1.安装
1.1 创建虚拟环境
mkdir myproject cd myproject python3 -m venv venv
1.2 进入虚拟环境
. venv/bin/activate
1.3 安装 flask
pip install Flask
2.上手
2.1 最小 Demo
将下列代码保存为hello.py:
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route("/")
def hello_world():
return "<p>Hello, World!</p>"
运行上述代码:
export FLASK_APP=hello flask run
这样访问:http://127.0.0.1:5000会看到 Hello, World!
2.2 基本知识
这里有 flask 的基本知识(非常重要的基础,大家可以自己看:链接
1.HTML Escaping (利用 Jinja,参考:链接
2.Routing (下面几个例子)
@app.route('/')
def index():
return 'Index Page'
@app.route('/hello')
def hello():
return 'Hello, World'
@app.route('/user/<username>')
def show_user_profile(username):
# show the user profile for that user
return f'User {escape(username)}'
@app.route('/post/<int:post_id>')
def show_post(post_id):
# show the post with the given id, the id is an integer
return f'Post {post_id}'
@app.route('/path/<path:subpath>')
def show_subpath(subpath):
# show the subpath after /path/
return f'Subpath {escape(subpath)}'
3.HTTP Methods
@app.route('/login', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def login():
if request.method == 'POST':
else:
4.Static Files (url_for('static', filename='style.css'))
5.Rendering Templates (这个参考之前的 Jinja)
6.File Uploads、Cookies、Redirects and Errors、About Responses、APIs with JSON、Sessions、Message Flashing、Logging 这些等我们实际用到时再过来看
3.解构官网指导 Demo
第 1 节教大家如何利用 python 虚拟环境,快速构建 flask 环境;第 2 节带着大家简单熟悉了 flask 的编程规则(或风格)。
大家在着手本节时,务必将第 2 节中的基础的代码跟着官网敲一下!因为,这一节我们不是由简到难一步步搭建 flask 服务器,而是直接拿搭建好的反过来分析。
3.1 克隆与代码架构分析
$ git clone https://github.com/pallets/flask $ cd flask $ cd examples/tutorial
代码目录结构如下:
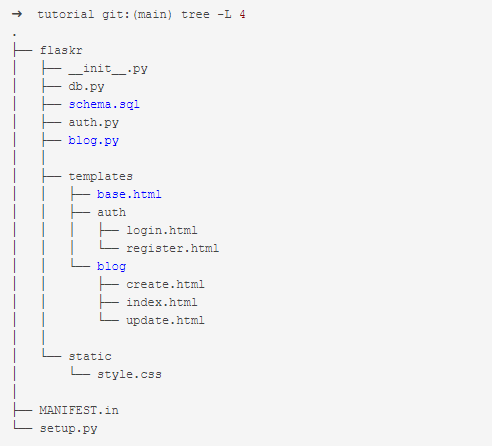
3.2 入口文件init.py
def create_app(test_config=None):
"""Create and configure an instance of the Flask application."""
# 1-创建一个 Flask 实例
# 并设置一些 APP 需要用到的参数
app = Flask(__name__, instance_relative_config=True)
app.config.from_mapping(
# a default secret that should be overridden by instance config
SECRET_KEY="dev",
# store the database in the instance folder
DATABASE=os.path.join(app.instance_path, "flaskr.sqlite"),
)
# 2-测试用的
if test_config is None:
# load the instance config, if it exists, when not testing
app.config.from_pyfile("config.py", silent=True)
else:
# load the test config if passed in
app.config.update(test_config)
# 3-创建一个文件夹,用来存 DB 运行时的产生的文件
# ensure the instance folder exists
try:
os.makedirs(app.instance_path)
except OSError:
pass
@app.route("/hello")
def hello():
return "Hello, World!"
# register the database commands
# 3.3 数据库设置(为 flask 新增一个 init_db 命令,这样直接敲 flask init_db 就能生成表)
from flaskr import db
db.init_app(app)
# apply the blueprints to the app
# #### 3.4 蓝图和视图(基于蓝图来管理组织视图,视图注册到蓝图,蓝图注册到应用)
from flaskr import auth, blog
app.register_blueprint(auth.bp)
app.register_blueprint(blog.bp)
# make url_for('index') == url_for('blog.index')
# in another app, you might define a separate main index here with
# app.route, while giving the blog blueprint a url_prefix, but for
# the tutorial the blog will be the main index
app.add_url_rule("/", endpoint="index")
return app
3.3 数据库设置
该项目采用了 SQLite 作为数据库(Python 内置了,免去安装和配置工作)。
1.SQL 文件 schema.sql
SQLite 的数据存储在表格中,在向表格增删改查数据前,需要先建表。该项目中的 schema.sql 编写了建表的 SQL 语句。分别创建了一个 user 表和 post 表。
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS user; DROP TABLE IF EXISTS post; CREATE TABLE user ( id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT, username TEXT UNIQUE NOT NULL, password TEXT NOT NULL ); CREATE TABLE post ( id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT, author_id INTEGER NOT NULL, created TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, title TEXT NOT NULL, body TEXT NOT NULL, FOREIGN KEY (author_id) REFERENCES user (id) );
2)与数据库建立连接与断开
def get_db():
"""Connect to the application's configured database. The connection
is unique for each request and will be reused if this is called
again.
"""
if "db" not in g:
g.db = sqlite3.connect(
current_app.config["DATABASE"], detect_types=sqlite3.PARSE_DECLTYPES
)
g.db.row_factory = sqlite3.Row
return g.db
def close_db(e=None):
"""If this request connected to the database, close the
connection.
"""
db = g.pop("db", None)
if db is not None:
db.close()
g 是一个特殊结构,对于每次请求,会产生一个。
3)数据库初始化(生成表)
第 1 节的 schema.sql 用于建表,那么如何执行其中的建表命令呢? db.py 中的 init_db 就是干这个事情的。
def init_db():
"""Clear existing data and create new tables."""
db = get_db() # 获取数据库(如果没有则创建)
# 读取 schema.sql 中的 SQL 命令,并用 db.executescript 执行 SQL 命令
with current_app.open_resource("schema.sql") as f:
db.executescript(f.read().decode("utf8"))
4)将 init_db 注册为 flask 命令
由于数据库初始化并不需要每次启动数据库时运行(不属于运行时需要执行的函数),我们需要将注册成 flask 一个指令,只要在命令行中敲flask init-db就能够执行init_db,其实现方法如下:
@click.command("init-db")
@with_appcontext
def init_db_command():
"""Clear existing data and create new tables."""
init_db()
click.echo("Initialized the database.")
def init_app(app):
"""Register database functions with the Flask app. This is called by
the application factory.
"""
app.teardown_appcontext(close_db) # 在返回响应后进行清理时调用该函数
app.cli.add_command(init_db_command) # 添加一个可以用flask命令调用的新命令
这样,执行完之后,flask.sqlite 文件将会出现在 instance 文件夹。
3.4 蓝图和视图
蓝图是一种组织一组相关视图和其他代码的方法。它们不是直接向应用程序注册视图和其他代码,而是向蓝图注册。然后,当蓝图在factory函数中可用时,它将在应用程序中注册。
该项目中有两个蓝图:auth 和 blog
bp = Blueprint("auth", __name__, url_prefix="/auth") # in auth.py
bp = Blueprint("blog", __name__) # in blog.py
参数分别是:蓝图的名字,import_name(一般为 __name__),url 前缀
[1].官方 Demo Github 仓库
1)auth 视图
这里主要有三个路由:
@bp.route("/register", methods=("GET", "POST"))
def register():
...
@bp.route("/login", methods=("GET", "POST"))
def login():
...
@bp.route("/logout")
def logout():
2)blog 视图
这里主要有四个路由:
@bp.route("/")
def index():
...
@bp.route("/create", methods=("GET", "POST"))
@login_required
def create():
...
@bp.route("/<int:id>/update", methods=("GET", "POST"))
@login_required
def update(id):
...
@bp.route("/<int:id>/delete", methods=("POST",))
@login_required
def delete(id):
...
3)注册视图中各个功能实现介绍
注册
注册逻辑为:首先从 POST 中获取 username 和 password,然后调用数据库插入操作:
- username = request.form["username"]
- password = request.form["password"]
- db.execute("INSERT INTO user (username, password) VALUES (?, ?)", (username, generate_password_hash(password)),)
登录
登录逻辑为:首先从 POST 中获取 username 和 password,然后调用数据库查询操作,获取该用户的密码,然后进行密码匹配:
- user = db.execute("SELECT * FROM user WHERE username = ?",username,)).fetchone()
- check_password_hash(user["password"], password)
密码匹配后,需要创建 session:
if error is None:
# store the user id in a new session and return to the index
session.clear()
session["user_id"] = user["id"]
return redirect(url_for("index"))
注销
注销需要清空 session:
session.clear()
Session
Session 逻辑如下:注册一个方法,让其在任何 URL 请求之前执行,在其中做 Session 管理:
@bp.before_app_request
def load_logged_in_user():
user_id = session.get('user_id')
if user_id is None:
g.user = None
else:
g.user = get_db().execute(
'SELECT * FROM user WHERE id = ?', (user_id,)
).fetchone()
其他 View 使用认证
其他 View 也想使用认证该如何做?在 auth.py 中实现 login_required 函数,判断 user 是否为空,如果为空,则跳转到登录页面:
def login_required(view):
@functools.wraps(view)
def wrapped_view(**kwargs):
if g.user is None:
return redirect(url_for('auth.login'))
return view(**kwargs)
return wrapped_view
4)博客视图中各个功能实现介绍
展示所有博客
逻辑如下:执行数据库查询操作,获取所有博客,然后加载:
@bp.route("/")
def index():
"""Show all the posts, most recent first."""
db = get_db()
posts = db.execute(
"SELECT p.id, title, body, created, author_id, username"
" FROM post p JOIN user u ON p.author_id = u.id"
" ORDER BY created DESC"
).fetchall()
return render_template("blog/index.html", posts=posts)
创建博客
逻辑如下:函数前加上@login_required前缀,这样就能自动判断是否已经登录,否则跳到登录页面;创建博客就是获取标题和内容,然后调用插入命令,进行插入:
@bp.route("/create", methods=("GET", "POST"))
@login_required
def create():
"""Create a new post for the current user."""
if request.method == "POST":
body = request.form["body"]
error = None
if not title:
error = "Title is required."
if error is not None:
flash(error)
else:
db = get_db()
db.execute(
"INSERT INTO post (title, body, author_id) VALUES (?, ?, ?)",
(title, body, g.user["id"]),
)
db.commit()
return redirect(url_for("blog.index"))
return render_template("blog/create.html")
更新和删除博客
更新和删除博客,需要传入一个 id,然后有一个内部函数用于判断该 id 是否存在:
def get_post(id, check_author=True):
"""Get a post and its author by id.
Checks that the id exists and optionally that the current user is
the author.
:param id: id of post to get
:param check_author: require the current user to be the author
:return: the post with author information
:raise 404: if a post with the given id doesn't exist
:raise 403: if the current user isn't the author
"""
post = (
get_db()
.execute(
"SELECT p.id, title, body, created, author_id, username"
" FROM post p JOIN user u ON p.author_id = u.id"
" WHERE p.id = ?",
(id,),
)
.fetchone()
)
if post is None:
abort(404, f"Post id {id} doesn't exist.")
if check_author and post["author_id"] != g.user["id"]:
abort(403)
return post
因此,更新的逻辑如下:
@bp.route("/<int:id>/update", methods=("GET", "POST"))
@login_required
def update(id):
"""Update a post if the current user is the author."""
post = get_post(id)
if request.method == "POST":
body = request.form["body"]
error = None
if not title:
error = "Title is required."
if error is not None:
flash(error)
else:
db = get_db()
db.execute(
"UPDATE post SET )
db.commit()
return redirect(url_for("blog.index"))
return render_template("blog/update.html", post=post)
删除的逻辑如下:
@bp.route("/<int:id>/delete", methods=("POST",))
@login_required
def delete(id):
"""Delete a post.
Ensures that the post exists and that the logged in user is the
author of the post.
"""
get_post(id)
db = get_db()
db.execute("DELETE FROM post WHERE id = ?", (id,))
db.commit()
return redirect(url_for("blog.index"))
4.其他
其他还有一些,是大家玩熟了之后才需要看的:
- 工程部署安装
- 工程自动化测试
5.跑起 DEMO
最后,我们跑起 Demo 看看效果:
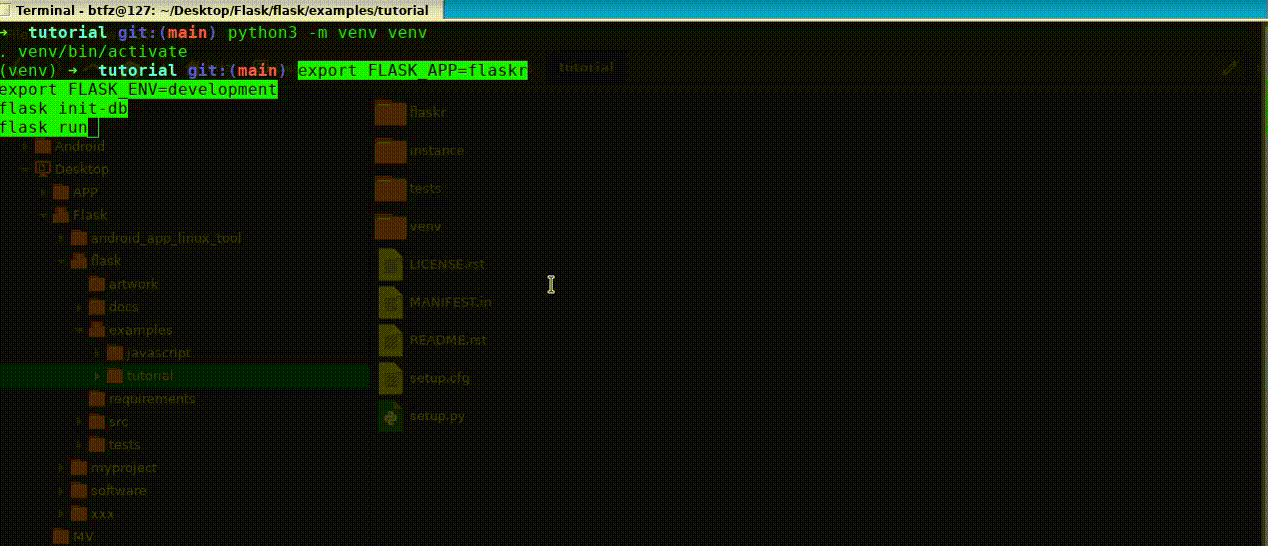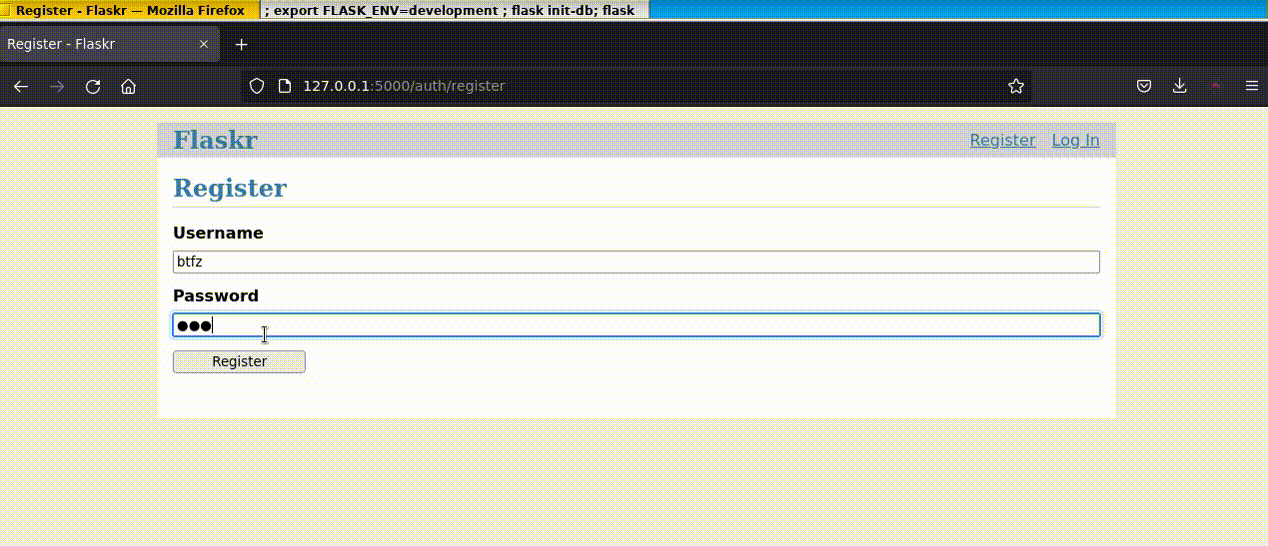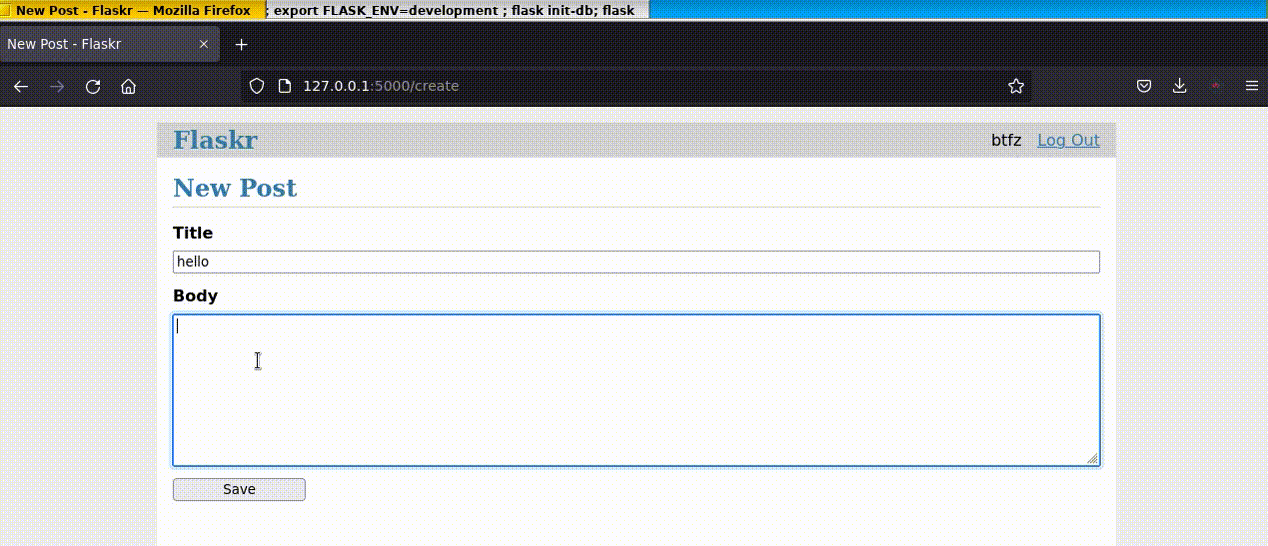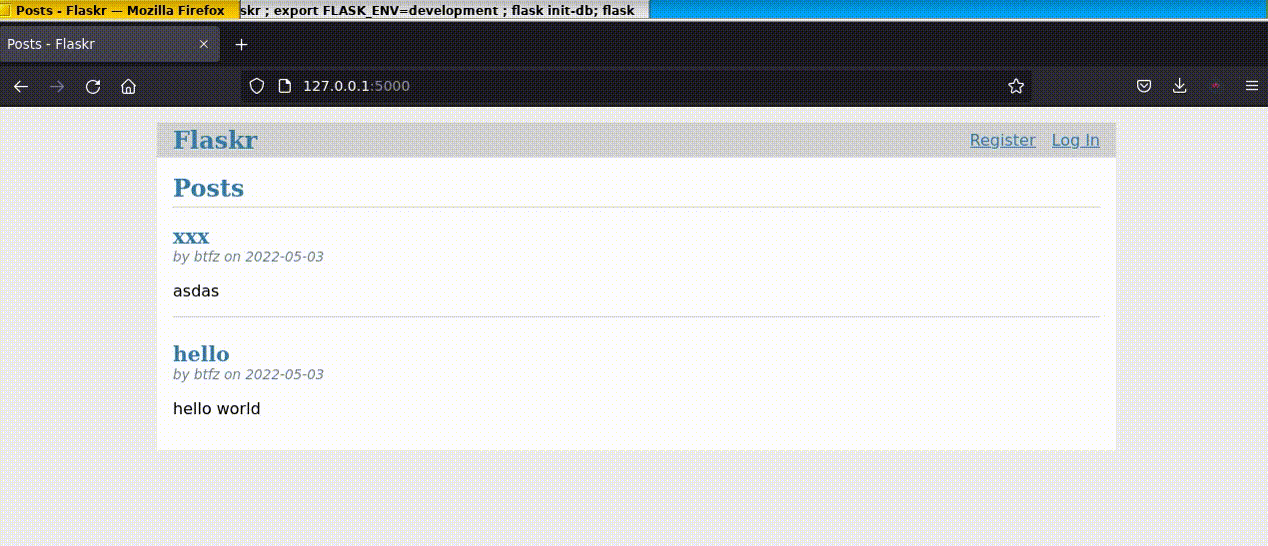
1)在 tutorial 目录下,创建虚拟环境,并安装 Flask:
python3 -m venv venv . venv/bin/activate pip install Flask
2)以开发者方式运行:
export FLASK_APP=flaskr export FLASK_ENV=development flask init-db flask run
效果如下:
以上就是详解Python Flask框架的安装及应用的详细内容,更多关于Python Flask框架的资料请关注服务器之家其它相关文章!
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/zjutlitao/p/16218348.html