引言
上次介绍到rank0的机器生成了ncclUniqueId,并完成了机器的bootstrap网络和通信网络的初始化,这节接着看下所有节点间bootstrap的连接是如何建立的。
rank0节点执行ncclGetUniqueId生成ncclUniqueId
通过mpi将Id广播到所有节点,然后所有节点都会执行ncclCommInitRank,这里其他节点也会进行初始化bootstrap网络和通信网络的操作,然后会执行到ncclCommInitRankSync。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
ncclResult_t ncclCommInitRankSync(ncclComm_t* newcomm, int nranks, ncclUniqueId commId, int myrank, int cudaDev) { ncclResult_t res; CUDACHECK(cudaSetDevice(cudaDev)); NCCLCHECKGOTO(commAlloc(newcomm, nranks, myrank), res, cleanup); NCCLCHECKGOTO(initTransportsRank(*newcomm, &commId), res, cleanup); NCCLCHECKGOTO(devCommSetup(*newcomm), res, cleanup); INFO(NCCL_INIT,"comm %p rank %d nranks %d cudaDev %d busId %x - Init COMPLETE", *newcomm, myrank, nranks, (*newcomm)->cudaDev, (*newcomm)->busId); return ncclSuccess;cleanup: if ((*newcomm) && (*newcomm)->bootstrap) bootstrapAbort((*newcomm)->bootstrap); *newcomm = NULL; return res;} |
ncclComm_t是指向ncclComm的指针,ncclComm是一个大杂烩,包含了通信用到的所有上下文信息,里面的字段等用到的时候再介绍,然后通过commAlloc分配newcom,并且完成初始化,比如当前是哪个卡,对应的pcie busid是什么,
执行initTransportsRank
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
static ncclResult_t initTransportsRank(struct ncclComm* comm, ncclUniqueId* commId) { // We use 3 AllGathers // 1. { peerInfo, comm } // 2. ConnectTransport[nranks], ConnectValue[nranks] // 3. { nThreads, nrings, compCap, prev[MAXCHANNELS], next[MAXCHANNELS] } int rank = comm->rank; int nranks = comm->nRanks; uint64_t commHash = getHash(commId->internal, NCCL_UNIQUE_ID_BYTES); TRACE(NCCL_INIT, "comm %p, commHash %lx, rank %d nranks %d - BEGIN", comm, commHash, rank, nranks); NCCLCHECK(bootstrapInit(commId, rank, nranks, &comm->bootstrap)); // AllGather1 - begin struct { struct ncclPeerInfo peerInfo; struct ncclComm* comm; } *allGather1Data; NCCLCHECK(ncclCalloc(&allGather1Data, nranks)); allGather1Data[rank].comm = comm; struct ncclPeerInfo* myInfo = &allGather1Data[rank].peerInfo; NCCLCHECK(fillInfo(comm, myInfo, commHash)); NCCLCHECK(bootstrapAllGather(comm->bootstrap, allGather1Data, sizeof(*allGather1Data))); NCCLCHECK(ncclCalloc(&comm->peerInfo, nranks+1)); // Extra rank to represent CollNet root for (int i = 0; i < nranks; i++) { memcpy(comm->peerInfo+i, &allGather1Data[i].peerInfo, sizeof(struct ncclPeerInfo)); if ((i != rank) && (comm->peerInfo[i].hostHash == myInfo->hostHash) && (comm->peerInfo[i].busId == myInfo->busId)) { WARN("Duplicate GPU detected : rank %d and rank %d both on CUDA device %x", rank, i, myInfo->busId); return ncclInvalidUsage; } } |
看下bootstrapInit
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
ncclResult_t bootstrapInit(ncclUniqueId * id, int rank, int nranks, void** commState) { ncclNetHandle_t* netHandle = (ncclNetHandle_t*) id; bool idFromEnv = getenv("NCCL_COMM_ID") != NULL; struct extState* state; NCCLCHECK(ncclCalloc(&state, 1)); state->rank = rank; state->nranks = nranks; *commState = state; TRACE(NCCL_INIT, "rank %d nranks %d", rank, nranks); struct extInfo info = { 0 }; info.rank = rank; info.nranks = nranks; void *tmpSendComm, *tmpRecvComm; // Pass the remote address to listen via info if (idFromEnv) { memcpy(&info.extHandleListen, netHandle, sizeof(ncclNetHandle_t)); memcpy(&info.extHandleListenRoot, netHandle, sizeof(ncclNetHandle_t)); } // listen will return the local address via info (specify interface type 'findSubnetIf') state->dev = idFromEnv ? findSubnetIf : 0; void* extBstrapListenCommRoot; NCCLCHECK(bootstrapNetListen(state->dev, &info.extHandleListen, &state->extBstrapListenComm)); NCCLCHECK(bootstrapNetListen(state->dev, &info.extHandleListenRoot, &extBstrapListenCommRoot)); // stagger connection times to avoid an overload of the root at very high rank counts if (nranks > 128) { long msec = rank; struct timespec tv; tv.tv_sec = msec / 1000; tv.tv_nsec = 1000000 * (msec % 1000); TRACE(NCCL_INIT, "rank %d delaying connection to root by %ld msec", rank, msec); (void) nanosleep(&tv, NULL); } // send info on my listening socket to root NCCLCHECK(bootstrapNetConnect(state->dev, netHandle, &tmpSendComm)); NCCLCHECK(bootstrapNetSend(tmpSendComm, &info, sizeof(info))); NCCLCHECK(bootstrapNetCloseSend(tmpSendComm)); // get info on my "next" rank in the bootstrap ring from root} |
首先看下commState
即ncclComm的bootstrap,类型为extState。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
struct extState { void* extBstrapListenComm; void* extBstrapRingRecvComm; void* extBstrapRingSendComm; ncclNetHandle_t* peerBstrapHandles; struct unexConn* unexpectedConnections; int rank; int nranks; int dev;}; |
其中extBstrapRingSendComm是当前节点连接next的socket连接,extBstrapRingRecvComm是当前节点和prev节点的socket连接,extBstrapListenComm是当前节点的监听socket,peerBstrapHandles是所有rank的ip port(对应extBstrapListenComm),dev默认为0,表示用第几个ip地址。
然后通过bootstrapNetListen创建extHandleListen和extHandleListenRoot两个bootstrap comm,如前文所述,bootstrap comm其实就是保存了fd,这里创建两个comm的原因是extHandleListen是rank之间实际使用的bootstrap连接,extHandleListenRoot是rank0节点和其他所有rank进行通信使用的连接。
|
1
|
static ncclResult_t bootstrapNetListen(int dev, ncclNetHandle_t* netHandle, void** listenComm) |
bootstrapNetListen函数上节有介绍过,会获取到第dev个当前机器的ip,然后listen获取监听fd,将ip port写到nethandle,获取到的bootstrap comm写到listencomm。
然后将rank,nrank,extHandleListen和extHandleListenRoot写到extInfo里。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
struct extInfo { int rank; int nranks; ncclNetHandle_t extHandleListenRoot; ncclNetHandle_t extHandleListen;}; |
netHandle为ncclUniqueId,即rank0的ip port,然后通过bootstrapNetConnect创建bootstrap send comm,类比bootstrapNetListen,bootstrapNetConnect就是建立到netHandle的socket连接,将socket写到sendComm里,这里dev并没有用到。
|
1
|
static ncclResult_t bootstrapNetConnect(int dev, ncclNetHandle_t* netHandle, void** sendComm) |
然后通过bootstrapNetSend将extInfo发送出去,即发给rank0:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
static ncclResult_t bootstrapNetSend(void* sendComm, void* data, int size) { struct bootstrapNetComm* comm = (struct bootstrapNetComm*)sendComm; NCCLCHECK(socketSend(comm->fd, &size, sizeof(int))); NCCLCHECK(socketSend(comm->fd, data, size)); return ncclSuccess;} |
其中socketSend就是执行send接口发送数据。
然后通过bootstrapNetCloseSend关闭fd
rank0收到数据后会做什么工作呢,回顾一下,rank0的节执行ncclGetUniqueId生成ncclUniqueId,其中在执行bootstrapCreateRoot的最后会启动一个线程执行bootstrapRoot。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
|
static void *bootstrapRoot(void* listenComm) { struct extInfo info; ncclNetHandle_t *rankHandles = NULL; ncclNetHandle_t *rankHandlesRoot = NULL; // for initial rank <-> root information exchange ncclNetHandle_t zero = { 0 }; // for sanity checking void* tmpComm; ncclResult_t res; setFilesLimit(); TRACE(NCCL_INIT, "BEGIN"); /* Receive addresses from all ranks */ int nranks = 0, c = 0; do { NCCLCHECKGOTO(bootstrapNetAccept(listenComm, &tmpComm), res, out); NCCLCHECKGOTO(bootstrapNetRecv(tmpComm, &info, sizeof(info)), res, out); NCCLCHECKGOTO(bootstrapNetCloseRecv(tmpComm), res, out); if (c == 0) { nranks = info.nranks; NCCLCHECKGOTO(ncclCalloc(&rankHandles, nranks), res, out); NCCLCHECKGOTO(ncclCalloc(&rankHandlesRoot, nranks), res, out); } if (nranks != info.nranks) { WARN("Bootstrap Root : mismatch in rank count from procs %d : %d", nranks, info.nranks); goto out; } if (memcmp(&zero, &rankHandlesRoot[info.rank], sizeof(ncclNetHandle_t)) != 0) { WARN("Bootstrap Root : rank %d of %d ranks has already checked in", info.rank, nranks); goto out; } // Save the connection handle for that rank memcpy(rankHandlesRoot+info.rank, info.extHandleListenRoot, sizeof(ncclNetHandle_t)); memcpy(rankHandles+info.rank, info.extHandleListen, sizeof(ncclNetHandle_t)); ++c; TRACE(NCCL_INIT, "Received connect from rank %d total %d/%d", info.rank, c, nranks); } while (c < nranks); TRACE(NCCL_INIT, "COLLECTED ALL %d HANDLES", nranks); // Send the connect handle for the next rank in the AllGather ring for (int r=0; r<nranks; ++r) { int next = (r+1) % nranks; void *tmpSendComm; NCCLCHECKGOTO(bootstrapNetConnect(0, rankHandlesRoot+r, &tmpSendComm), res, out); NCCLCHECKGOTO(bootstrapNetSend(tmpSendComm, rankHandles+next, sizeof(ncclNetHandle_t)), res, out); NCCLCHECKGOTO(bootstrapNetCloseSend(tmpSendComm), res, out); } TRACE(NCCL_INIT, "SENT OUT ALL %d HANDLES", nranks);out: bootstrapNetCloseListen(listenComm); if (rankHandles) free(rankHandles); if (rankHandlesRoot) free(rankHandlesRoot); TRACE(NCCL_INIT, "DONE"); return NULL;} |
listenComm是上一个博文中rank0创建的监听fd,bootstrapNetAccept是从listenComm中获取一个新连接,使用新连接的fd创建recvcomm。
|
1
|
static ncclResult_t bootstrapNetAccept(void* listenComm, void** recvComm) |
然后通过bootstrapNetRecv读取tmpComm的数据,即其他rank发送来的extInfo,然后保存其他rank的extHandleListen和extHandleListenRoot,这个时候rank0就获取到其他所有rank的ip和port了。
获取完所有rank的info之后开始建环,将节点(r+1) % nranks的extHandleListen发送给节点r,就是说将节点r的next节点的nethandle发送给节点r。这里可以看出,每个节点创建了两个listen comm,其中rank0使用extHandleListenRoot进行通信,其他节点之间通过extHandleListen进行通信。
然后再回去接着看bootstrapInit
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
ncclResult_t bootstrapInit(ncclUniqueId * id, int rank, int nranks, void** commState) { // get info on my "next" rank in the bootstrap ring from root ncclNetHandle_t extHandleNext; NCCLCHECK(bootstrapNetAccept(extBstrapListenCommRoot, &tmpRecvComm)); NCCLCHECK(bootstrapNetRecv(tmpRecvComm, &extHandleNext, sizeof(extHandleNext))); NCCLCHECK(bootstrapNetCloseRecv(tmpRecvComm)); NCCLCHECK(bootstrapNetCloseListen(extBstrapListenCommRoot)); NCCLCHECK(bootstrapNetConnect(state->dev, &extHandleNext, &state->extBstrapRingSendComm)); // Accept the connect request from the previous rank in the AllGather ring NCCLCHECK(bootstrapNetAccept(state->extBstrapListenComm, &state->extBstrapRingRecvComm)); // AllGather all listen handlers NCCLCHECK(ncclCalloc(&state->peerBstrapHandles, nranks)); memcpy(state->peerBstrapHandles+rank, info.extHandleListen, sizeof(ncclNetHandle_t)); NCCLCHECK(bootstrapAllGather(state, state->peerBstrapHandles, sizeof(ncclNetHandle_t))); TRACE(NCCL_INIT, "rank %d nranks %d - DONE", rank, nranks); return ncclSuccess;} |
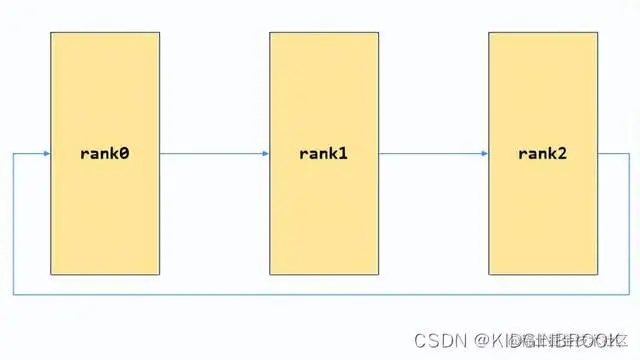
接着所有rank都会在extHandleListenRoot上接收新连接创建tmpRecvComm,然后接收到当前rank的next的ip,port;然后连接next创建bscomm到state->extBstrapRingSendComm,接收prev的连接创建bscomm到state->extBstrapRingRecvComm,到现在bootstrap网络连接就完全建立起来了,如下图:
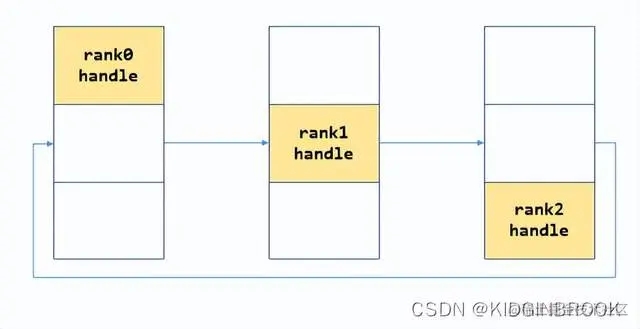
最后gather所有rank的ip port
首先将自己的nethandle放到peerBstrapHandles的对应位置,如下所示。
然后执行bootstrapAllGather:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
ncclResult_t bootstrapAllGather(void* commState, void* allData, int size) { struct extState* state = (struct extState*)commState; char* data = (char*)allData; int rank = state->rank; int nranks = state->nranks; TRACE(NCCL_INIT, "rank %d nranks %d size %d", rank, nranks, size); /* Simple ring based AllGather * At each step i receive data from (rank-i-1) from left * and send previous step's data from (rank-i) to right */ for (int i=0; i<nranks-1; i++) { size_t rslice = (rank - i - 1 + nranks) % nranks; size_t sslice = (rank - i + nranks) % nranks; // Send slice to the right NCCLCHECK(bootstrapNetSend(state->extBstrapRingSendComm, data+sslice*size, size)); // Recv slice from the left NCCLCHECK(bootstrapNetRecv(state->extBstrapRingRecvComm, data+rslice*size, size)); } TRACE(NCCL_INIT, "rank %d nranks %d size %d - DONE", rank, nranks, size); return ncclSuccess;} |
每一次将自己的data发送给对应的rank,然后接收其他rank发送过来的data,如下图。
第一步:
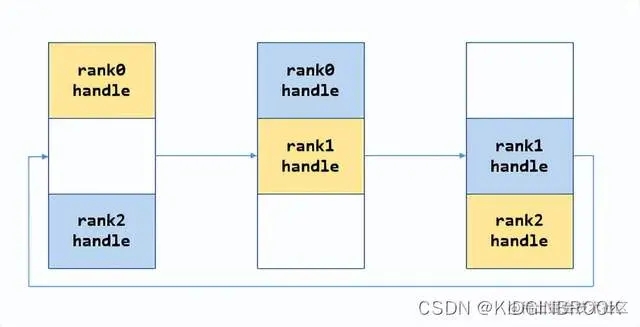
第二步:
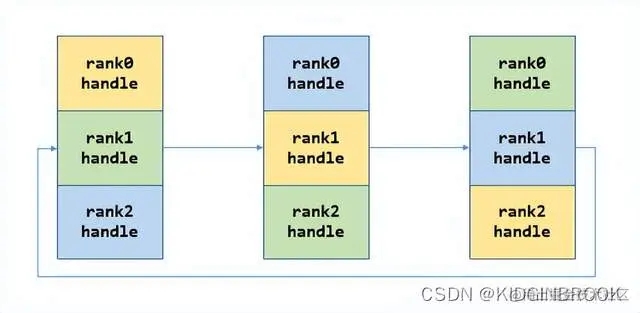
到这里每个rank就都有了全局所有rank的ip port。
最后总结一下,本节主要创建了bootstrap环形网络连接,并保存到ncclComm里。
欢迎 Star、试用 OneFlow 最新版本:github.com/Oneflow-Inc…
以上就是NCCL深度学习Bootstrap网络连接建立源码解析的详细内容,更多关于NCCL Bootstrap网络连接的资料请关注服务器之家其它相关文章!
原文链接:https://juejin.cn/post/7219229724958277688