前言
在Android项目中经常有碰到这样的问题,在子线程中完成耗时操作之后要更新UI,下面就自己经历的一些项目总结一下更新的方法。话不多说了,来一起看看详细的介绍吧
引子:
情形1
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);TextView textView = findViewById(R.id.home_tv);ImageView imageView = findViewById(R.id.home_img);new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { textView.setText("更新TextView"); imageView.setImageResource(R.drawable.img); }}).start();} |
运行结果:正常运行!!!
情形二
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);TextView textView = findViewById(R.id.home_tv);ImageView imageView = findViewById(R.id.home_img);new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(5000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } textView.setText("更新TextView"); imageView.setImageResource(R.drawable.img); }}).start();} |
运行结果:异常
android.view.ViewRootImpl$CalledFromWrongThreadException: Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views.
at android.view.ViewRootImpl.checkThread(ViewRootImpl.java:6357)
at android.view.ViewRootImpl.requestLayout(ViewRootImpl.java:874)
at android.view.View.requestLayout(View.java:17476)
at android.view.View.requestLayout(View.java:17476)
at android.view.View.requestLayout(View.java:17476)
at android.view.View.requestLayout(View.java:17476)
at android.view.View.requestLayout(View.java:17476)
at android.view.View.requestLayout(View.java:17476)
at android.widget.RelativeLayout.requestLayout(RelativeLayout.java:360)
at android.view.View.requestLayout(View.java:17476)
at android.widget.TextView.checkForRelayout(TextView.java:6871)
at android.widget.TextView.setText(TextView.java:4057)
at android.widget.TextView.setText(TextView.java:3915)
at android.widget.TextView.setText(TextView.java:3890)
at com.dong.demo.MainActivity$1.run(MainActivity.java:44)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:818)
不是说,子线程不能更新UI吗,为什么情形一可以正常运行,情形二不能正常运行呢;
子线程修改UI出现异常,与什么方法有关
首先从出现异常的log日志入手,发现出现异常的方法调用顺序如下:
TextView.setText(TextView.java:4057)
TextView.checkForRelayout(TextView.java:6871)
View.requestLayout(View.java:17476)
RelativeLayout.requestLayout(RelativeLayout.java:360)
View.requestLayout(View.java:17476)
ViewRootImpl.requestLayout(ViewRootImpl.java:874)
ViewRootImpl.checkThread(ViewRootImpl.java:6357)
更改ImageView时,出现的异常类似;
首先看TextView.setText()方法的源码
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
private void setText(CharSequence text, BufferType type, boolean notifyBefore, int oldlen) {//省略其他代码if (mLayout != null) { checkForRelayout();}sendOnTextChanged(text, 0, oldlen, textLength);onTextChanged(text, 0, oldlen, textLength);//省略其他代码 |
然后,查看以下checkForRelayout()方法的与源码。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
private void checkForRelayout() {// If we have a fixed width, we can just swap in a new text layout// if the text height stays the same or if the view height is fixed.if ((mLayoutParams.width != LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT //省略代码 // We lose: the height has changed and we have a dynamic height. // Request a new view layout using our new text layout. requestLayout(); invalidate();} else { // Dynamic width, so we have no choice but to request a new // view layout with a new text layout. nullLayouts(); requestLayout(); invalidate();}} |
checkForReLayout方法,首先会调用需要改变的View的requestLayout方法,然后执行invalidate()重绘操作;
TextView没有重写requestLayout方法,requestLayout方法由View实现;
查看RequestLayout方法的源码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public void requestLayout() {//省略其他代码if (mParent != null && !mParent.isLayoutRequested()) { mParent.requestLayout();}if (mAttachInfo != null && mAttachInfo.mViewRequestingLayout == this) { mAttachInfo.mViewRequestingLayout = null;}} |
View获取到父View(类型是ViewParent,ViewPaerent是个接口,requestLayout由子类来具体实现),mParent,然后调用父View的requestLayout方法,比如示例中的父View就是xml文件的根布局就是RelativeLayout。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
@Overridepublic void requestLayout() {super.requestLayout();mDirtyHierarchy = true;} |
继续跟踪super.requestLayout()方法,即ViewGroup没有重新,即调用的是View的requestLayout方法。
经过一系列的调用ViewParent的requestLayout方法,最终调用到ViewRootImp的requestLayout方法。ViewRootImp实现了ViewParent接口,继续查看ViewRootImp的requestLayout方法源码。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
@Overridepublic void requestLayout() { if (!mHandlingLayoutInLayoutRequest) { checkThread(); mLayoutRequested = true; scheduleTraversals(); }} |
ViewRootImp的requestLayout方法中有两个方法:
一、checkThread,检查线程,源码如下
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
void checkThread() { if (mThread != Thread.currentThread()) { throw new CalledFromWrongThreadException( "Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views."); }} |
判断当前线程,是否是创建ViewRootImp的线程,而创建ViewRootImp的线程就是主线程,当前线程不是主线程的时候,就抛出异常。
二、scheduleTraversals(),查看源码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
void scheduleTraversals() { if (!mTraversalScheduled) { mTraversalScheduled = true; mTraversalBarrier = mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().postSyncBarrier(); mChoreographer.postCallback( Choreographer.CALLBACK_TRAVERSAL, mTraversalRunnable, null); if (!mUnbufferedInputDispatch) { scheduleConsumeBatchedInput(); } notifyRendererOfFramePending(); pokeDrawLockIfNeeded(); }} |
查看mTraversalRunnable中run()方法的具体操作
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
final class TraversalRunnable implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { doTraversal(); }} |
继续追踪doTraversal()方法
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
void doTraversal() { if (mTraversalScheduled) { mTraversalScheduled = false; mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().removeSyncBarrier(mTraversalBarrier); if (mProfile) { Debug.startMethodTracing("ViewAncestor"); } performTraversals(); if (mProfile) { Debug.stopMethodTracing(); mProfile = false; } }} |
查看到performTraversals()方法,熟悉了吧,这是View绘制的起点。
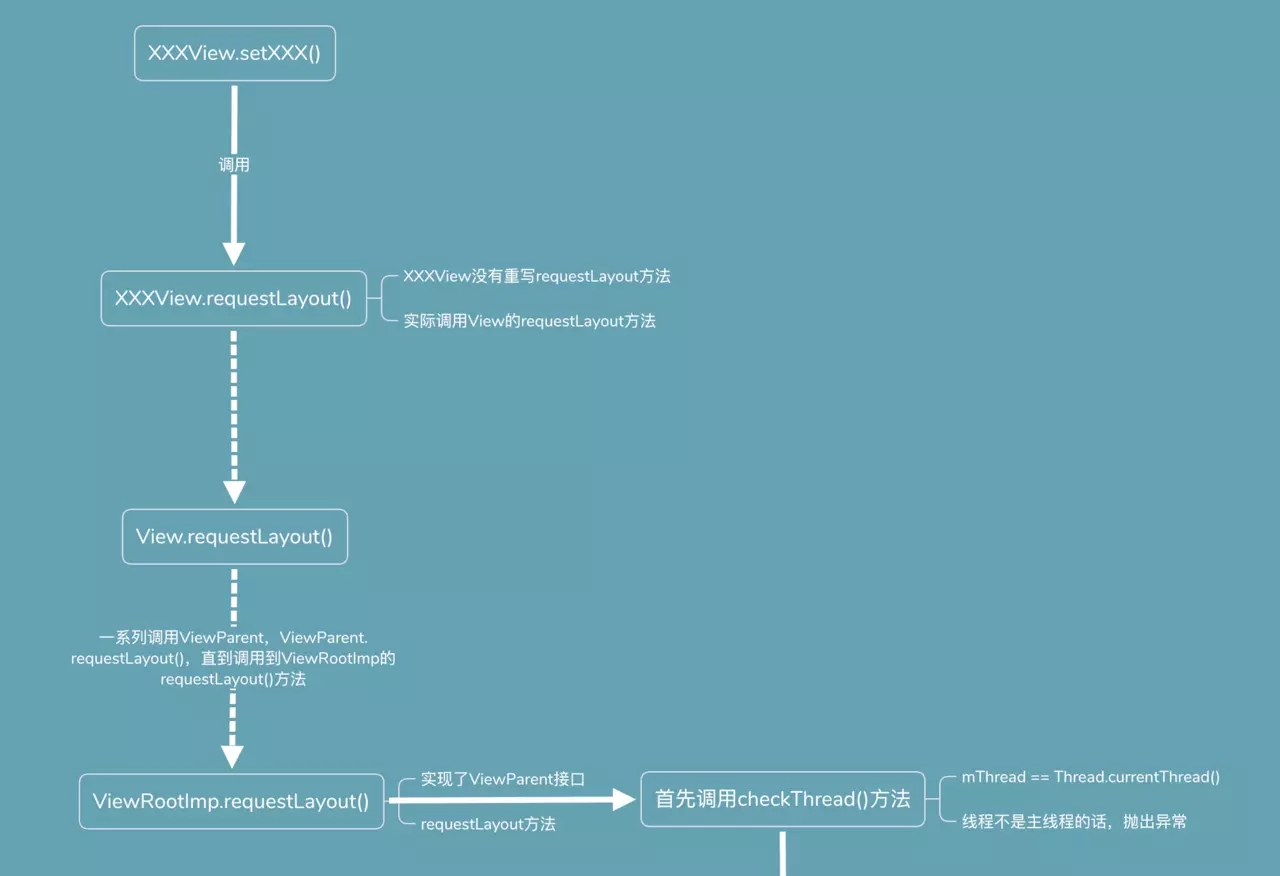
总结一下:
1.Android更新UI会调用View的requestLayout()方法,在requestLayout方法中,获取ViewParent,然后调用ViewParent的requestLayout()方法,一直调用下去,直到调用到ViewRootImp的requestLayout方法;
2.ViewRootImp的requetLayout方法,主要有两部操作一个是checkThread()方法,检测线程,一个是scheduleTraversals,执行绘制相关工作;
情形3
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { Log.i("Dong", "Activity: onCreate"); super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { Looper.prepare(); try { Thread.sleep(5000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "显示Toast", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); Looper.loop(); } }).start();} |
运行结果:正常
分析
下面从Toast源码进行分析:
|
1
2
3
|
public static Toast makeText(Context context, CharSequence text, @Duration int duration) { return makeText(context, null, text, duration);} |
makeText方法调用了他的重载方法,继续追踪
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
public static Toast makeText(@NonNull Context context, @Nullable Looper looper, @NonNull CharSequence text, @Duration int duration) { Toast result = new Toast(context, looper); LayoutInflater inflate = (LayoutInflater) context.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE); View v = inflate.inflate(com.android.internal.R.layout.transient_notification, null); TextView tv = (TextView)v.findViewById(com.android.internal.R.id.message); tv.setText(text); result.mNextView = v; result.mDuration = duration; return result;} |
新建了一个Toast对象,然后对显示的布局、内容、时长进行了设置,并返回Toast对象。
继续查看new Toast()的源码
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
public Toast(@NonNull Context context, @Nullable Looper looper) { mContext = context; mTN = new TN(context.getPackageName(), looper); mTN.mY = context.getResources().getDimensionPixelSize( com.android.internal.R.dimen.toast_y_offset); mTN.mGravity = context.getResources().getInteger( com.android.internal.R.integer.config_toastDefaultGravity);} |
继续查看核心代码 mTN = new TN(context.getPackageName(), looper);
TN初始化的源码为:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
TN(String packageName, @Nullable Looper looper) { //省略部分不相关代码 if (looper == null) { // 没有传入Looper对象的话,使用当前线程对应的Looper对象 looper = Looper.myLooper(); if (looper == null) { throw new RuntimeException( "Can't toast on a thread that has not called Looper.prepare()"); } } //初始化了Handler对象 mHandler = new Handler(looper, null) { @Override public void handleMessage(Message msg) { switch (msg.what) { case SHOW: { IBinder token = (IBinder) msg.obj; handleShow(token); break; } case HIDE: { handleHide(); // Don't do this in handleHide() because it is also invoked by // handleShow() mNextView = null; break; } case CANCEL: { handleHide(); // Don't do this in handleHide() because it is also invoked by // handleShow() mNextView = null; try { getService().cancelToast(mPackageName, TN.this); } catch (RemoteException e) { } break; } } } };} |
继续追踪handleShow(token)方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
public void handleShow(IBinder windowToken) { //省略部分代码 if (mView != mNextView) { // remove the old view if necessary handleHide(); mView = mNextView; Context context = mView.getContext().getApplicationContext(); String packageName = mView.getContext().getOpPackageName(); if (context == null) { context = mView.getContext(); } mWM = (WindowManager)context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE); /* ·*省略设置显示属性的代码 ·*/ if (mView.getParent() != null) { if (localLOGV) Log.v(TAG, "REMOVE! " + mView + " in " + this); mWM.removeView(mView); }= try { mWM.addView(mView, mParams); trySendAccessibilityEvent(); } catch (WindowManager.BadTokenException e) { /* ignore */ } } } |
通过源码可以看出,Toast显示内容是通过mWM(WindowManager类型)的直接添加的,更正:mWm.addView 时,对应的ViewRootImp初始化发生在子线程,checkThread方法中的mThread != Thread.currentThread()判断为true,所以不会抛出只能在主线程更新UI的异常。
总结
以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,如果有疑问大家可以留言交流,谢谢大家对服务器之家的支持。
原文链接:https://juejin.im/post/5c7e19b7518825196101a47d