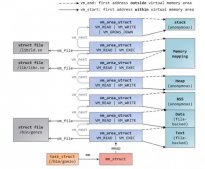
引言
随着计算需求规模的不断增大,应用程序对内存的需求也越来越大。为了实现虚拟内存管理机制,操作系统对内存实行分页管理。自内存“分页机制”提出之始,内存页面的默认大小便被设置为 4096 字节(4KB),虽然原则上内存页面大小是可配置的,但绝大多数的操作系统实现中仍然采用默认的 4KB 页面。 4KB 大小的页面在“分页机制”提出的时候是合理的,因为当时的内存大小不过几十兆字节,然而当物理内存容量增长到几 G 甚至几十 G 的时候,操作系统仍然以 4KB 大小为页面的基本单位,是否依然合理呢?
在 Linux 操作系统上运行内存需求量较大的应用程序时,由于其采用的默认页面大小为 4KB,因而将会产生较多 TLB Miss 和缺页中断,从而大大影响应用程序的性能。当操作系统以 2MB 甚至更大作为分页的单位时,将会大大减少 TLB Miss 和缺页中断的数量,显著提高应用程序的性能。这也正是 Linux 内核引入大页面支持的直接原因。好处是很明显的,假设应用程序需要 2MB 的内存,如果操作系统以 4KB 作为分页的单位,则需要 512 个页面,进而在 TLB 中需要 512 个表项,同时也需要 512 个页表项,操作系统需要经历至少 512 次 TLB Miss 和 512 次缺页中断才能将 2MB 应用程序空间全部映射到物理内存;然而,当操作系统采用 2MB 作为分页的基本单位时,只需要一次 TLB Miss 和一次缺页中断,就可以为 2MB 的应用程序空间建立虚实映射,并在运行过程中无需再经历 TLB Miss 和缺页中断(假设未发生 TLB 项替换和 Swap)。
为了能以最小的代价实现大页面支持,Linux 操作系统采用了基于 hugetlbfs 特殊文件系统 2M 字节大页面支持。这种采用特殊文件系统形式支持大页面的方式,使得应用程序可以根据需要灵活地选择虚存页面大小,而不会被强制使用 2MB 大页面。

Redis在Linux中启动时通常会报“WARNING you have Transparent Huge Pages (THP) support enabled in your kernel”的警告信息,意思是:你使用的是透明大页,可能导致redis延迟和内存使用问题。
关于透明大页,我们看看官方的介绍
Transparent Huge Pages (THP) are enabled by default in RHEL 6 for all applications. The kernel attempts to allocate hugepages whenever possible and any Linux process will receive 2MB pages if the mmap region is 2MB naturally aligned. The main kernel address space itself is mapped with hugepages, reducing TLB pressure from kernel code. For general information on Hugepages, see: What are Huge Pages and what are the advantages of using them?
The kernel will always attempt to satisfy a memory allocation using hugepages. If no hugepages are available (due to non availability of physically continuous memory for example) the kernel will fall back to the regular 4KB pages. THP are also swappable (unlike hugetlbfs). This is achieved by breaking the huge page to smaller 4KB pages, which are then swapped out normally.
But to use hugepages effectively, the kernel must find physically continuous areas of memory big enough to satisfy the request, and also properly aligned. For this, a khugepaged kernel thread has been added. This thread will occasionally attempt to substitute smaller pages being used currently with a hugepage allocation, thus maximizing THP usage.
In userland, no modifications to the applications are necessary (hence transparent). But there are ways to optimize its use. For applications that want to use hugepages, use of posix_memalign() can also help ensure that large allocations are aligned to huge page (2MB) boundaries.
Also, THP is only enabled for anonymous memory regions. There are plans to add support for tmpfs and page cache. THP tunables are found in the /sys tree under /sys/kernel/mm/redhat_transparent_hugepage.
查看是否启用透明大页
1:命令cat /sys/kernel/mm/redhat_transparent_hugepage/enabled 该命令适用于Red Hat Enterprise Linux系统
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
[root@getlnx06 ~]# more /etc/issue Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server release 6.6 (Santiago) Kernel \r on an \m [root@getlnx06 ~]# cat /sys/kernel/mm/redhat_transparent_hugepage/enabled [always] madvise never |
2:命令cat /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled 该命令适用于其它Linux系统
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
[root@getlnx06 ~]# cat /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled always madvise [never] [root@getlnx06 ~]# |
使用命令查看时,如果输出结果为[always]表示透明大页启用了。[never]表示透明大页禁用、[madvise]表示
3:如何HugePages_Total返回0,也意味着透明大页禁用了
|
1
2
3
|
[root@getlnx06 ~]# grep -i HugePages_Total /proc/meminfo HugePages_Total: 0 |
4:cat /proc/sys/vm/nr_hugepages返回0也意味着透明大页禁用了。
|
1
2
3
|
[root@getlnx06 ~]# cat /proc/sys/vm/nr_hugepages 0 |
禁用、启用透明大页功能
方法1:设置/etc/grub.conf文件,在系统启动是禁用。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
[root@getlnx06 ~]# vi /etc/grub.conf# grub.conf generated by anaconda## Note that you do not have to rerun grub after making changes to this file# NOTICE: You have a /boot partition. This means that# all kernel and initrd paths are relative to /boot/, eg.# root (hd0,0)# kernel /vmlinuz-version ro root=/dev/mapper/VolGroup--LogVol0-LogVol01# initrd /initrd-[generic-]version.img#boot=/dev/sdadefault=0timeout=5splashimage=(hd0,0)/grub/splash.xpm.gzhiddenmenutitle Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 (2.6.32-504.el6.x86_64) root (hd0,0) kernel /vmlinuz-2.6.32-504.el6.x86_64 ro root=/dev/mapper/VolGroup--LogVol0-LogVol01 rd_NO_LUKS LANG=en_US.UTF-8 rd_NO_MD SYSFONT=latarcyrheb-sun16 crashkernel=auto rd_LVM_LV=VolGroup-LogVol0/LogVol01 rd_LVM_LV=VolGroup-LogVol0/LogVol00 KEYBOARDTYPE=pc KEYTABLE=us rd_NO_DM rhgb quiet initrd /initramfs-2.6.32-504.el6.x86_64.imgtransparent_hugepage=never |
方法2:设置/etc/rc.local文件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
[root@getlnx06 ~]# vi /etc/rc.local#!/bin/sh## This script will be executed *after* all the other init scripts.# You can put your own initialization stuff in here if you don't# want to do the full Sys V style init stuff.touch /var/lock/subsys/localif test -f /sys/kernel/mm/redhat_transparent_hugepage/enabled; then echo never > /sys/kernel/mm/redhat_transparent_hugepage/enabledfi |
使用上面的配置后必须重启操作系统才能生效,你也可以运行下面命令不用重启操作系统。
|
1
2
3
4
|
[root@getlnx06 ~]# echo never > /sys/kernel/mm/redhat_transparent_hugepage/enabled[root@getlnx06 ~]# cat /sys/kernel/mm/redhat_transparent_hugepage/enabledalways madvise [never][root@getlnx06 ~]# |
小知识点:
1:从RedHat 6, OEL 6, SLES 11 and UEK2 kernels 开始,系统缺省会启用 Transparent HugePages :用来提高内存管理的性能透明大页(Transparent HugePages )和之前版本中的大页功能上类似。主要的区别是:Transparent HugePages 可以实时配置,不需要重启才能生效配置;
2:Transparent Huge Pages在32位的RHEL 6中是不支持的。
3: ORACLE官方不建议我们使用RedHat 6, OEL 6, SLES 11 and UEK2 kernels 时的开启透明大页(Transparent HugePages ), 因为透明大页(Transparent HugePages ) 存在一些问题:
- 在RAC环境下 透明大页(Transparent HugePages )会导致异常节点重启,和性能问题
- 在单机环境中,透明大页(Transparent HugePages ) 也会导致一些异常的性能问题
总结
以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,谢谢大家对服务器之家的支持。如果你想了解更多相关内容请查看下面相关链接
原文链接:http://www.codetc.com/article-319-1.html