在用Spring Security项目开发中,有时候需要放通某一个接口时,我们需要在配置中把接口地址配置上,这样做有时候显得麻烦,而且不够优雅。我们能不能通过一个注解的方式,在需要放通的接口上加上该注解,这样接口就能放通了。答案肯定是可以的啦,今天我们一起来看看实现过程吧。
1.SpringBoot版本
本文基于的Spring Boot的版本是2.6.7
2.实现思路
新建一个AnonymousAccess注解,该注解是应用于Controller方法上的
新建一个存放所有请求方式的枚举类
通过判断Controller方法上是否存在该注解
在SecurityConfig上进行策略的配置
3.实现过程
3.1新建注解
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
@Inherited@Documented@Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE})@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)public @interface AnonymousAccess { } |
3.2新建请求枚举类
该类是存放所有的请求类型的,代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
|
@Getter@AllArgsConstructorpublic enum RequestMethodEnum { /** * 搜寻 @AnonymousGetMapping */ GET("GET"), /** * 搜寻 @AnonymousPostMapping */ POST("POST"), /** * 搜寻 @AnonymousPutMapping */ PUT("PUT"), /** * 搜寻 @AnonymousPatchMapping */ PATCH("PATCH"), /** * 搜寻 @AnonymousDeleteMapping */ DELETE("DELETE"), /** * 否则就是所有 Request 接口都放行 */ ALL("All"); /** * Request 类型 */ private final String type; public static RequestMethodEnum find(String type) { for (RequestMethodEnum value : RequestMethodEnum.values()) { if (value.getType().equals(type)) { return value; } } return ALL; }} |
3.3判断Controller方法上是否存在该注解
在SecurityConfig类中定义一个私有方法getAnonymousUrl,该方法主要作用是判断controller那些方法加上了AnonymousAccess的注解
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
private Map<String, Set<String>> getAnonymousUrl(Map<RequestMappingInfo, HandlerMethod> handlerMethodMap) { Map<String, Set<String>> anonymousUrls = new HashMap<>(8); Set<String> get = new HashSet<>(); Set<String> post = new HashSet<>(); Set<String> put = new HashSet<>(); Set<String> patch = new HashSet<>(); Set<String> delete = new HashSet<>(); Set<String> all = new HashSet<>(); for (Map.Entry<RequestMappingInfo, HandlerMethod> infoEntry : handlerMethodMap.entrySet()) { HandlerMethod handlerMethod = infoEntry.getValue(); AnonymousAccess anonymousAccess = handlerMethod.getMethodAnnotation(AnonymousAccess.class); if (null != anonymousAccess) { List<RequestMethod> requestMethods = new ArrayList<>(infoEntry.getKey().getMethodsCondition().getMethods()); RequestMethodEnum request = RequestMethodEnum.find(requestMethods.size() == 0 ? RequestMethodEnum.ALL.getType() : requestMethods.get(0).name()); switch (Objects.requireNonNull(request)) { case GET: get.addAll(infoEntry.getKey().getPatternsCondition().getPatterns()); break; case POST: post.addAll(infoEntry.getKey().getPatternsCondition().getPatterns()); break; case PUT: put.addAll(infoEntry.getKey().getPatternsCondition().getPatterns()); break; case PATCH: patch.addAll(infoEntry.getKey().getPatternsCondition().getPatterns()); break; case DELETE: delete.addAll(infoEntry.getKey().getPatternsCondition().getPatterns()); break; default: all.addAll(infoEntry.getKey().getPatternsCondition().getPatterns()); break; } } } anonymousUrls.put(RequestMethodEnum.GET.getType(), get); anonymousUrls.put(RequestMethodEnum.POST.getType(), post); anonymousUrls.put(RequestMethodEnum.PUT.getType(), put); anonymousUrls.put(RequestMethodEnum.PATCH.getType(), patch); anonymousUrls.put(RequestMethodEnum.DELETE.getType(), delete); anonymousUrls.put(RequestMethodEnum.ALL.getType(), all); return anonymousUrls;} |
3.4在SecurityConfig上进行策略的配置
通过一个SpringUtil工具类获取到requestMappingHandlerMapping的Bean,然后通过getAnonymousUrl方法把标注AnonymousAccess接口找出来。最后,通过antMatchers细腻化到每个 Request 类型。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
@Overrideprotected void configure(HttpSecurity httpSecurity) throws Exception { // 搜寻匿名标记 url: @AnonymousAccess RequestMappingHandlerMapping requestMappingHandlerMapping = (RequestMappingHandlerMapping) SpringUtil.getBean("requestMappingHandlerMapping"); Map<RequestMappingInfo, HandlerMethod> handlerMethodMap = requestMappingHandlerMapping.getHandlerMethods(); // 获取匿名标记 Map<String, Set<String>> anonymousUrls = getAnonymousUrl(handlerMethodMap); httpSecurity //禁用CSRF .csrf().disable() .authorizeRequests() // 自定义匿名访问所有url放行:细腻化到每个 Request 类型 // GET .antMatchers(HttpMethod.GET,anonymousUrls.get(RequestMethodEnum.GET.getType()).toArray(new String[0])).permitAll() // POST .antMatchers(HttpMethod.POST,anonymousUrls.get(RequestMethodEnum.POST.getType()).toArray(new String[0])).permitAll() // PUT .antMatchers(HttpMethod.PUT,anonymousUrls.get(RequestMethodEnum.PUT.getType()).toArray(new String[0])).permitAll() // PATCH .antMatchers(HttpMethod.PATCH,anonymousUrls.get(RequestMethodEnum.PATCH.getType()).toArray(new String[0])).permitAll() // DELETE .antMatchers(HttpMethod.DELETE,anonymousUrls.get(RequestMethodEnum.DELETE.getType()).toArray(new String[0])).permitAll() // 所有类型的接口都放行 .antMatchers(anonymousUrls.get(RequestMethodEnum.ALL.getType()).toArray(new String[0])).permitAll() // 所有请求都需要认证 .anyRequest().authenticated(); } |
3.5在Controller方法上应用
在Controller上把需要的放通的接口上加上注解,即可不需要认证就可以访问了,是不是很方便呢。例如,验证码不需要认证访问的,代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
@ApiOperation(value = "获取验证码", notes = "获取验证码")@AnonymousAccess@GetMapping("/code")public Object getCode(){ Captcha captcha = loginProperties.getCaptcha(); String uuid = "code-key-"+IdUtil.simpleUUID(); //当验证码类型为 arithmetic时且长度 >= 2 时,captcha.text()的结果有几率为浮点型 String captchaValue = captcha.text(); if(captcha.getCharType()-1 == LoginCodeEnum.ARITHMETIC.ordinal() && captchaValue.contains(".")){ captchaValue = captchaValue.split("\\.")[0]; } // 保存 redisUtils.set(uuid,captchaValue,loginProperties.getLoginCode().getExpiration(), TimeUnit.MINUTES); // 验证码信息 Map<String,Object> imgResult = new HashMap<String,Object>(2){{ put("img",captcha.toBase64()); put("uuid",uuid); }}; return imgResult;} |
3.6效果展示
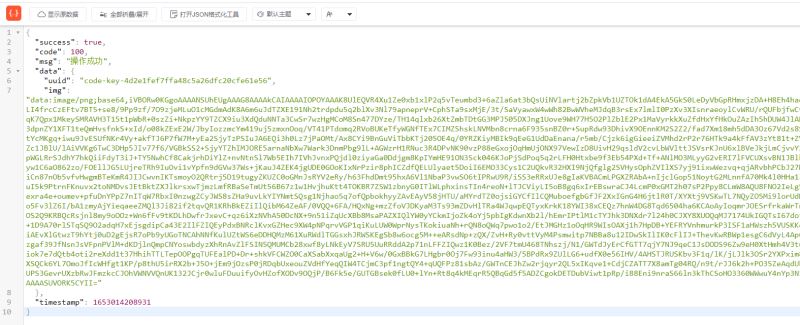
以上就是Spring Security实现接口放通的方法详解的详细内容,更多关于Spring Security接口放通的资料请关注服务器之家其它相关文章!
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/alanlin/p/16291601.html