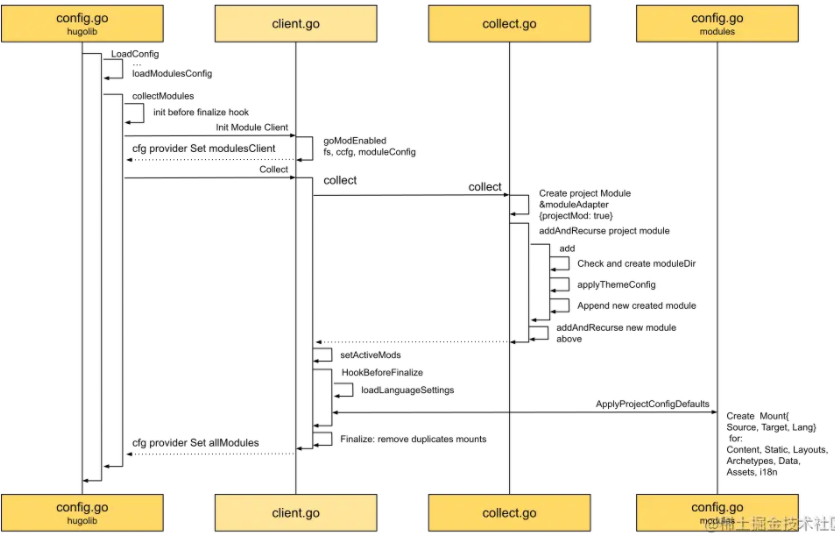
了然于胸 - collectModules时序图
经过loadConfig和applyConfigDefaults,我们已经将用户自定义信息和默认信息都归置妥当,并且放在了Config Provider中,方便查用。
Hugo在拿到这些信息后,立马着手的事情就是collectModules,也就是收集模块信息了。

正如上图中loadModulesConfig所示,拿到配置信息后,就进行解码decodeConfig操作。 在我们的示例中,我们的项目用到了名为mytheme的主题,所以在项目配置信息中,我们需要把主题添加到导入项Imports中。
准备好了模块的配置信息后,接下来就是要根据这些配置信息,对模块进行处理了。
需要先准备好回调函数beforeFinalizeHook,为什么要准备这和个回调函数呢? 我们先把这个疑问放一放,一会我们就能发现实际的触发场景。
回调函数设置好后,接着就开始收集模块了。 如上图左上角所示,首先需要创建Module Client用来具体处理模块的收集工作。 为什么要叫Client呢? 这是因为现在Hugo支持Golang的mod模式,意味着可以用go.mod来导入主题,那我们就需要下载依赖包 - 主题工程来管理依赖了。 这样来看,叫客户端是不是就不难理解了。 在我们的示例中,主题目录是用来做流程讲解示范的,只有一个文本文件,所以这里的场景并不涉线上go模块加载。
客户端设置好后,开始收集,如上图中间所示,收集过程总共分四步:
- 按配置递归收集所有模块 - Collect
- 设置处于活跃状态的模块 - setActiveMods
- 触发提前设置的回调函数 - HookBeforeFinalize
- 移除重复的挂载信息 - Finalize
Collect
先为项目创建工程模块Project Module,然后开始递归收集模块:
func (c *collector) collect() {
...
// c.gomods is [], GetMain() returns ni
projectMod := createProjectModule(c.gomods.GetMain(), c.ccfg.WorkingDir, c.moduleConfig)
// module structure, [project, others...]
if err := c.addAndRecurse(projectMod, false); err != nil {
c.err = err
return
}
...
}
这里为什么会用到递归呢? 因为在Hugo中,模块之间是有相互依赖的。 通过最开始的模块配置信息也可以看出,我们把依赖的模块放在了Imports中,Project Module就需要导入"mytheme"模块。 在实际情况中,"mytheme"有可能也是依赖于其它的主题,所以也需要导入其它模块。
从上面时序图右下方可以看到,addAndRecurse做了四件事:
- 为导入的模块创建模块文件夹,用来放置模块所有文件
- 应用主题配置,就像最开始解析项目模块的配置信息一样,看是否还需要导入其它模块
- 将模块添加到模块列表中
- 为新模块重复上述步骤
这样,我们就能顺着项目模块的配置信息,逐个将所有的模块信息收集齐全了。
setActiveMods
递归收集完所有模块信息后,需要根据用户配置,进一步将禁用的模块给过滤到,留下这一次构建所需要的模块。
HookBeforeFinalize
过滤完模块后,在Finalize敲定前,是时候回调我们之前设置好地回调函数了。
除了加载多语言设置处,回调函数所做的操作主要集中在上面时序图的右下脚。 就是为项目模块准备好所有的挂载Mount,包括Content, Static, Layouts, Archetypes, Data, Assets, i18n,共七个组件。 其中Content和其它的组件有点不一样。 因为Content挂载点和多语言一一对应,也就是说有几种语言,就会有几个内容目录。
Finalize
等有了所有的模块的信息,挂载点也收集完毕后,我们还要做一件事情。 那就是要保证这些挂载点在全局视野下,没有重复。
结合时序图,我们进一步将其中的关键对象结构体,根据这些结构体的属性和行为,按流程处理后所得到的最终结果放在一起,可视化出来。 方便大家理解:

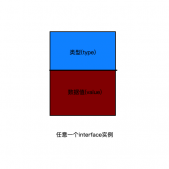
抽象总结 - 输入不同类型的值,输出标准的configProvider
在上图中,通过下方输出部分可以看出,一个模块配置项,对应一个模块。
在左边的模块配置信息中,包含了模块之间的依赖信息。 在上面的示例中项目模块饱含了主题模块。
在右边的模块实例中,首先要区分哪一个是项目模块,因为项目模块是站点构建的起点。 所以在模块中需要能标识身份信息的字段projectMod。
如果从挂载Mounts的角度来看模块,那每个模块实际上就是一个合并后的根文件系统。 Hugo将这个文件系统用七个组件进行了划分。
项目模块必需得包含这些信息,但因为依赖于其它模块,所以需要将项目模块放在最后处理。 Hugo将项目模块放在了模块队列的第一个,并用一个回调函数帮助在合适的时间点,对项目模的挂载进行了统一的处理。
再用Input -> [?] -> Output模型来进行分析,可以抽象为以下模型:
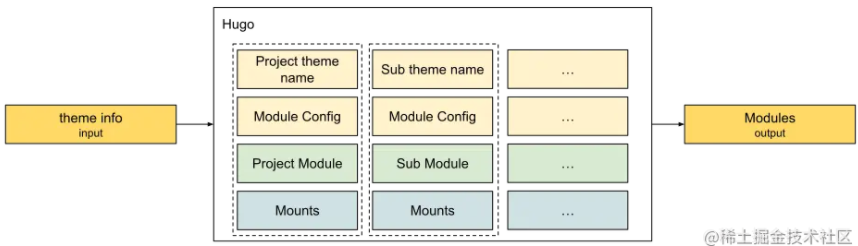
主题信息来源于用户自定义信息,作为输入传入收集模块功能单元。 在处理过程中,Hugo按Name, Module Config, Module, Mounts的对应关系,将模块相关信息进行处理。 最终生成所有模块的信息,并通过将这些信息设置在Config Provider中,为后续的操作做好准备。
动手实践 - Show Me the Code of collectModules
在知道collectModules的实现原理后。 按照我们的传统,让我们动动小手,用代码来总结代码,巩固一下知识。
可以这里线上尝试,Show Me the Code, try it yourself
代码里有注解说明,代码样例:
package main
import "fmt"
type Mount struct {
// relative path in source repo, e.g. "scss"
Source string
// relative target path, e.g. "assets/bootstrap/scss"
Target string
// any language code associated with this mount.
Lang string
}
type Import struct {
// Module path
Path string
}
// Config holds a module config.
type Config struct {
Mounts []Mount
Imports []Import
}
type Module interface {
// Config The decoded module config and mounts.
Config() Config
// Owner In the dependency tree, this is the first module that defines this module
// as a dependency.
Owner() Module
// Mounts Any directory remappings.
Mounts() []Mount
}
type Modules []Module
var modules Modules
// moduleAdapter implemented Module interface
type moduleAdapter struct {
projectMod bool
owner Module
mounts []Mount
config Config
}
func (m *moduleAdapter) Config() Config {
return m.config
}
func (m *moduleAdapter) Mounts() []Mount {
return m.mounts
}
func (m *moduleAdapter) Owner() Module {
return m.owner
}
// happy path to easily understand
func main() {
// project module config
moduleConfig := Config{}
imports := []string{"mytheme"}
for _, imp := range imports {
moduleConfig.Imports = append(moduleConfig.Imports, Import{
Path: imp,
})
}
// Need to run these after the modules are loaded, but before
// they are finalized.
collectHook := func(mods Modules) {
// Apply default project mounts.
// Default folder structure for hugo project
ApplyProjectConfigDefaults(mods[0])
}
collectModules(moduleConfig, collectHook)
for _, m := range modules {
fmt.Printf("%#v\n", m)
}
}
// Module folder structure
const (
ComponentFolderArchetypes = "archetypes"
ComponentFolderStatic = "static"
ComponentFolderLayouts = "layouts"
ComponentFolderContent = "content"
ComponentFolderData = "data"
ComponentFolderAssets = "assets"
ComponentFolderI18n = "i18n"
)
// ApplyProjectConfigDefaults applies default/missing module configuration for
// the main project.
func ApplyProjectConfigDefaults(mod Module) {
projectMod := mod.(*moduleAdapter)
type dirKeyComponent struct {
key string
component string
multilingual bool
}
dirKeys := []dirKeyComponent{
{"contentDir", ComponentFolderContent, true},
{"dataDir", ComponentFolderData, false},
{"layoutDir", ComponentFolderLayouts, false},
{"i18nDir", ComponentFolderI18n, false},
{"archetypeDir", ComponentFolderArchetypes, false},
{"assetDir", ComponentFolderAssets, false},
{"", ComponentFolderStatic, false},
}
var mounts []Mount
for _, d := range dirKeys {
if d.multilingual {
// based on language content configuration
// multiple language has multiple source folders
if d.component == ComponentFolderContent {
mounts = append(mounts, Mount{Lang: "en", Source: "mycontent", Target: d.component})
}
} else {
mounts = append(mounts, Mount{Source: d.component, Target: d.component})
}
}
projectMod.mounts = mounts
}
func collectModules(modConfig Config, hookBeforeFinalize func(m Modules)) {
projectMod := &moduleAdapter{
projectMod: true,
config: modConfig,
}
// module structure, [project, others...]
addAndRecurse(projectMod)
// Add the project mod on top.
modules = append(Modules{projectMod}, modules...)
if hookBeforeFinalize != nil {
hookBeforeFinalize(modules)
}
}
// addAndRecurse Project Imports -> Import imports
func addAndRecurse(owner *moduleAdapter) {
moduleConfig := owner.Config()
// theme may depend on other theme
for _, moduleImport := range moduleConfig.Imports {
tc := add(owner, moduleImport)
if tc == nil {
continue
}
// tc is mytheme with no config file
addAndRecurse(tc)
}
}
func add(owner *moduleAdapter, moduleImport Import) *moduleAdapter {
fmt.Printf("start to create `%s` module\n", moduleImport.Path)
ma := &moduleAdapter{
owner: owner,
// in the example, mytheme has no other import
config: Config{},
}
modules = append(modules, ma)
return ma
}
输出结果:
# collect theme as module
start to create `mytheme` module
# project module has no owner with default mounts
&main.moduleAdapter{projectMod:true, owner:main.Module(nil), mounts:[]main.Mount{main.Mount{Source:"mycontent", Target:"content", Lang:"en"}, main.Mount{Source:"data", Target:"data", Lang:""}, main.Mount{Source:"layouts", Target:"layouts", Lang:""}, main.Mount{Source:"i18n", Target:"i18n", Lang:""}, main.Mount{Source:"archetypes", Target:"archetypes", Lang:""}, main.Mount{Source:"assets", Target:"assets", Lang:""}, main.Mount{Source:"static", Target:"static", Lang:""}}, config:main.Config{Mounts:[]main.Mount(nil), Imports:[]main.Import{main.Import{Path:"mytheme"}}}}
# theme module owned by project module with no import in the example
&main.moduleAdapter{projectMod:false, owner:(*main.moduleAdapter)(0xc000102120), mounts:[]main.Mount(nil), config:main.Config{Mounts:[]main.Mount(nil), Imports:[]main.Import(nil)}}
Program exited.
以上就是Hugo Config模块构建实现源码剖析的详细内容,更多关于Hugo Config模块构建的资料请关注服务器之家其它相关文章!
原文链接:https://juejin.cn/post/7158065831790772261