原理简介:
zookeeper实现分布式锁的原理就是多个节点同时在一个指定的节点下面创建临时会话顺序节点,谁创建的节点序号最小,谁就获得了锁,并且其他节点就会监听序号比自己小的节点,一旦序号比自己小的节点被删除了,其他节点就会得到相应的事件,然后查看自己是否为序号最小的节点,如果是,则获取锁。
zookeeper节点图分析
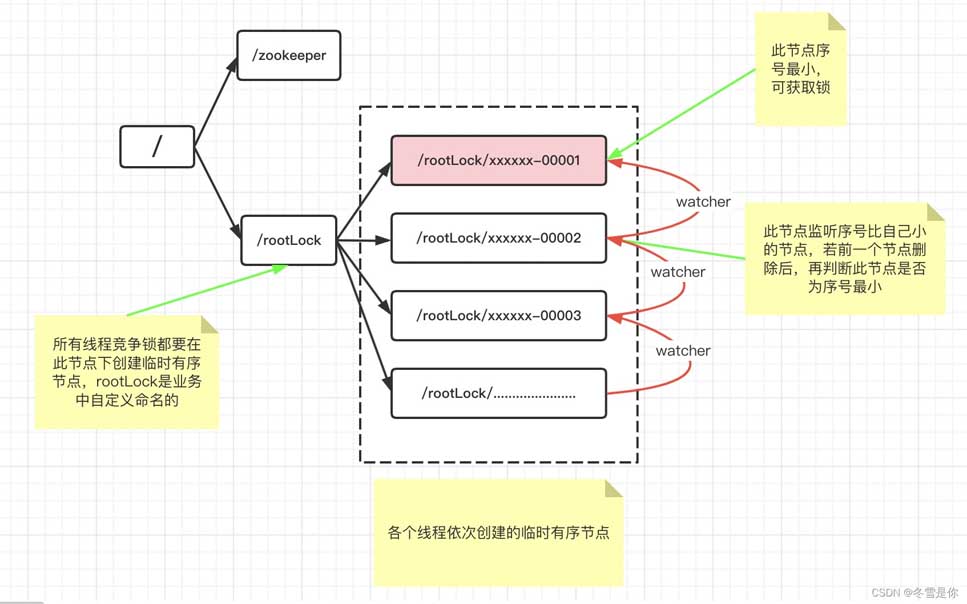
InterProcessMutex实现的锁机制是公平且互斥的,公平的方式是按照每个请求的顺序进行排队的。
InterProcessMutex实现的InterProcessLock接口,InterProcessLock主要规范了如下几个方法:
// 获取互斥锁 public void acquire() throws Exception; // 在给定的时间内获取互斥锁 public boolean acquire(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception; // 释放锁处理 public void release() throws Exception; // 如果此JVM中的线程获取了互斥锁,则返回true boolean isAcquiredInThisProcess();
接下来我们看看InterProcessMutex中的实现,它究竟有哪些属性,以及实现细节
public class InterProcessMutex implements InterProcessLock, Revocable<InterProcessMutex> {
// LockInternals是真正实现操作zookeeper的类,它内部包含连接zookeeper客户端的CuratorFramework
// LockInternals的具体实现后面我会讲到
private final LockInternals internals;
// basePath是锁的根结点,所有的临时有序的节点都是basePath的子节点,
private final String basePath;
//
private final ConcurrentMap<Thread, LockData> threadData = Maps.newConcurrentMap();
// LockData封装了请求对应的线程(owningThread)、锁的重入的次数(lockCount)、线程对应的临时节点(lockPath)
private static class LockData {
final Thread owningThread;
final String lockPath;
// 原子性的
final AtomicInteger lockCount = new AtomicInteger(1);
private LockData(Thread owningThread, String lockPath)
{
this.owningThread = owningThread;
this.lockPath = lockPath;
}
}
private static final String LOCK_NAME = "lock-";
// 获取互斥锁,阻塞【InterProcessLock的实现】
@Override
public void acquire() throws Exception {
// 获取锁,一直等待
if ( !internalLock(-1, null) ) {
throw new IOException("Lost connection while trying to acquire lock: " + basePath);
}
}
// 获取互斥锁,指定时间time【InterProcessLock的实现】
@Override
public boolean acquire(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception {
return internalLock(time, unit);
}
// 当前线程是否占用锁中【InterProcessLock的实现】
@Override
public boolean isAcquiredInThisProcess() {
return (threadData.size() > 0);
}
//如果调用线程与获取互斥锁的线程相同,则执行一次互斥锁释放。如果线程已多次调用acquire,当此方法返回时,互斥锁仍将保留 【InterProcessLock的实现】
@Override
public void release() throws Exception {
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread(); //当前线程
LockData lockData = threadData.get(currentThread); //线程对应的锁信息
if ( lockData == null ) {
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException("You do not own the lock: " + basePath);
}
// 因为获取到的锁是可重入的,对lockCount进行减1,lockCount=0时才是真正释放锁
int newLockCount = lockData.lockCount.decrementAndGet();
if ( newLockCount > 0 ) {
return;
}
if ( newLockCount < 0 ) {
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException("Lock count has gone negative for lock: " + basePath);
}
try {
// 到这里时lockCount=0,具体释放锁的操作交给LockInternals中的releaseLock方法实现
internals.releaseLock(lockData.lockPath);
}
finally {
threadData.remove(currentThread);
}
}
// 获取basePath根结点下的所有临时节点的有序集合
public Collection<String> getParticipantNodes() throws Exception {
return LockInternals.getParticipantNodes(internals.getClient(), basePath, internals.getLockName(), internals.getDriver());
}
boolean isOwnedByCurrentThread() {
LockData lockData = threadData.get(Thread.currentThread());
return (lockData != null) && (lockData.lockCount.get() > 0);
}
protected String getLockPath() {
LockData lockData = threadData.get(Thread.currentThread());
return lockData != null ? lockData.lockPath : null;
}
// acquire()中调用的internalLock()方法
private boolean internalLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception {
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
LockData lockData = threadData.get(currentThread);
if ( lockData != null ) {
// 如果当前线程已经获取到了锁,那么将重入次数lockCount+1,返回true
lockData.lockCount.incrementAndGet();
return true;
}
// attemptLock方法是获取锁的真正实现,lockPath是当前线程成功在basePath下创建的节点,若lockPath不为空代表成功获取到锁
String lockPath = internals.attemptLock(time, unit, getLockNodeBytes());
if ( lockPath != null ) {
// lockPath封装到当前线程对应的锁信息中
LockData newLockData = new LockData(currentThread, lockPath);
threadData.put(currentThread, newLockData);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
接下来我们看看InterProcessMutex中使用的LockInternals类的实现细节
public class LockInternals {
private final CuratorFramework client; // 连接zookeeper的客户端
private final String path; // 等于basePath,InterProcessMutex中传进来的
private final String basePath; // 根结点
private final LockInternalsDriver driver; // 操作zookeeper节点的driver
private final String lockName; // "lock-"
private final AtomicReference<RevocationSpec> revocable = new AtomicReference<RevocationSpec>(null);
private final CuratorWatcher revocableWatcher = new CuratorWatcher() {
@Override
public void process(WatchedEvent event) throws Exception {
if ( event.getType() == Watcher.Event.EventType.NodeDataChanged ) {
checkRevocableWatcher(event.getPath());
}
}
};
// 监听节点的监听器,若被监听的节点有动静,则唤醒 notifyFromWatcher()=>notifyAll();
private final Watcher watcher = new Watcher() {
@Override
public void process(WatchedEvent event) {
notifyFromWatcher();
}
};
private volatile int maxLeases;
// 获取basePath的子节点,排序后的
public static List<String> getSortedChildren(CuratorFramework client, String basePath, final String lockName, final LockInternalsSorter sorter) throws Exception
{
List<String> children = client.getChildren().forPath(basePath);
List<String> sortedList = Lists.newArrayList(children);
Collections.sort
(
sortedList,
new Comparator<String>()
{
@Override
public int compare(String lhs, String rhs)
{
return sorter.fixForSorting(lhs, lockName).compareTo(sorter.fixForSorting(rhs, lockName));
}
}
);
return sortedList;
}
// 尝试获取锁【internalLock=>attemptLock】
String attemptLock(long time, TimeUnit unit, byte[] lockNodeBytes) throws Exception
{ // 开始时间
final long startMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 记录等待时间
final Long millisToWait = (unit != null) ? unit.toMillis(time) : null;
final byte[] localLockNodeBytes = (revocable.get() != null) ? new byte[0] : lockNodeBytes;
// 重试次数
int retryCount = 0;
// 当前节点
String ourPath = null;
// 是否获取到锁的标志
boolean hasTheLock = false;
// 是否放弃获取到标志
boolean isDone = false;
// 不停尝试获取
while ( !isDone )
{
isDone = true;
try
{ // 创建当前线程对应的节点
ourPath = driver.createsTheLock(client, path, localLockNodeBytes);
// internalLockLoop中获取
hasTheLock = internalLockLoop(startMillis, millisToWait, ourPath);
}
catch ( KeeperException.NoNodeException e )
{ // 是否可再次尝试
if ( client.getZookeeperClient().getRetryPolicy().allowRetry(retryCount++, System.currentTimeMillis() - startMillis, RetryLoop.getDefaultRetrySleeper()) )
{
isDone = false;
}
else
{
throw e;
}
}
}
// 获取到锁后,返回当前线程对应创建的节点路径
if ( hasTheLock )
{
return ourPath;
}
return null;
}
// 循环获取【attemptLock=>internalLockLoop】
private boolean internalLockLoop(long startMillis, Long millisToWait, String ourPath) throws Exception
{
boolean haveTheLock = false; // 是否拥有分布式锁
boolean doDelete = false; // 是否需要删除当前节点
try
{
if ( revocable.get() != null )
{
client.getData().usingWatcher(revocableWatcher).forPath(ourPath);
}
// 循环尝试获取锁
while ( (client.getState() == CuratorFrameworkState.STARTED) && !haveTheLock )
{ // 得到basePath下排序后的临时子节点
List<String> children = getSortedChildren();
// 获取之前创建的当前线程对应的子节点
String sequenceNodeName = ourPath.substring(basePath.length() + 1); // +1 to include the slash
// 判断是否获取到锁,没有就返回监听路径
PredicateResults predicateResults = driver.getsTheLock(client, children, sequenceNodeName, maxLeases);
// 成功获取到
if ( predicateResults.getsTheLock() )
{
haveTheLock = true;
}
else
{ // 没有获取到锁,监听前一个临时顺序节点
String previousSequencePath = basePath + "/" + predicateResults.getPathToWatch();
synchronized(this)
{
try
{
// 上一个临时顺序节点如果被删除,会唤醒当前线程继续竞争锁
client.getData().usingWatcher(watcher).forPath(previousSequencePath);
if ( millisToWait != null )
{
millisToWait -= (System.currentTimeMillis() - startMillis);
startMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 获取锁超时
if ( millisToWait <= 0 )
{
doDelete = true; // timed out - delete our node
break;
}
wait(millisToWait);
}
else
{
wait();
}
}
catch ( KeeperException.NoNodeException e )
{
// it has been deleted (i.e. lock released). Try to acquire again
}
}
}
}
}
catch ( Exception e )
{
ThreadUtils.checkInterrupted(e);
doDelete = true;
throw e;
}
finally
{
if ( doDelete )
{
// 因为获取锁超时,所以删除之前创建的临时子节点
deleteOurPath(ourPath);
}
}
return haveTheLock;
}
private void deleteOurPath(String ourPath) throws Exception {
try
{
// 删除
client.delete().guaranteed().forPath(ourPath);
}
catch ( KeeperException.NoNodeException e )
{
// ignore - already deleted (possibly expired session, etc.)
}
}
}
StandardLockInternalsDriver implements LockInternalsDriver
// 前面internalLockLoop方法中driver.getsTheLock执行的方法
@Override
public PredicateResults getsTheLock(CuratorFramework client, List<String> children, String sequenceNodeName, int maxLeases) throws Exception
{
// 获取子节点在临时顺序节点列表中的位置
int ourIndex = children.indexOf(sequenceNodeName);
// 检验子节点在临时顺序节点列表中是否有效
validateOurIndex(sequenceNodeName, ourIndex);
// 若当前子节点的位置<maxLeases,代表可获取锁【maxLeases默认=1,若ourIndex=0,代笔自己位置最小】
boolean getsTheLock = ourIndex < maxLeases;
// getsTheLock=true,则不需要监听前maxLeases的节点【maxLeases默认=1,代表监听前面最靠近自己的节点】
String pathToWatch = getsTheLock ? null : children.get(ourIndex - maxLeases);
return new PredicateResults(pathToWatch, getsTheLock);
}
用InterProcessMutex在自己业务实现分布式锁,请点击此链接阅读点我
到此这篇关于InterProcessMutex实现zookeeper分布式锁原理的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关InterProcessMutex实现zookeeper分布式锁内容请搜索服务器之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持服务器之家!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_45097637/article/details/123591672