一、总结
1、使用pypy
2、减少函数化调用
3、减少文件的打开即with的调用,将这一调用放在for循环前面,然后传递至后面需要用到的地方
4、if函数判断条件多的尽量在前面
全面加速(pypy)
二、全面加速(pypy)
将python换为pypy,在纯python代码下,pypy的兼容性就不影响使用了,因为一些纯python的代码常常会用pypy进行一下加速
测试代码,for循环10000000次
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
start = time.time()for i in range(10000000): print(i,end="\r")end = time.time()print(f"耗费时间{end-start}秒>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>") |
pypy的耗时为:
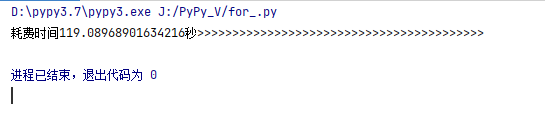
而python耗时为
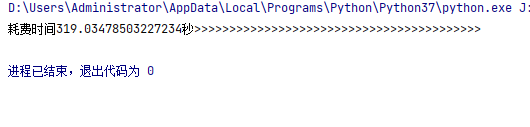
大致三倍,但是循环越多估计越快,据说有6倍左右
二、减少文件的打开即with的调用
原代码的with在调用函数内,即每次调用函数都要打开并关闭文件,造成大量耗时
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
def bmes(word,tag): with open(r"j:\pycharm项目\学习进行中\nlp教程\nlp教程\数据集\词性标注\nature2ner.txt","a+",encoding="utf-8")as f_: if len(word) == 1: """单字""" f_.write(word + " " + f"s-{tag.upper()}" + "\n") else: """多字""" for index, word_ in enumerate(word): if index == 0: f_.write(word_ + " " + f"b-{tag.upper()}" + "\n") elif 0 < index < len(word) - 1: f_.write(word_ + " " + f"m-{tag.upper()}" + "\n") else: f_.write(word_ + " " + f"e-{tag.upper()}" + "\n")#后续在多个if-elif-else中调用 |
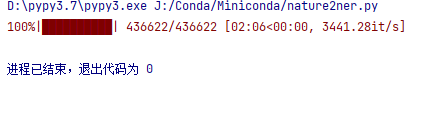
耗时为
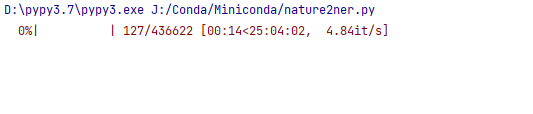
tqdm预估时间在15~25个小时左右跳动
将with放在循环前面
如
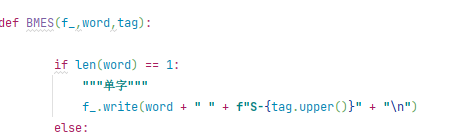
将with的内容作为f_传递进来

后的耗时为:
测试如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
import os, warnings,time,tqdmdef txt(word): with open("ceshi.txt","a+",encoding="utf-8")as f: if len(str(word))<=2: word+=100 f.write(str(word)+"\n") elif 2<len(str(word))<=4: word+=200 f.write(str(word)+"\n") else: f.write(str(word) + "\n")if __name__=="__main__": start = time.time() for i in tqdm.tqdm(range(100000)): txt(i) end = time.time() print(f"耗费时间{end-start}秒>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>") |
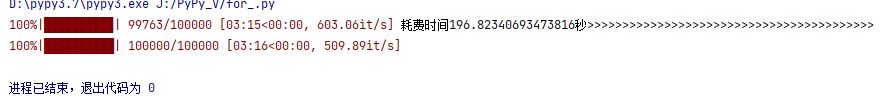
耗时结果为:
将文件的打开即with的调用放在外面
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
import os, warnings,time,tqdmdef txt(f,word): if len(str(word))<=2: word+=100 f.write(str(word)+"\n") elif 2<len(str(word))<=4: word+=200 f.write(str(word)+"\n") else: f.write(str(word) + "\n")if __name__=="__main__": start = time.time() with open("ceshi.txt", "a+", encoding="utf-8")as f: for i in tqdm.tqdm(range(100000)): txt(f,i) end = time.time() print(f"耗费时间{end-start}秒>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>") |
耗时为
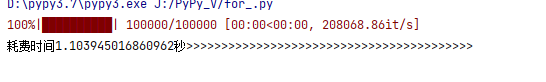
结论:快了119倍,而实际加速远远大于这个倍数
三、if判断靠前
如:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
if tag in ["nts", "nto", "ntc", "ntcb", "ntcf", "ntch", "nth", "ntu", "nt"]: bmes(f_,i2, tag="org") elif tag in ["nb", "nba", "nbc", "nbp", "nf", "nm", "nmc", "nhm", "nh"]: bmes(f_,i2, tag="obj") elif tag in ["nnd", "nnt", "nn"]: bmes(f_,i2, tag="job") elif tag in ["nr", "nrf"]: bmes(f_,i2, tag="per") elif tag in ["t"]: bmes(f_,i2, tag="time") elif tag in ["ns", "nsf"]: bmes(f_,i2, tag="loc") else: for i3 in list(i2): f_.write(i3 + " " + f"o" + "\n") |
满足条件的可以先跳出判断
到此这篇关于python运行加速的几种方式的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python运行加速的几种方式内容请搜索服务器之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持服务器之家!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/python__reported/article/details/118660689