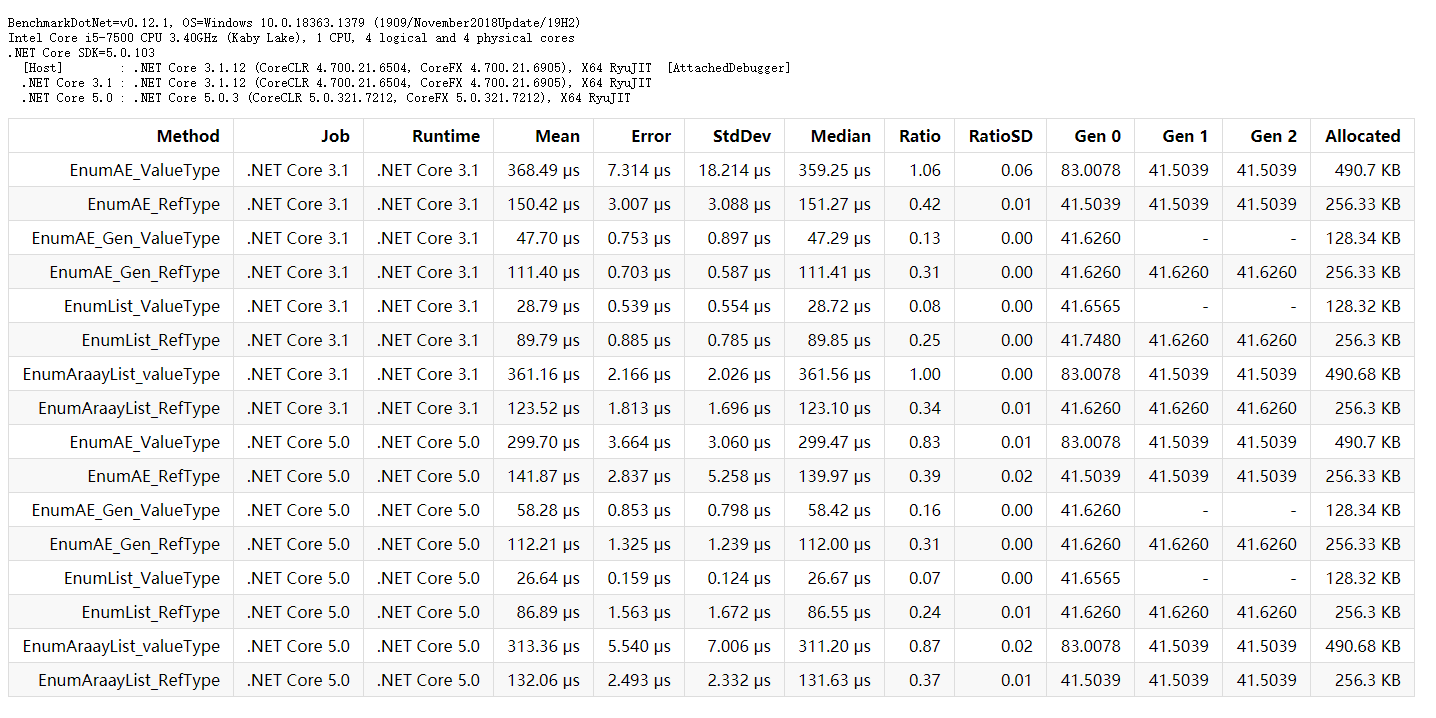
用更直观的柱形图来呈现:
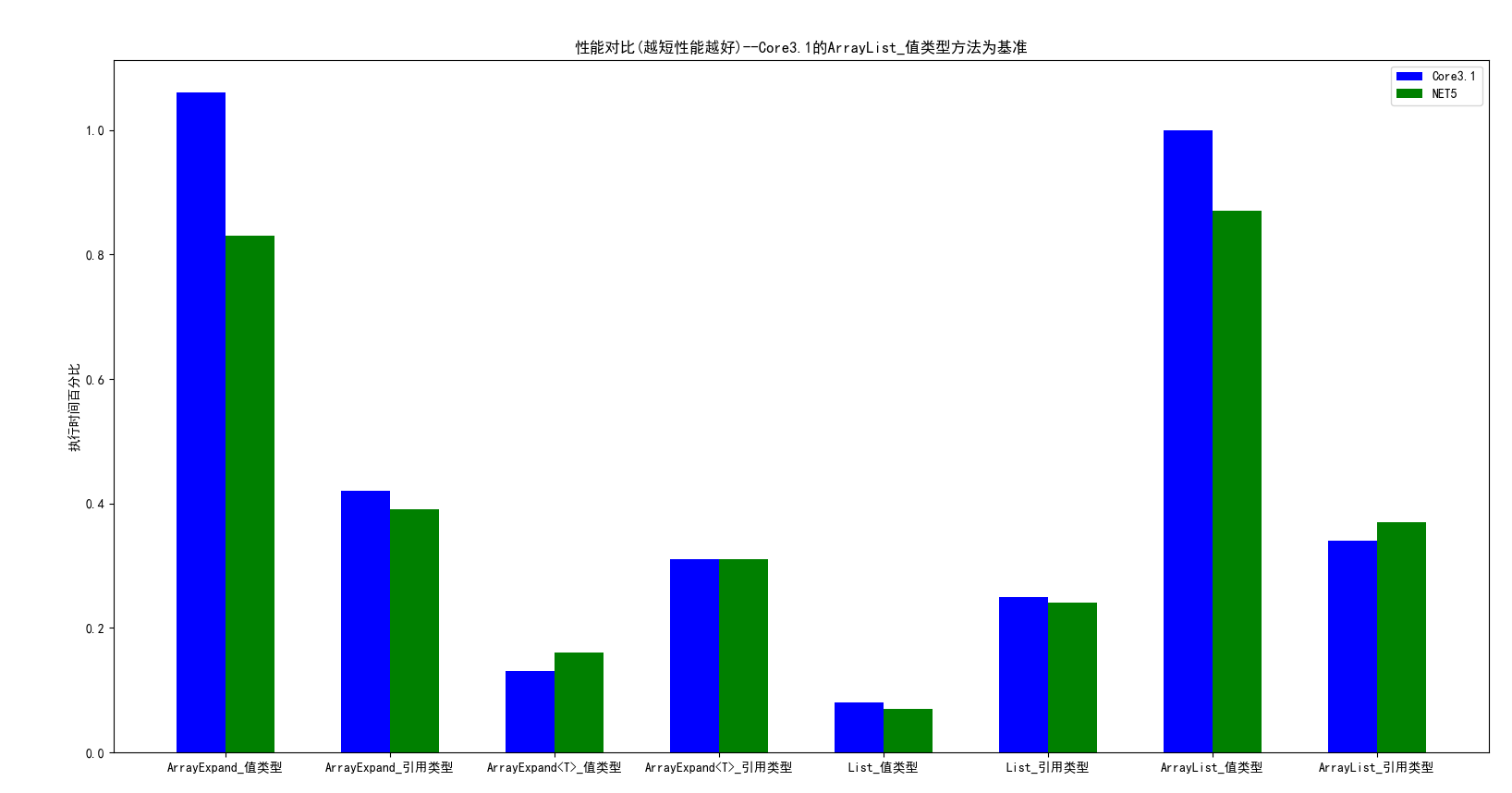
我们能看到在这里List的性能在引用类型和值类型中都是所以当中是最好的,不管是执行时间、GC次数,分配的内存空间大小,都是最优的,同时.NET5在几乎所有的方法中性能都是优于.NETCore3.1,这里还提一句,我实现的ArrayExpandable和ArrayExpandable<T>性能都差于ArrayList和List,我还没实现IList和各种方法,只能说句dotnet基金会牛逼
三.泛型的多态性#
多态的声明#
类、结构、接口、方法、和委托可以声明一个或者多个类型参数,我们直接看代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
interface IFoo<InterfaceT>{ void InterfaceMenthod(InterfaceT interfaceT);}class Foo<ClassT, ClassT1>: IFoo<StringBuilder>{ public ClassT1 Field; public delegate void MyDelegate<DelegateT>(DelegateT delegateT); public void DelegateMenthod<DelegateT>(DelegateT delegateT, MyDelegate<DelegateT> myDelegate) { myDelegate(delegateT); } public static string operator +(Foo<ClassT, ClassT1> foo,string s) { return $"{s}:{foo.GetType().Name}"; } public List<ClassT> Property{ get; set; } public ClassT1 Property1 { get; set; } public ClassT this[int index] => Property[index];//没判断越界 public Foo(List<ClassT> classT, ClassT1 classT1) { Property = classT; Property1 = classT1; Field = classT1; Console.WriteLine($"构造函数:parameter1 type:{Property.GetType().Name},parameter2 type:{Property1.GetType().Name}"); } //方法声明了多个新的类型参数 public void Method<MenthodT, MenthodT1>(MenthodT menthodT, MenthodT1 menthodT1) { Console.WriteLine($"Method<MenthodT, MenthodT1>:{(menthodT.GetType().Name)}:{menthodT.ToString()}," + $"{menthodT1.GetType().Name}:{menthodT1.ToString()}"); } public void Method(ClassT classT) { Console.WriteLine($"{nameof(Method)}:{classT.GetType().Name}:classT?.ToString()"); } public void InterfaceMenthod(StringBuilder interfaceT) { Console.WriteLine(interfaceT.ToString()); }} |
控制台测试代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
static void Main(string[] args){ Test(); Console.ReadLine();}static void Test(){ var list = new List<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4 }; var foo = new Foo<int, string>(list, "ryzen"); var index = 0; Console.WriteLine($"索引:索引{index}的值:{foo[index]}"); Console.WriteLine($"Filed:{foo.Field}"); foo.Method(2333); foo.Method<DateTime, long>(DateTime.Now, 2021); foo.DelegateMenthod<string>("this is a delegate", DelegateMenthod); foo.InterfaceMenthod(new StringBuilder().Append("InterfaceMenthod:this is a interfaceMthod")); Console.WriteLine(foo+"重载+运算符");}static void DelegateMenthod(string str){ Console.WriteLine($"{nameof(DelegateMenthod)}:{str}");} |
输出如下:
构造函数:parameter1 type:List`1,parameter2 type:String
索引:索引0的值:1
Filed:ryzen
Method:Int32:classT?.ToString()
Method<MenthodT, MenthodT1>:DateTime:2021/03/02 11:45:40,Int64:2021
DelegateMenthod:this is a delegate
InterfaceMenthod:this is a interfaceMthod
重载+运算符:Foo`2
我们通过例子可以看到的是:
- 类(结构也可以),接口,委托,方法都可以声明一个或多个类型参数,体现了声明的多态性
- 类的函数成员:属性,字段,索引,构造器,运算符只能引入类声明的类型参数,不能够声明,唯有方法这一函数成员具备声明和引用类型参数两种功能,由于具备声明功能,因此可以声明和委托一样的类型参数并且引用它,这也体现了方法的多态性
多态的继承#
父类和实现类或接口的接口都可以是实例化类型,直接看代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
interface IFooBase<IBaseT>{}interface IFoo<InterfaceT>: IFooBase<string>{ void InterfaceMenthod(InterfaceT interfaceT);}class FooBase<ClassT>{}class Foo<ClassT, ClassT1>: FooBase<ClassT>,IFoo<StringBuilder>{} |
我们可以通过例子看出:
- 由于Foo的基类FooBase定义的和Foo有着共享的类型参数ClassT,因此可以在继承的时候不实例化类型
- 而Foo和IFoo接口没定义相同的类型参数,因此可以在继承的时候实例化出接口的类型参数StringBuild出来
- IFoo和IFooBase没定义相同的类型参数,因此可以在继承的时候实例化出接口的类型参数string出来
- 上述都体现出继承的多态性
多态的递归#
我们定义如下一个类和一个方法,且不会报错:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
class D<T> { }class C<T> : D<C<C<T>>> { void Foo(){ var foo = new C<C<T>>(); Console.WriteLine(foo.ToString());}} |
因为T能在实例化的时候确定其类型,因此也支持这种循环套用自己的类和方法的定义
四.泛型的约束#
where的约束#
我们先上代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
class FooBase{ }class Foo : FooBase { }class someClass<T,K> where T:struct where K :FooBase,new(){}static void TestConstraint(){ var someClass = new someClass<int, Foo>();//通过编译 //var someClass = new someClass<string, Foo>();//编译失败,string不是struct类型 //var someClass = new someClass<string, long>();//编译失败,long不是FooBase类型} |
再改动下Foo类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
class Foo : FooBase { public Foo(string str) { }}static void TestConstraint(){ var someClass = new someClass<int, Foo>();//编译失败,因为new()约束必须类含有一个无参构造器,可以再给Foo类加上个无参构造器就能编译通过} |
我们可以看到,通过where语句,可以对类型参数进行约束,而且一个类型参数支持多个约束条件(例如K),使其在实例化类型参数的时候,必须按照约束的条件对应实例符合条件的类型,而where条件约束的作用就是起在编译期约束类型参数的作用
out和in的约束#
说到out和in之前,我们可以说下协变和逆变,在C#中,只有泛型接口和泛型委托可以支持协变和逆变
协变#
我们先看下代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
class FooBase{ }class Foo : FooBase {}interface IBar<T> { T GetValue(T t);}class Bar<T> : IBar<T>{ public T GetValue(T t) { return t; }}static void Test(){ var foo = new Foo(); FooBase fooBase = foo;//编译成功 IBar<Foo> bar = new Bar<Foo>(); IBar<FooBase> bar1 = bar;//编译失败 } |
这时候你可能会有点奇怪,为啥那段代码会编译失败,明明Foo类可以隐式转为FooBase,但作为泛型接口类型参数实例化却并不能呢?使用out约束泛型接口IBar的T,那段代码就会编译正常,但是会引出另外一段编译报错:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
interface IBar<out T> { T GetValue(string str);//编译成功 //T GetValue(T t);//编译失败 T不能作为形参输入,用out约束T支持协变,T可以作为返回值输出 }IBar<Foo> bar = new Bar<Foo>();IBar<FooBase> bar1 = bar;//编译正常 |
因此我们可以得出以下结论:
- 由于Foo继承FooBase,本身子类Foo包含着父类允许访问的成员,因此能隐式转换父类,这是类型安全的转换,因此叫协变
- 在为泛型接口用out标识其类型参数支持协变后,约束其方法的返回值和属性的Get(本质也是个返回值的方法)才能引用所声明的类型参数,也就是作为输出值,用out很明显的突出了这一意思
而支持迭代的泛型接口IEnumerable也是这么定义的:
|
1
2
3
4
|
public interface IEnumerable<out T> : IEnumerable{ new IEnumerator<T> GetEnumerator();} |
逆变#
我们将上面代码改下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
class FooBase{ }class Foo : FooBase {}interface IBar<T> { T GetValue(T t);}class Bar<T> : IBar<T>{ public T GetValue(T t) { return t; }}static void Test1(){ var fooBase = new FooBase(); Foo foo = (Foo)fooBase;//编译通过,运行时报错 IBar<FooBase> bar = new Bar<FooBase>(); IBar<Foo> bar1 = (IBar<Foo>)bar;//编译通过,运行时报错} |
我们再改动下IBar,发现出现另外一处编译失败
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
interface IBar<in T> { void GetValue(T t);//编译成功 //T GetValue(T t);//编译失败 T不能作为返回值输出,用in约束T支持逆变,T可以作为返回值输出} IBar<FooBase> bar = new Bar<FooBase>(); IBar<Foo> bar1 = (IBar<Foo>)bar;//编译通过,运行时不报错 IBar<Foo> bar1 = bar;//编译通过,运行时不报错 |
因此我们可以得出以下结论:
- 由于FooBase是Foo的父类,并不包含子类的自由的成员,转为为子类Foo是类型不安全的,因此在运行时强式转换的报错了,但编译期是不能够确认的
- 在为泛型接口用in标识其类型参数支持逆变后,in约束其接口成员不能将其作为返回值(输出值),我们会发现协变和逆变正是一对反义词
- 这里提一句,值类型是不支持协变和逆变的
同样的泛型委托Action就是个逆变的例子:
|
1
|
public delegate void Action<in T>(T obj); |
五.泛型的反射#
我们先来看看以下代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
static void Main(string[] args){ var lsInt = new ArrayExpandable<int>(); lsInt.Add(1); var lsStr = new ArrayExpandable<string>(); lsStr.Add("ryzen"); var lsStr1 = new ArrayExpandable<string>(); lsStr.Add("ryzen");} |
然后通过ildasm查看其IL,开启视图-》显示标记值,查看Main方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
void Main(string[] args) cil managed{ .entrypoint // 代码大小 52 (0x34) .maxstack 2 .locals /*11000001*/ init (class MetaTest.ArrayExpandable`1/*02000003*/<int32> V_0, class MetaTest.ArrayExpandable`1/*02000003*/<string> V_1, class MetaTest.ArrayExpandable`1/*02000003*/<string> V_2) IL_0000: nop IL_0001: newobj instance void class MetaTest.ArrayExpandable`1/*02000003*/<int32>/*1B000001*/::.ctor() /* 0A00000C */ IL_0006: stloc.0 IL_0007: ldloc.0 IL_0008: ldc.i4.1 IL_0009: callvirt instance void class MetaTest.ArrayExpandable`1/*02000003*/<int32>/*1B000001*/::Add(!0) /* 0A00000D */ IL_000e: nop IL_000f: newobj instance void class MetaTest.ArrayExpandable`1/*02000003*/<string>/*1B000002*/::.ctor() /* 0A00000E */ IL_0014: stloc.1 IL_0015: ldloc.1 IL_0016: ldstr "ryzen" /* 70000001 */ IL_001b: callvirt instance void class MetaTest.ArrayExpandable`1/*02000003*/<string>/*1B000002*/::Add(!0) /* 0A00000F */ IL_0020: nop IL_0021: newobj instance void class MetaTest.ArrayExpandable`1/*02000003*/<string>/*1B000002*/::.ctor() /* 0A00000E */ IL_0026: stloc.2 IL_0027: ldloc.1 IL_0028: ldstr "ryzen" /* 70000001 */ IL_002d: callvirt instance void class MetaTest.ArrayExpandable`1/*02000003*/<string>/*1B000002*/::Add(!0) /* 0A00000F */ IL_0032: nop IL_0033: ret} // end of method Program::Main |
打开元数据表将上面所涉及到的元数据定义表和类型规格表列出:
metainfo:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
|
-----------定义部分TypeDef #2 (02000003)------------------------------------------------------- TypDefName: MetaTest.ArrayExpandable`1 (02000003) Flags : [Public] [AutoLayout] [Class] [AnsiClass] [BeforeFieldInit] (00100001) Extends : 0100000C [TypeRef] System.Object 1 Generic Parameters (0) GenericParamToken : (2a000001) Name : T flags: 00000000 Owner: 02000003 Method #8 (0600000a) ------------------------------------------------------- MethodName: Add (0600000A) Flags : [Public] [HideBySig] [ReuseSlot] (00000086) RVA : 0x000021f4 ImplFlags : [IL] [Managed] (00000000) CallCnvntn: [DEFAULT] hasThis ReturnType: Void 1 Arguments Argument #1: Var!0 1 Parameters (1) ParamToken : (08000007) Name : value flags: [none] (00000000) ------类型规格部分TypeSpec #1 (1b000001)------------------------------------------------------- TypeSpec : GenericInst Class MetaTest.ArrayExpandable`1< I4> //14代表int32 MemberRef #1 (0a00000c) ------------------------------------------------------- Member: (0a00000c) .ctor: CallCnvntn: [DEFAULT] hasThis ReturnType: Void No arguments. MemberRef #2 (0a00000d) ------------------------------------------------------- Member: (0a00000d) Add: CallCnvntn: [DEFAULT] hasThis ReturnType: Void 1 Arguments Argument #1: Var!0TypeSpec #2 (1b000002)------------------------------------------------------- TypeSpec : GenericInst Class MetaTest.ArrayExpandable`1< String> MemberRef #1 (0a00000e) ------------------------------------------------------- Member: (0a00000e) .ctor: CallCnvntn: [DEFAULT] hasThis ReturnType: Void No arguments. MemberRef #2 (0a00000f) ------------------------------------------------------- Member: (0a00000f) Add: CallCnvntn: [DEFAULT] hasThis ReturnType: Void 1 Arguments Argument #1: Var!0 |
这时候我们就可以看出,元数据为泛型类ArrayExpandable<T>定义一份定义表,生成两份规格,也就是当你实例化类型参数为int和string的时候,分别生成了两份规格代码,同时还发现以下的现象:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
var lsInt = new ArrayExpandable<int>();//引用的是类型规格1b000001的成员0a00000c .ctor构造lsInt.Add(1);//引用的是类型规格1b000001的成员0a00000d Add var lsStr = new ArrayExpandable<string>();//引用的是类型规格1b000002的成员0a00000e .ctor构造lsStr.Add("ryzen");//引用的是类型规格1b000002的成员0a00000f Addvar lsStr1 = new ArrayExpandable<string>();//和lsStr一样lsStr.Add("ryzen");//和lsStr一样 |
非常妙的是,当你实例化两个一样的类型参数string,是共享一份类型规格的,也就是同享一份本地代码,因此上面的代码在线程堆栈和托管堆的大致是这样的:
由于泛型也有元数据的存在,因此可以对其做反射:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
Console.WriteLine($"-----------{nameof(lsInt)}---------------");Console.WriteLine($"{nameof(lsInt)} is generic?:{lsInt.GetType().IsGenericType}");Console.WriteLine($"Generic type:{lsInt.GetType().GetGenericArguments()[0].Name}");Console.WriteLine("---------Menthods:");foreach (var method in lsInt.GetType().GetMethods()){ Console.WriteLine(method.Name);}Console.WriteLine("---------Properties:");foreach (var property in lsInt.GetType().GetProperties()){ Console.WriteLine($"{property.PropertyType.ToString()}:{property.Name}");}Console.WriteLine($"\n-----------{nameof(lsStr)}---------------");Console.WriteLine($"{nameof(lsStr)} is generic?:{lsStr.GetType().IsGenericType}");Console.WriteLine($"Generic type:{lsStr.GetType().GetGenericArguments()[0].Name}");Console.WriteLine("---------Menthods:");foreach (var method in lsStr.GetType().GetMethods()){ Console.WriteLine(method.Name);}Console.WriteLine("---------Properties:");foreach (var property in lsStr.GetType().GetProperties()){ Console.WriteLine($"{property.PropertyType.ToString()}:{property.Name}");} |
输出:
-----------lsInt---------------
lsInt is generic?:True
Generic type:Int32
---------Menthods:
get_Item
set_Item
get_Capacity
set_Capacity
get_Count
Add
GetType
ToString
Equals
GetHashCode
---------Properties:
System.Int32:Item
System.Int32:Capacity
System.Int32:Count
-----------lsStr---------------
lsStr is generic?:True
Generic type:String
---------Menthods:
get_Item
set_Item
get_Capacity
set_Capacity
get_Count
Add
GetType
ToString
Equals
GetHashCode
---------Properties:
System.String:Item
System.Int32:Capacity
System.Int32:Count
六.总结#
泛型编程作为.NET体系中一个很重要的编程思想,主要有以下亮点:
- 编译期确定类型,避免值类型的拆装箱和不必要的运行时类型检验,同样运行时也能通过is和as进行类型检验
- 通过约束进行对类型参数实例化的范围
- 同时在IL层面,实例化相同类型参数的时候共享一份本地代码
- 由于元数据的存在,也能在运行时进行反射,增强其灵活性
参考#
Design and Implementation of Generics for the .NET Common Language Runtime
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/csharp/programming-guide/generics/
《CLR Via C# 第四版》
《你必须知道的.NET(第二版)》
到此这篇关于C#泛型运作原理的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C#泛型运作原理内容请搜索服务器之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持服务器之家!
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/ryzen/p/14480171.html