1.二叉树基本概念见上节:详解Java中二叉树的基础概念(递归&迭代)
2.本次展示链式存储
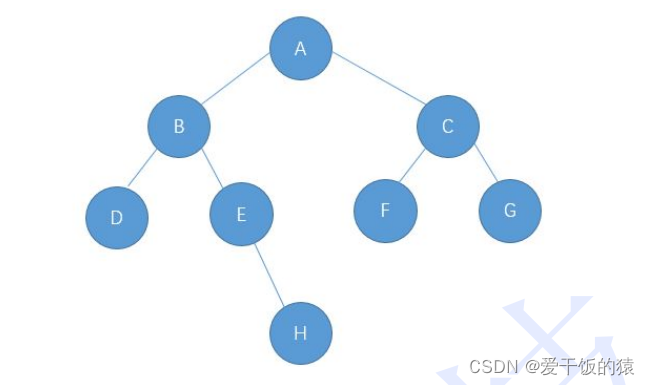
以此图为例,完整代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
|
//基础二叉树实现//使用左右孩子表示法 import java.util.*;import java.util.Deque; public class myBinTree { private static class TreeNode{ char val; TreeNode left; TreeNode right; public TreeNode(char val) { this.val = val; } } public static TreeNode build(){ TreeNode nodeA=new TreeNode('A'); TreeNode nodeB=new TreeNode('B'); TreeNode nodeC=new TreeNode('C'); TreeNode nodeD=new TreeNode('D'); TreeNode nodeE=new TreeNode('E'); TreeNode nodeF=new TreeNode('F'); TreeNode nodeG=new TreeNode('G'); TreeNode nodeH=new TreeNode('H'); nodeA.left=nodeB; nodeA.right=nodeC; nodeB.left=nodeD; nodeB.right=nodeE; nodeE.right=nodeH; nodeC.left=nodeF; nodeC.right=nodeG; return nodeA; } //方法1(递归) //先序遍历: 根左右 public static void preOrder(TreeNode root){ if(root==null){ return; } System.out.print(root.val+" "); preOrder(root.left); preOrder(root.right); } //方法1(递归) //中序遍历 public static void inOrder(TreeNode root){ if(root==null){ return; } inOrder(root.left); System.out.print(root.val+" "); inOrder(root.right); } //方法1(递归) //后序遍历 public static void postOrder(TreeNode root){ if(root==null){ return; } postOrder(root.left); postOrder(root.right); System.out.print(root.val+" "); } //方法2(迭代) //先序遍历 (迭代) public static void preOrderNonRecursion(TreeNode root){ if(root==null){ return ; } Deque<TreeNode> stack=new LinkedList<>(); stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()){ TreeNode cur=stack.pop(); System.out.print(cur.val+" "); if(cur.right!=null){ stack.push(cur.right); } if(cur.left!=null){ stack.push(cur.left); } } } //方法2(迭代) //中序遍历 (迭代) public static void inorderTraversalNonRecursion(TreeNode root) { if(root==null){ return ; } Deque<TreeNode> stack=new LinkedList<>(); // 当前走到的节点 TreeNode cur=root; while (!stack.isEmpty() || cur!=null){ // 不管三七二十一,先一路向左走到根儿~ while (cur!=null){ stack.push(cur); cur=cur.left; } // 此时cur为空,说明走到了null,此时栈顶就存放了左树为空的节点 cur=stack.pop(); System.out.print(cur.val+" "); // 继续访问右子树 cur=cur.right; } } //方法2(迭代) //后序遍历 (迭代) public static void postOrderNonRecursion(TreeNode root){ if(root==null){ return; } Deque<TreeNode> stack=new LinkedList<>(); TreeNode cur=root; TreeNode prev=null; while (!stack.isEmpty() || cur!=null){ while (cur!=null){ stack.push(cur); cur=cur.left; } cur=stack.pop(); if(cur.right==null || prev==cur.right){ System.out.print(cur.val+" "); prev=cur; cur=null; }else { stack.push(cur); cur=cur.right; } } } //方法1(递归) //传入一颗二叉树的根节点,就能统计出当前二叉树中一共有多少个节点,返回节点数 //此时的访问就不再是输出节点值,而是计数器 + 1操作 public static int getNodes(TreeNode root){ if(root==null){ return 0; } return 1+getNodes(root.left)+getNodes(root.right); } //方法2(迭代) //使用层序遍历来统计当前树中的节点个数 public static int getNodesNoRecursion(TreeNode root){ if(root==null){ return 0; } int size=0; Deque<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { TreeNode cur = queue.poll(); size++; if (cur.left != null) { queue.offer(cur.left); } if (cur.right != null) { queue.offer(cur.right); } } return size; } //方法1(递归) //传入一颗二叉树的根节点,就能统计出当前二叉树的叶子结点个数 public static int getLeafNodes(TreeNode root){ if(root==null){ return 0; } if(root.left==null && root.right==null){ return 1; } return getLeafNodes(root.left)+getLeafNodes(root.right); } //方法2(迭代) //使用层序遍历来统计叶子结点的个数 public static int getLeafNodesNoRecursion(TreeNode root){ if(root==null){ return 0; } int size=0; Deque<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()){ TreeNode cur=queue.poll(); if(cur.left==null && cur.right==null){ size++; } if(cur.left!=null){ queue.offer(cur.left); } if(cur.right!=null){ queue.offer(cur.right); } } return size; } //层序遍历 public static void levelOrder(TreeNode root) { if(root==null){ return ; } // 借助队列来实现遍历过程 Deque<TreeNode> queue =new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()){ int size=queue.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { TreeNode cur=queue.poll(); System.out.print(cur.val+" "); if(cur.left!=null){ queue.offer(cur.left); } if(cur.right!=null){ queue.offer(cur.right); } } } } //传入一个以root为根节点的二叉树,就能求出该树的高度 public static int height(TreeNode root){ if(root==null){ return 0; } return 1+ Math.max(height(root.left),height(root.right)); } //求出以root为根节点的二叉树第k层的节点个数 public static int getKLevelNodes(TreeNode root,int k){ if(root==null || k<=0){ return 0; } if(k==1){ return 1; } return getKLevelNodes(root.left,k-1)+getKLevelNodes(root.right,k-1); } //判断当前以root为根节点的二叉树中是否包含指定元素val, //若存在返回true,不存在返回false public static boolean contains(TreeNode root,char value){ if(root==null){ return false; } if(root.val==value){ return true; } return contains(root.left,value) || contains(root.right,value); } public static void main(String[] args) { TreeNode root=build(); System.out.println("方法1(递归):前序遍历的结果为:"); preOrder(root); System.out.println(); System.out.println("方法2(迭代):前序遍历的结果为:"); preOrderNonRecursion(root); System.out.println(); System.out.println("方法1(递归):中序遍历的结果为:"); inOrder(root); System.out.println(); System.out.println("方法2(迭代):中序遍历的结果为:"); inorderTraversalNonRecursion(root); System.out.println(); System.out.println("方法1(递归):后序遍历的结果为:"); postOrder(root); System.out.println(); System.out.println("方法2(迭代):后序遍历的结果为:"); postOrderNonRecursion(root); System.out.println(); System.out.println(); System.out.println("层序遍历的结果为:"); levelOrder(root); System.out.println(); System.out.println(); System.out.println("方法1(递归):当前二叉树一共有:"+getNodes(root)+"个节点数"); System.out.println("方法2(迭代):当前二叉树一共有:"+getNodesNoRecursion(root)+"个节点数"); System.out.println("方法1(递归):当前二叉树一共有:"+getLeafNodes(root)+"个叶子节点数"); System.out.println("方法2(迭代):当前二叉树一共有:"+getLeafNodesNoRecursion(root)+"个叶子节点数"); System.out.println(contains(root,'E')); System.out.println(contains(root,'P')); System.out.println("当前二叉树的高度为:"+height(root)); System.out.println("当前二叉树第3层的节点个数为:"+getKLevelNodes(root,3)); }} |
如上main引用结果如下:

到此这篇关于Java实现二叉树的示例代码(递归&迭代)的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java二叉树内容请搜索服务器之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持服务器之家!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_62218217/article/details/123072827