前言
Spring cache是一个缓存API层,封装了对多种缓存的通用操作,可以借助注解方便地为程序添加缓存功能。
常见的注解有@Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict,有没有想过背后的原理是什么?楼主带着疑问,阅读完Spring cache的源码后,做一个简要总结。
先说结论,核心逻辑在CacheAspectSupport类,封装了所有的缓存操作的主体逻辑,下面详细介绍。
题外话:如何阅读开源代码?
有2种方法,可以结合起来使用:
- 静态代码阅读:查找关键类、方法的usage之处,熟练使用find usages功能,找到所有相关的类、方法,静态分析核心逻辑的执行过程,一步步追根问底,直至建立全貌
- 运行时debug:在关键方法上加上断点,并且写一个单元测试调用类库/框架,熟练使用step into/step over/resume来动态分析代码的执行过程
核心类图
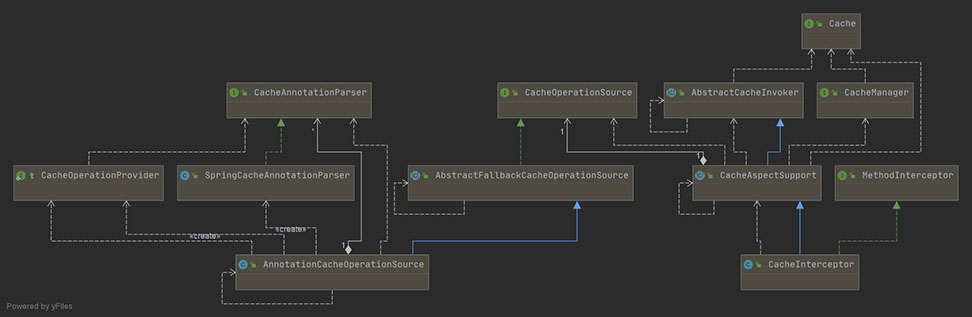
如图所示,可以分成以下几类class:
- Cache、CacheManager:Cache抽象了缓存的通用操作,如get、put,而CacheManager是Cache的集合,之所以需要多个Cache对象,是因为需要多种缓存失效时间、缓存条目上限等
- CacheInterceptor、CacheAspectSupport、AbstractCacheInvoker:CacheInterceptor是一个AOP方法拦截器,在方法前后做额外的逻辑,也即查询缓存、写入缓存等,它继承了CacheAspectSupport(缓存操作的主体逻辑)、AbstractCacheInvoker(封装了对Cache的读写)
- CacheOperation、AnnotationCacheOperationSource、SpringCacheAnnotationParser:CacheOperation定义了缓存操作的缓存名字、缓存key、缓存条件condition、CacheManager等,AnnotationCacheOperationSource是一个获取缓存注解对应CacheOperation的类,而SpringCacheAnnotationParser是真正解析注解的类,解析后会封装成CacheOperation集合供AnnotationCacheOperationSource查找
源码分析(带注释解释)
下面对Spring cache源码做分析,带注释解释,只摘录核心代码片段。
1、解析注解
首先看看注解是如何解析的。注解只是一个标记,要让它真正工作起来,需要对注解做解析操作,并且还要有对应的实际逻辑。
SpringCacheAnnotationParser:负责解析注解,返回CacheOperation集合
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
|
public class SpringCacheAnnotationParser implements CacheAnnotationParser, Serializable { // 解析类级别的缓存注解 @Override public Collection<CacheOperation> parseCacheAnnotations(Class<?> type) { DefaultCacheConfig defaultConfig = getDefaultCacheConfig(type); return parseCacheAnnotations(defaultConfig, type); } // 解析方法级别的缓存注解 @Override public Collection<CacheOperation> parseCacheAnnotations(Method method) { DefaultCacheConfig defaultConfig = getDefaultCacheConfig(method.getDeclaringClass()); return parseCacheAnnotations(defaultConfig, method); } // 解析缓存注解 private Collection<CacheOperation> parseCacheAnnotations(DefaultCacheConfig cachingConfig, AnnotatedElement ae) { Collection<CacheOperation> ops = null; // 解析@Cacheable注解 Collection<Cacheable> cacheables = AnnotatedElementUtils.getAllMergedAnnotations(ae, Cacheable.class); if (!cacheables.isEmpty()) { ops = lazyInit(ops); for (Cacheable cacheable : cacheables) { ops.add(parseCacheableAnnotation(ae, cachingConfig, cacheable)); } } // 解析@CacheEvict注解 Collection<CacheEvict> evicts = AnnotatedElementUtils.getAllMergedAnnotations(ae, CacheEvict.class); if (!evicts.isEmpty()) { ops = lazyInit(ops); for (CacheEvict evict : evicts) { ops.add(parseEvictAnnotation(ae, cachingConfig, evict)); } } // 解析@CachePut注解 Collection<CachePut> puts = AnnotatedElementUtils.getAllMergedAnnotations(ae, CachePut.class); if (!puts.isEmpty()) { ops = lazyInit(ops); for (CachePut put : puts) { ops.add(parsePutAnnotation(ae, cachingConfig, put)); } } // 解析@Caching注解 Collection<Caching> cachings = AnnotatedElementUtils.getAllMergedAnnotations(ae, Caching.class); if (!cachings.isEmpty()) { ops = lazyInit(ops); for (Caching caching : cachings) { Collection<CacheOperation> cachingOps = parseCachingAnnotation(ae, cachingConfig, caching); if (cachingOps != null) { ops.addAll(cachingOps); } } } return ops; } |
AnnotationCacheOperationSource:调用SpringCacheAnnotationParser获取注解对应CacheOperation
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
public class AnnotationCacheOperationSource extends AbstractFallbackCacheOperationSource implements Serializable { // 查找类级别的CacheOperation列表 @Override protected Collection<CacheOperation> findCacheOperations(final Class<?> clazz) { return determineCacheOperations(new CacheOperationProvider() { @Override public Collection<CacheOperation> getCacheOperations(CacheAnnotationParser parser) { return parser.parseCacheAnnotations(clazz); } }); } // 查找方法级别的CacheOperation列表 @Override protected Collection<CacheOperation> findCacheOperations(final Method method) { return determineCacheOperations(new CacheOperationProvider() { @Override public Collection<CacheOperation> getCacheOperations(CacheAnnotationParser parser) { return parser.parseCacheAnnotations(method); } }); }} |
AbstractFallbackCacheOperationSource:AnnotationCacheOperationSource的父类,实现了获取CacheOperation的通用逻辑
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
|
public abstract class AbstractFallbackCacheOperationSource implements CacheOperationSource { /** * Cache of CacheOperations, keyed by method on a specific target class. * <p>As this base class is not marked Serializable, the cache will be recreated * after serialization - provided that the concrete subclass is Serializable. */ private final Map<Object, Collection<CacheOperation>> attributeCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<Object, Collection<CacheOperation>>(1024); // 根据Method、Class反射信息,获取对应的CacheOperation列表 @Override public Collection<CacheOperation> getCacheOperations(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) { if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) { return null; } Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(method, targetClass); Collection<CacheOperation> cached = this.attributeCache.get(cacheKey); // 因解析反射信息较耗时,所以用map缓存,避免重复计算 // 如在map里已记录,直接返回 if (cached != null) { return (cached != NULL_CACHING_ATTRIBUTE ? cached : null); } // 否则做一次计算,然后写入map else { Collection<CacheOperation> cacheOps = computeCacheOperations(method, targetClass); if (cacheOps != null) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Adding cacheable method '" + method.getName() + "' with attribute: " + cacheOps); } this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, cacheOps); } else { this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, NULL_CACHING_ATTRIBUTE); } return cacheOps; } } // 计算缓存操作列表,优先用target代理类的方法上的注解,如果不存在则其次用target代理类,再次用原始类的方法,最后用原始类 private Collection<CacheOperation> computeCacheOperations(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) { // Don't allow no-public methods as required. if (allowPublicMethodsOnly() && !Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) { return null; } // The method may be on an interface, but we need attributes from the target class. // If the target class is null, the method will be unchanged. Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, targetClass); // If we are dealing with method with generic parameters, find the original method. specificMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod); // 调用findCacheOperations(由子类AnnotationCacheOperationSource实现),最终通过SpringCacheAnnotationParser来解析 // First try is the method in the target class. Collection<CacheOperation> opDef = findCacheOperations(specificMethod); if (opDef != null) { return opDef; } // Second try is the caching operation on the target class. opDef = findCacheOperations(specificMethod.getDeclaringClass()); if (opDef != null && ClassUtils.isUserLevelMethod(method)) { return opDef; } if (specificMethod != method) { // Fallback is to look at the original method. opDef = findCacheOperations(method); if (opDef != null) { return opDef; } // Last fallback is the class of the original method. opDef = findCacheOperations(method.getDeclaringClass()); if (opDef != null && ClassUtils.isUserLevelMethod(method)) { return opDef; } } return null; } |
2、逻辑执行
以@Cacheable背后的逻辑为例。预期是先查缓存,如果缓存命中了就直接使用缓存值,否则执行业务逻辑,并把结果写入缓存。
ProxyCachingConfiguration:是一个配置类,用于生成CacheInterceptor类和CacheOperationSource类的Spring bean
CacheInterceptor:是一个AOP方法拦截器,它通过CacheOperationSource获取第1步解析注解的CacheOperation结果(如缓存名字、缓存key、condition条件),本质上是拦截原始方法的执行,在之前、之后增加逻辑
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
// 核心类,缓存拦截器public class CacheInterceptor extends CacheAspectSupport implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable { // 拦截原始方法的执行,在之前、之后增加逻辑 @Override public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable { Method method = invocation.getMethod(); // 封装原始方法的执行到一个回调接口,便于后续调用 CacheOperationInvoker aopAllianceInvoker = new CacheOperationInvoker() { @Override public Object invoke() { try { // 原始方法的执行 return invocation.proceed(); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new ThrowableWrapper(ex); } } }; try { // 调用父类CacheAspectSupport的方法 return execute(aopAllianceInvoker, invocation.getThis(), method, invocation.getArguments()); } catch (CacheOperationInvoker.ThrowableWrapper th) { throw th.getOriginal(); } }} |
CacheAspectSupport:缓存切面支持类,是CacheInterceptor的父类,封装了所有的缓存操作的主体逻辑
主要流程如下:
- 通过CacheOperationSource,获取所有的CacheOperation列表
- 如果有@CacheEvict注解、并且标记为在调用前执行,则做删除/清空缓存的操作
- 如果有@Cacheable注解,查询缓存
- 如果缓存未命中(查询结果为null),则新增到cachePutRequests,后续执行原始方法后会写入缓存
- 缓存命中时,使用缓存值作为结果;缓存未命中、或有@CachePut注解时,需要调用原始方法,使用原始方法的返回值作为结果
- 如果有@CachePut注解,则新增到cachePutRequests
- 如果缓存未命中,则把查询结果值写入缓存;如果有@CachePut注解,也把方法执行结果写入缓存
- 如果有@CacheEvict注解、并且标记为在调用后执行,则做删除/清空缓存的操作
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
|
// 核心类,缓存切面支持类,封装了所有的缓存操作的主体逻辑public abstract class CacheAspectSupport extends AbstractCacheInvoker implements BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean, SmartInitializingSingleton { // CacheInterceptor调父类的该方法 protected Object execute(CacheOperationInvoker invoker, Object target, Method method, Object[] args) { // Check whether aspect is enabled (to cope with cases where the AJ is pulled in automatically) if (this.initialized) { Class<?> targetClass = getTargetClass(target); // 通过CacheOperationSource,获取所有的CacheOperation列表 Collection<CacheOperation> operations = getCacheOperationSource().getCacheOperations(method, targetClass); if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(operations)) { // 继续调一个private的execute方法执行 return execute(invoker, method, new CacheOperationContexts(operations, method, args, target, targetClass)); } } // 如果spring bean未初始化完成,则直接调用原始方法。相当于原始方法没有缓存功能。 return invoker.invoke(); } private的execute方法 private Object execute(final CacheOperationInvoker invoker, Method method, CacheOperationContexts contexts) { // Special handling of synchronized invocation if (contexts.isSynchronized()) { CacheOperationContext context = contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class).iterator().next(); if (isConditionPassing(context, CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT)) { Object key = generateKey(context, CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT); Cache cache = context.getCaches().iterator().next(); try { return wrapCacheValue(method, cache.get(key, new Callable<Object>() { @Override public Object call() throws Exception { return unwrapReturnValue(invokeOperation(invoker)); } })); } catch (Cache.ValueRetrievalException ex) { // The invoker wraps any Throwable in a ThrowableWrapper instance so we // can just make sure that one bubbles up the stack. throw (CacheOperationInvoker.ThrowableWrapper) ex.getCause(); } } else { // No caching required, only call the underlying method return invokeOperation(invoker); } } // 如果有@CacheEvict注解、并且标记为在调用前执行,则做删除/清空缓存的操作 // Process any early evictions processCacheEvicts(contexts.get(CacheEvictOperation.class), true, CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT); // 如果有@Cacheable注解,查询缓存 // Check if we have a cached item matching the conditions Cache.ValueWrapper cacheHit = findCachedItem(contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class)); // 如果缓存未命中(查询结果为null),则新增到cachePutRequests,后续执行原始方法后会写入缓存 // Collect puts from any @Cacheable miss, if no cached item is found List<CachePutRequest> cachePutRequests = new LinkedList<CachePutRequest>(); if (cacheHit == null) { collectPutRequests(contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class), CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT, cachePutRequests); } Object cacheValue; Object returnValue; if (cacheHit != null && cachePutRequests.isEmpty() && !hasCachePut(contexts)) { // 缓存命中的情况,使用缓存值作为结果 // If there are no put requests, just use the cache hit cacheValue = cacheHit.get(); returnValue = wrapCacheValue(method, cacheValue); } else { // 缓存未命中、或有@CachePut注解的情况,需要调用原始方法 // Invoke the method if we don't have a cache hit // 调用原始方法,得到结果值 returnValue = invokeOperation(invoker); cacheValue = unwrapReturnValue(returnValue); } // 如果有@CachePut注解,则新增到cachePutRequests // Collect any explicit @CachePuts collectPutRequests(contexts.get(CachePutOperation.class), cacheValue, cachePutRequests); // 如果缓存未命中,则把查询结果值写入缓存;如果有@CachePut注解,也把方法执行结果写入缓存 // Process any collected put requests, either from @CachePut or a @Cacheable miss for (CachePutRequest cachePutRequest : cachePutRequests) { cachePutRequest.apply(cacheValue); } // 如果有@CacheEvict注解、并且标记为在调用后执行,则做删除/清空缓存的操作 // Process any late evictions processCacheEvicts(contexts.get(CacheEvictOperation.class), false, cacheValue); return returnValue; } private Cache.ValueWrapper findCachedItem(Collection<CacheOperationContext> contexts) { Object result = CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT; for (CacheOperationContext context : contexts) { // 如果满足condition条件,才查询缓存 if (isConditionPassing(context, result)) { // 生成缓存key,如果注解中指定了key,则按照Spring表达式解析,否则使用KeyGenerator类生成 Object key = generateKey(context, result); // 根据缓存key,查询缓存值 Cache.ValueWrapper cached = findInCaches(context, key); if (cached != null) { return cached; } else { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("No cache entry for key '" + key + "' in cache(s) " + context.getCacheNames()); } } } } return null; } private Cache.ValueWrapper findInCaches(CacheOperationContext context, Object key) { for (Cache cache : context.getCaches()) { // 调用父类AbstractCacheInvoker的doGet方法,查询缓存 Cache.ValueWrapper wrapper = doGet(cache, key); if (wrapper != null) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Cache entry for key '" + key + "' found in cache '" + cache.getName() + "'"); } return wrapper; } } return null; } |
AbstractCacheInvoker:CacheAspectSupport的父类,封装了最终查询Cache接口的逻辑
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
public abstract class AbstractCacheInvoker { // 最终查询缓存的方法 protected Cache.ValueWrapper doGet(Cache cache, Object key) { try { // 调用Spring Cache接口的查询方法 return cache.get(key); } catch (RuntimeException ex) { getErrorHandler().handleCacheGetError(ex, cache, key); return null; // If the exception is handled, return a cache miss } }} |
总结
到此这篇关于Spring cache源码解析的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Spring cache源码内容请搜索服务器之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持服务器之家!
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/toplist/p/16032955.html