




/*
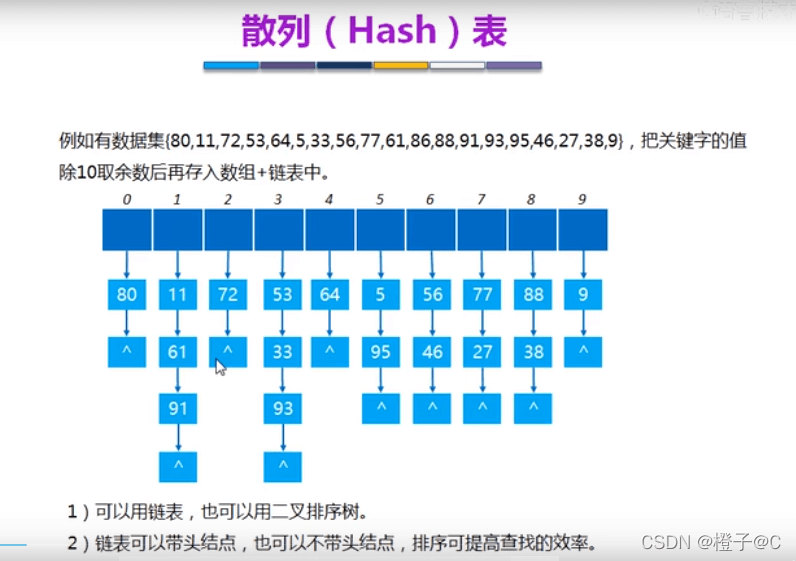
* 程序名:hash.c,此程序演示哈希表的实现,数据元素单链表带头结点。
*
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
// 哈希表中数据元素的结构体。
typedef struct Element
{
unsigned int key; // 关键字。
int value; // 数据元素其它数据项,可以是任意数据类型。
// char value[1001]; // 数据元素其它数据项,可以是任意数据类型。
}Element;
// 数据元素单链表。
typedef struct Node
{
Element elem; // 数据元素。
struct Node *next; // next指针。
}Node;
// 哈希表
typedef struct HashTable
{
struct Node *head; // 数据元素存储基址,动态分配数组。
int tablesize; // 哈希表当前大小,即表长。
int count; // 哈希表中数据元素的个数。
}HashTable;
// 初始化哈希表,tablesize为哈希表的表长,返回哈希表的地址。
HashTable *InitHashTable(const unsigned int tablesize)
{
// 分配哈希表。
HashTable *hh=(HashTable *)malloc(sizeof(HashTable));
hh->tablesize=tablesize; // 哈希表长。
// 分配和初始化数据元素单链表的头结点。
hh->head=(Node *)malloc((hh->tablesize)*sizeof(Node));
memset(hh->head,0,(hh->tablesize)*sizeof(Node));
hh->count=0; // 哈希表中数据元素个数置为0。
return hh;
}
// 哈希函数。
unsigned int Hash(HashTable *hh,unsigned int key)
{
return key%hh->tablesize; // 对表长取余。
}
// 在哈希表中查找关键字,成功返回单链表结点的地址,失败返回空。
Node *LookUp(HashTable *hh,unsigned int key)
{
int ii;
ii=Hash(hh,key); // 获取关键key的哈希地址。
Node *pp=hh->head[ii].next;
// 遍历单链表。
while( (pp!=NULL) && (pp->elem.key!=key) )
{
pp=pp->next;
}
return pp;
}
// 从哈希表中删除关键及其数据,成功返回1,如果关键字不存在返回0。
int Delete(HashTable *hh,unsigned int key)
{
int ii;
ii=Hash(hh,key); // 获取关键key的哈希地址。
Node *pp=&hh->head[ii];
// 遍历单链表,pp指针停留在待删除关键key的前一结点。
while( (pp->next!=NULL) && (pp->next->elem.key!=key) )
{
pp=pp->next;
}
if (pp->next==NULL) return 0; // 查找失败。
Node *tmp=pp->next; // tmp为将要删除的结点。
pp->next=pp->next->next; // 写成p->next=tmp->next更简洁。
free(tmp); // 释放结点。
hh->count--; // 表中元素个数减1。
return 1;
}
// 向哈希表中插入数据元素,成功返回1,如果数据元素关键字已存在,返回0。
int Insert(HashTable *hh,Element *ee)
{
// 查找关键字是否已存在,如果存在,插入失败。
Node *pp=LookUp(hh,ee->key);
if (pp!=NULL) { printf("关键字%d已存在。\n",ee->key); return 0; }
Node *qq=(Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
memcpy(&qq->elem,ee,sizeof(Element));
// 用头插法插入新数据元素。
int ii=Hash(hh,ee->key);
qq->next=hh->head[ii].next;
hh->head[ii].next=qq;
hh->count++; // 表中元素个数加1。
return 1;
}
// 销毁哈希表
void FreeHashTable(HashTable *hh)
{
int ii;
Node *pp,*qq;
// 释放全部的单链表。
for(ii=0;ii<hh->tablesize;ii++)
{
pp=hh->head[ii].next;
while(pp)
{
qq=pp->next;
free(pp);
pp=qq;
}
}
// 释放全部单链表的头结点数组。
free(hh->head);
free(hh); // 释放哈希表。
}
// 打印哈希表。
void PrintTable(HashTable *hh)
{
int ii;
for (ii=0;ii<hh->tablesize;ii++)
{
Node *pp=hh->head[ii].next;
while (pp)
{
printf("[%d-%d] ",pp->elem.key,pp->elem.value);
// printf("[%d-%s] ",pp->elem.key,pp->elem.value);
pp=pp->next;
}
printf("^\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
// 初始化哈希表。
HashTable *hh=InitHashTable(10);
Element ee;
// 插入数据元素,关键字从10到20。
ee.key=10; ee.value=110; Insert(hh,&ee);
ee.key=11; ee.value=111; Insert(hh,&ee);
ee.key=12; ee.value=112; Insert(hh,&ee);
ee.key=13; ee.value=113; Insert(hh,&ee);
ee.key=14; ee.value=114; Insert(hh,&ee);
ee.key=15; ee.value=115; Insert(hh,&ee);
ee.key=16; ee.value=116; Insert(hh,&ee);
ee.key=17; ee.value=117; Insert(hh,&ee);
ee.key=18; ee.value=118; Insert(hh,&ee);
ee.key=19; ee.value=119; Insert(hh,&ee);
// 插入数据元素,关键字从20到30。
ee.key=20; ee.value=120; Insert(hh,&ee);
ee.key=21; ee.value=121; Insert(hh,&ee);
ee.key=22; ee.value=122; Insert(hh,&ee);
ee.key=23; ee.value=123; Insert(hh,&ee);
ee.key=24; ee.value=124; Insert(hh,&ee);
ee.key=25; ee.value=125; Insert(hh,&ee);
ee.key=26; ee.value=126; Insert(hh,&ee);
ee.key=27; ee.value=127; Insert(hh,&ee);
ee.key=28; ee.value=128; Insert(hh,&ee);
ee.key=29; ee.value=129; Insert(hh,&ee);
// 插入数据元素,关键字从30到32。
ee.key=30; ee.value=130; Insert(hh,&ee);
ee.key=31; ee.value=131; Insert(hh,&ee);
ee.key=32; ee.value=132; Insert(hh,&ee);
printf("count=%d\n",hh->count);
PrintTable(hh); // 打印哈希表
Delete(hh,12); // 删除哈希表中关键字为12的数据元素。
printf("count=%d\n",hh->count);
PrintTable(hh); // 打印哈希表
// 在哈希表中查找关键字18。
Node *pp=LookUp(hh,18);
if (pp==0) printf("LookUp(18) failed.\n");
else printf("key=18,value=%d.\n",pp->elem.value);
// ee.key=10; strcpy(ee.value,"<no>00010<no/><name>西施</name><yz>绝世美人</yz>"); Insert(hh,&ee);
// PrintTable(hh); // 打印哈希表
FreeHashTable(hh); // 销毁哈希表
return 0;
}
到此这篇关于C语言数据结构哈希表详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C语言 哈希表内容请搜索服务器之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持服务器之家!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41962968/article/details/122758753