删除的范围
- 过期的 key
- 在内存满了的情况下,如果继续执行 set 等命令,且所有 key 都没有过期,那么会按照缓存淘汰策略选中的 key
过期删除
redis 中设置了过期时间的 key 会单独存储一份
- typedef struct redisDb {
- dict *dict; // 所有的键值对
- dict *expires; //设置了过期时间的键值对
- // ...
- } redisDb;
设置有效期
Redis 中有 4 个命令可以给 key 设置过期时间,分别是 expire pexpire expireat pexpireat
设置相对时间
expire <key> <ttl>:将 key 值的过期时间设置为 ttl 秒。
- // src/expire.c
- /* EXPIRE key seconds */
- void expireCommand(client *c) {
- expireGenericCommand(c,mstime(),UNIT_SECONDS);
- }
pexpire <key> <ttl>:将 key 值的过期时间设置为 ttl 毫秒。
- // src/expire.c
- /* PEXPIRE key milliseconds */
- void pexpireCommand(client *c) {
- expireGenericCommand(c,mstime(),UNIT_MILLISECONDS);
- }
设置绝对时间
expireat <key> <timestamp>:将 key 值的过期时间设置为指定的 timestamp 秒数。
- // src/expire.c
- /* EXPIREAT key time */
- void expireatCommand(client *c) {
- expireGenericCommand(c,0,UNIT_SECONDS);
- }
pexpireat <key> <timestamp>:将 key 值的过期时间设置为指定的 timestamp 毫秒数。
- // src/expire.c
- /* PEXPIREAT key ms_time */
- void pexpireatCommand(client *c) {
- expireGenericCommand(c,0,UNIT_MILLISECONDS);
- }
以上 4 种方法最终都会调用下面的通用函数 expireGenericCommand :
- // src/expire.c
- void expireGenericCommand(client *c, long long basetime, int unit) {
- robj *key = c->argv[1], *param = c->argv[2];
- // 获取数据对象
- long long when;
- if (getLongLongFromObjectOrReply(c, param, &when, NULL) != C_OK)
- return;
- // 将时间转化成以 ms 为单位
- if (unit == UNIT_SECONDS) when *= 1000;
- when += basetime;
- // 在 master 节点上,如果设置的过期时间小于当前时间,那么将命令转化成 DEL 指令
- if (when <= mstime() && !server.loading && !server.masterhost) {
- robj *aux;
- int deleted = server.lazyfree_lazy_expire ? dbAsyncDelete(c->db,key) :
- dbSyncDelete(c->db,key);
- // ...
- // 将删除命令同步给 slave 和 AOF
- // ...
- } else {
- // 设置过期时间
- setExpire(c,c->db,key,when);
- // ...
- // 构造返回值和发布对象更新消息
- // ...
- return;
- }
- }
设置过期时间的操作由 setExpire 执行,他将 dictEntry 的 union v 中的 s64 设为过期时间
- // src/db.c
- void setExpire(client *c, redisDb *db, robj *key, long long when) {
- dictEntry *kde, *de;
- // 找出 db->dict 中对应的存储对象,这里的查询和用 get 查询数据是逻辑一样,通过 hashFunc(key) & sizemask
- // 找到 bucket 后在链表中遍历
- kde = dictFind(db->dict,key->ptr);
- // 找出 db->expires 中对应的存储对象,如果没有则新建一个
- de = dictAddOrFind(db->expires,dictGetKey(kde));
- //
- dictSetSignedIntegerVal(de,when);
- // ...
- }
- #define dictSetSignedIntegerVal(entry, _val_) \
- do { (entry)->v.s64 = _val_; } while(0)
db->expires 中存储的 dictEntry 表示的是过期 key 和过期时间,存储过期时间的 v 是一个 union ,可见在 redis 中不同使用场景或不同编码下 v 的意义不同
- typedef struct dictEntry {
- void *key;
- union {
- void *val;
- uint64_t u64;
- int64_t s64;
- double d;
- } v;
- struct dictEntry *next;
- } dictEntry;
查询过期时间
ttl key 返回 key 剩余过期秒数。
- // src/expire.c
- /* TTL key */
- void ttlCommand(client *c) {
- ttlGenericCommand(c, 0);
- }
pttl key 返回 key 剩余过期的毫秒数。
- // src/expire.c
- /* PTTL key */
- void pttlCommand(client *c) {
- ttlGenericCommand(c, 1);
- }
以上 2 种查看方式最终都会调用下面的通用函数 ttlGenericCommand :
- // src/expire.c
- /* Implements TTL and PTTL */
- void ttlGenericCommand(client *c, int output_ms) {
- // ...
- // key 不存在时报错
- // ...
- // 获取过期时间,如果没有过期时间则
- expire = getExpire(c->db,c->argv[1]);
- if (expire != -1) {
- ttl = expire-mstime();
- if (ttl < 0) ttl = 0;
- }
- if (ttl == -1) {
- addReplyLongLong(c,-1);
- } else {
- // 根据指定的单位返回结果,以秒为单位时向上取整
- addReplyLongLong(c,output_ms ? ttl : ((ttl+500)/1000));
- }
- }
获取过期时间的操作由 getExpire 执行,在 db->expires 中查询到对象后,获取 union v 中的成员 s64
- // src/expire.c
- // 返回过期时间的绝对时间
- long long getExpire(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
- dictEntry *de;
- // 查询对象
- if (dictSize(db->expires) == 0 ||
- // 如果返回为 NULL 表示没有设置过期时间,向上返回 -1
- (de = dictFind(db->expires,key->ptr)) == NULL) return -1;
- // 获取 v.s64
- return dictGetSignedIntegerVal(de);
- }
- #define dictGetSignedIntegerVal(he) ((he)->v.s64)
过期策略
Redis 综合使用 惰性删除 和 定期扫描 实现
惰性删除
每次访问时会调用 expireIfNeeded 判断 key 是否过期,如果过期就删除该键,否则返回键对应的值。单独使用这种策略可能会浪费很多内存。
- // src/db.c
- int expireIfNeeded(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
- mstime_t when = getExpire(db,key);
- mstime_t now;
- // 没有设置过期时间,直接返回
- if (when < 0) return 0;
- // 从硬盘中加载数据时不执行过期操作
- if (server.loading) return 0;
- // 参考 GitHub Issue #1525
- // 对于 master,在执行 Lua Script 的过程中,可能会用某个 key 是否存在当作判断条件
- // 为了避免一个脚本中前后条件不一致,将当前时间强制设为脚本开始时间
- now = server.lua_caller ? server.lua_time_start : mstime();
- // 对于 slave,返回此时 key 是否已过期,但不执行后续删除操作
- if (server.masterhost != NULL) return now > when;
- // key 未过期
- if (now <= when) return 0;
- // 统计过期 key 的个数
- server.stat_expiredkeys++;
- // 向所有的 slave 和 AOF 文件写入一条 DEL 指令
- propagateExpire(db,key,server.lazyfree_lazy_expire);
- // 向 keyspace channel 中发布一条 key 过期的消息
- notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_EXPIRED,
- "expired",key,db->id);
- // 根据配置决定是同步删除还是异步删除(仅删除引用,由后台线程执行物理删除)
- return server.lazyfree_lazy_expire ? dbAsyncDelete(db,key) :
- dbSyncDelete(db,key);
- }
特殊处理
在 master 节点执行 Lua 脚本时
参考 GitHub Issue #1525,对于 master,在执行 Lua Script 的过程中,可能会用某个 key 是否存在当作判断条件。为了避免一个脚本中前后条件不一致,将当前时间强制设为脚本开始时间。
例如多次执行如下 Lua 脚本 /tmp/myscript.lua 出现的结果可能不一致
- -- /tmp/myscript.lua
- if redis.call("exists",KEYS[1]) == 1
- then
- redis.call("incr","mycounter")
- end
- if redis.call("exists",KEYS[1]) == 1
- then
- return redis.call("incr","mycounter")
- end
具体复现操作可以参考下面的 bash 脚本:
- while [ 1 ]
- do
- redis-cli set x foo px 100 > /dev/null
- sleep 0.092
- redis-cli --eval /tmp/myscript.lua x > /dev/null
- sleep 0.1
- redis-cli get mycounter
- redis-cli -p 6380 get mycounter
- done
对于 slave 节点
在 slave 节点上,key 的删除操作由 master 发来的 DEL 执行,因此这里只返回是否过期的结果给客户端,而不执行删除操作
正在从 RDB 和 AOF 读取数据时跳过这个步骤
定期扫描
系统每隔一段时间就定期扫描一次,发现过期的键就进行删除。单独使用这种策略可能出现键已经过期但没有删除的情况
Redis 默认每 100ms 执行一次(通过 hz 参数配置,执行周期为 1s/hz)过期扫描。由于 redisDb 中设置了过期时间的 key 会单独存储,所以不会出现扫描所有 key 的情况
具体步骤由 activeExpireCycle 函数执行
activeExpireCycle、incrementallyRehash 等后台操作都是由 databasesCron 触发的
- void activeExpireCycle(int type) {
- // ...
- // 依次遍历各个 db
- for (j = 0; j < dbs_per_call && timelimit_exit == 0; j++) {
- int expired;
- redisDb *db = server.db+(current_db % server.dbnum);
- // 记录下一个执行的 db,这样如果因为超时意外退出,下次可以继续从这个 db 开始,
- // 从而在所有 db 上均匀执行清除操作
- current_db++;
- do {
- // ...
- // 跳过没有设置过期时间的 key 等不需要执行的情况
- // ...
- // 抽样个数,默认为 20
- if (num > ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP)
- num = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP;
- // 从设置了过期时间的 key 中随机抽取 20 个
- while (num--) {
- dictEntry *de;
- long long ttl;
- // 随机挑选 dict 中的一个 key
- if ((de = dictGetRandomKey(db->expires)) == NULL) break;
- ttl = dictGetSignedIntegerVal(de)-now;
- // 执行删除,具体删除操作和惰性删除中类似
- if (activeExpireCycleTryExpire(db,de,now)) expired++;
- // ...
- }
- // ...
- // 更新统计数据等操作
- // ...
- // 如果每次删除的 key 超过了样本数的 25%,说明过期键占的比例较高,需要再重复执行依次
- } while (expired > ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_LOOKUPS_PER_LOOP/4);
- }
- // ...
- }
随机抽样由 dictGetRandomKey 执行
- // src/dict.c
- /* Return a random entry from the hash table. Useful to
- * implement randomized algorithms */
- dictEntry *dictGetRandomKey(dict *d)
- {
- dictEntry *he, *orighe;
- unsigned long h;
- int listlen, listele;
- // 没有数据,返回为 NULL,外层函数接收到 NULL 后会中断过期操作的执行
- if (dictSize(d) == 0) return NULL;
- // 根据 rehashidx 参数判断是否正在执行 rehash,如果正在执行,
- // 则先执行 rehash 中的一个步骤
- if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
- if (dictIsRehashing(d)) {
- do {
- // 正在执行 rehash,所以两个 ht 中的对象都要考虑
- //
- // 由于正在执行 rehash,所以可以肯定 ht[0] 中下标小于等于 rehashidx 的 bucket
- // 肯定没有数据,所以只从 ht[0] 中大于 rehashidx 的 bucket 和 ht[1] 中抽取
- h = d->rehashidx + (random() % (d->ht[0].size +
- d->ht[1].size -
- d->rehashidx));
- he = (h >= d->ht[0].size) ? d->ht[1].table[h - d->ht[0].size] :
- d->ht[0].table[h];
- // 取到空 bucket 时重试
- } while(he == NULL);
- } else {
- do {
- // 参考写入 ht 时计算下标的规则 hashFunc(key) & sizemake
- // 这里 random() & sizemask 是随机取一个下标
- h = random() & d->ht[0].sizemask;
- he = d->ht[0].table[h];
- // 取到空 bucket 时重试
- } while(he == NULL);
- }
- // 到这一步 he 是 ht[n] 中某个 bucket 中完整的链表
- // 所以还要从这个链表中随机取一个对象
- // 遍历计算整个链表的长度
- listlen = 0;
- orighe = he;
- while(he) {
- he = he->next;
- listlen++;
- }
- // 随机取链表中某个对象的下标
- listele = random() % listlen;
- he = orighe;
- // 重新遍历链表获取指定下标的对象
- while(listele--) he = he->next;
- return he;
- }
缓存淘汰
配置最大内存限制
在 redis.conf 中配置
redis server 启动时加载配置文件和命令行参数中的 maxmemory ,存入 Server 对象的 maxmemory 字段
main 中在 redis server 启动时执行初始化等操作,其中会执行加载配置文件的 loadServerConfig 函数
- // src/server.c
- int main(int argc, char **argv) {
- // ..
- // 加载配置
- loadServerConfig(configfile,options);
- // ..
- // 警告过小的配置
- if (server.maxmemory > 0 && server.maxmemory < 1024*1024) {
- serverLog(LL_WARNING,"WARNING: You specified a maxmemory value that is less than 1MB (current value is %llu bytes). Are you sure this is what you really want?", server.maxmemory);
- }
- }
loadServerConfig 中将配置文件、stdin、命令行参数加载到 config 字符串中,然后调用 loadServerConfigFromString
- // src/config.c
- void loadServerConfig(char *filename, char *options) {
- sds config = sdsempty();
- char buf[CONFIG_MAX_LINE+1];
- // 加载配置文件
- if (filename) {
- FILE *fp;
- // 启动命令为 ./redis-server - 则从 stdin 中读取,需要用 <C-D> 触发 EOF
- if (filename[0] == '-' && filename[1] == '\0') {
- fp = stdin;
- } else {
- // 第一个参数不是 -,则尝试打开这个参数指定的文件
- if ((fp = fopen(filename,"r")) == NULL) {
- serverLog(LL_WARNING,
- "Fatal error, can't open config file '%s'", filename);
- exit(1);
- }
- }
- // 将配置文件中的每一行追加到 config 中
- while(fgets(buf,CONFIG_MAX_LINE+1,fp) != NULL)
- config = sdscat(config,buf);
- if (fp != stdin) fclose(fp);
- }
- // 添加其他选项,例如 ./redis-server --port 8080 后面的参数,直接加到 config 中
- if (options) {
- config = sdscat(config,"\n");
- config = sdscat(config,options);
- }
- loadServerConfigFromString(config);
- sdsfree(config);
- }
loadServerConfigFromString 从上一步中的 config 字符串中逐行读取配置,并写入 server 对象
- // src/config.c
- void loadServerConfigFromString(char *config) {
- // ...
- // 按行读取配置文件
- lines = sdssplitlen(config,strlen(config),"\n",1,&totlines);
- for (i = 0; i < totlines; i++) {
- // 跳过无效的配置和注释
- // ...
- argv = sdssplitargs(lines[i],&argc);
- // 将配置命令转化成小写
- sdstolower(argv[0]);
- // 根据配置命令初始化配置,strcasecmp 比较
- if (!strcasecmp(argv[0],"timeout") && argc == 2) {
- server.maxidletime = atoi(argv[1]);
- if (server.maxidletime < 0) {
- err = "Invalid timeout value"; goto loaderr;
- }
- // ...
- } else if (!strcasecmp(argv[0],"maxmemory") && argc == 2) {
- // memtoll 将字符串形式的配置转化成对应的 long long 值
- // 例如 1kb -> 1024
- server.maxmemory = memtoll(argv[1],NULL);
- }
- }
- }
使用 CONFIG SET 命令配置
Redis Server 接收到客户端的 CONFIG SET 命令后调用 configSetCommand 函数
服务端接收到命令时将命令和参数存入 Redis Server 的 argc 和 argv
- argc: 4
- argv: 0 1 2 3
- config set maxmemory 10mb
动态配置 maxmemory 后会立即尝试触发内存回收,而修改其他内存相关配置(例如: maxmemory_policy)时不会触发
- if (0) {
- // ...
- } config_set_memory_field("maxmemory",server.maxmemory) {
- // 配置不为 0,表示之前限制过内存
- if (server.maxmemory) {
- if (server.maxmemory < zmalloc_used_memory()) {
- serverLog(LL_WARNING,"WARNING: the new maxmemory value set via CONFIG SET is smaller than the current memory usage. This will result in keys eviction and/or inability to accept new write commands depending on the maxmemory-policy.");
- }
- freeMemoryIfNeeded();
- }
- // ...
- }
32 位机器的内存限制
对于 64 位机器,将 maxmemory 设置为 0 表示不限制内存,但由于 32 位寻址空间最多只有 4 GB,所以默认内存限制设为 3 GB,缓存淘汰策略设为 noeviction
- // src/server.c
- // ...
- if (server.arch_bits == 32 && server.maxmemory == 0) {
- serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Warning: 32 bit instance detected but no memory limit set. Setting 3 GB maxmemory limit with 'noeviction' policy now.");
- server.maxmemory = 3072LL*(1024*1024); /* 3 GB */
- server.maxmemory_policy = MAXMEMORY_NO_EVICTION;
- }
淘汰策略
淘汰策略使用 CONFIG SET maxmemory-policy 配置
默认:
- **noeviction: **内存满了后对于 set 等命令直接返回错误
针对所有 key:
- allkeys-lru: 在所有 key 的范围内使用 LRU 算法执行删除,如果内存仍然不够,则报错
- **allkeys-lfu: **在所有 key 的范围内使用 LRU 算法执行删除,如果内存仍然不够,则报错
- **allkeys-random: **在所有 key 的范围内随机执行删除,如果内存仍然不够,则报错
针对设置了过期时间的 key:
- **volatile-lru: **在设置了过期时间的 key 中使用 LRU 算法执行删除,如果内存仍然不够,则报错
- **volatile-lfu: **在设置了过期时间的 key 中使用 LRU 算法执行删除,如果内存仍然不够,则报错
- **volatile-random: **在设置了过期时间的 key 中随机执行删除,如果内存仍然不够,则报错
- **volatile-ttl: **删除即将过期的 key,如果内存仍然不够,则报错
Redis 在执行淘汰之前会计算部分对象的 idle 值,使用不同淘汰策略时计算 idle 值的方法也不同, idle 值越大表示这个值越需要优先删除。
下面主要介绍 LRU 和 LFU 中 idle 值的计算方法
LRU 淘汰策略
抽样删除,样本数量通过 CONFIG SET maxmemory-samples 100 控制,对应 RedisObject 中的 maxmemory_samples 参数,抽样数量越多和传统的 LRU 算法越接近
优化策略
为了避免传统的 LRU 算法通常使用 hashmap + 链表实现带来的开销,Redis 进行了如下优化:
RedisObject 结构中设置了一个 lru 字段,用来记录数据的访问时间戳,而不是每次调整对象在链表中的位置
- typedef struct redisObject {
- // 对象类型
- unsigned type:4;
- // 对象编码
- unsigned encoding:4;
- // LRU 算法和 LFU 算法公用 lru 这个字段
- //
- // LRU_BITS 默认为 24,因此最大只能存储 194 天的时间戳,
- // 创建对象时会写入这个字段,访问对象时会更新这个字段,
- // 超过之后再从 0 开始计算
- unsigned lru:LRU_BITS;
- int refcount;
- void *ptr;
- } robj;
使用抽样数组代替链表,后续在候选集合中根据 lru 字段值的大小进行筛选,避免了链表带来的开销。候选集合中的对象用 evictionPoolEntry 表示
- struct evictionPoolEntry {
- unsigned long long idle; // 用于淘汰排序,在不同算法中意义不同
- sds key; // 键的名字
- // ...
- };
计算方法
全局对象 lru_clock 记录了当前的 unix 时间戳,由 serverCron 调用 updateCachedTime 默认每 100 ms 更新一次。更新频率与 hz 参数有关, 1s/hz 即为更新间隔时间。
LRU_CLOCK_RESOLUTION 的值为 1000,因此使用 LRU_CLOCK 函数获取 lru_clock 时,如果每秒更新频率在 1 次以上,会使用全局变量中缓存的 lrulcock
- unsigned int LRU_CLOCK(void) {
- unsigned int lruclock;
- if (1000/server.hz <= LRU_CLOCK_RESOLUTION) {
- atomicGet(server.lruclock,lruclock);
- } else {
- lruclock = getLRUClock();
- }
- return lruclock;
- }
如果更新频率不到每秒 1 次,则会用函数 getLRUClock 实时计算 lruclock
- unsigned int getLRUClock(void) {
- // mstime() 获取 unix 时间戳,单位时毫秒
- // 除以 LRU_CLOCK_RESOLUTION(值为 1000),将时间戳转化为秒
- return (mstime()/LRU_CLOCK_RESOLUTION) & LRU_CLOCK_MAX;
- }
其中 LRU_CLOCK_MAX 表示 lru_clock 最大的可能值,这个值与 redisObject 中 lru 最大的可能值一样,定义如下:
- #define LRU_CLOCK_MAX ((1<<LRU_BITS)-1)
所以最终比较时 lru_clock 和 robj.lru 的值都在 [0, LRU_CLOCK_MAX] 的范围内。
从逻辑上讲, 当前时间戳应该永远大于上次访问的时间戳 ,因此正常的计算规则应该是 lru_clock-robj.lru 。
但是由于 lru_clock 和 robj.lru 是当前时间戳取模后的值,所以可能出现 lru_clock 小于 robj.lru 的情况,所以这种情况下计算规则应该改为 lru_clock+194天-robj.lru
但是对于 lru_clock 和 robj.lru 间隔超过 194 天的情况仍然无法判断,所以更能存在删除不准确的情况。
将上述的逻辑组合起来就是 LRU 算法下获取 idle 值的函数:
- // src/evict.c
- // 以秒为精度计算对象距离上一次访问的间隔时间,然后转化成毫秒返回
- unsigned long long estimateObjectIdleTime(robj *o) {
- unsigned long long lruclock = LRU_CLOCK();
- if (lruclock >= o->lru) {
- return (lruclock - o->lru) * LRU_CLOCK_RESOLUTION;
- } else {
- return (lruclock + (LRU_CLOCK_MAX - o->lru)) *
- LRU_CLOCK_RESOLUTION;
- }
- }
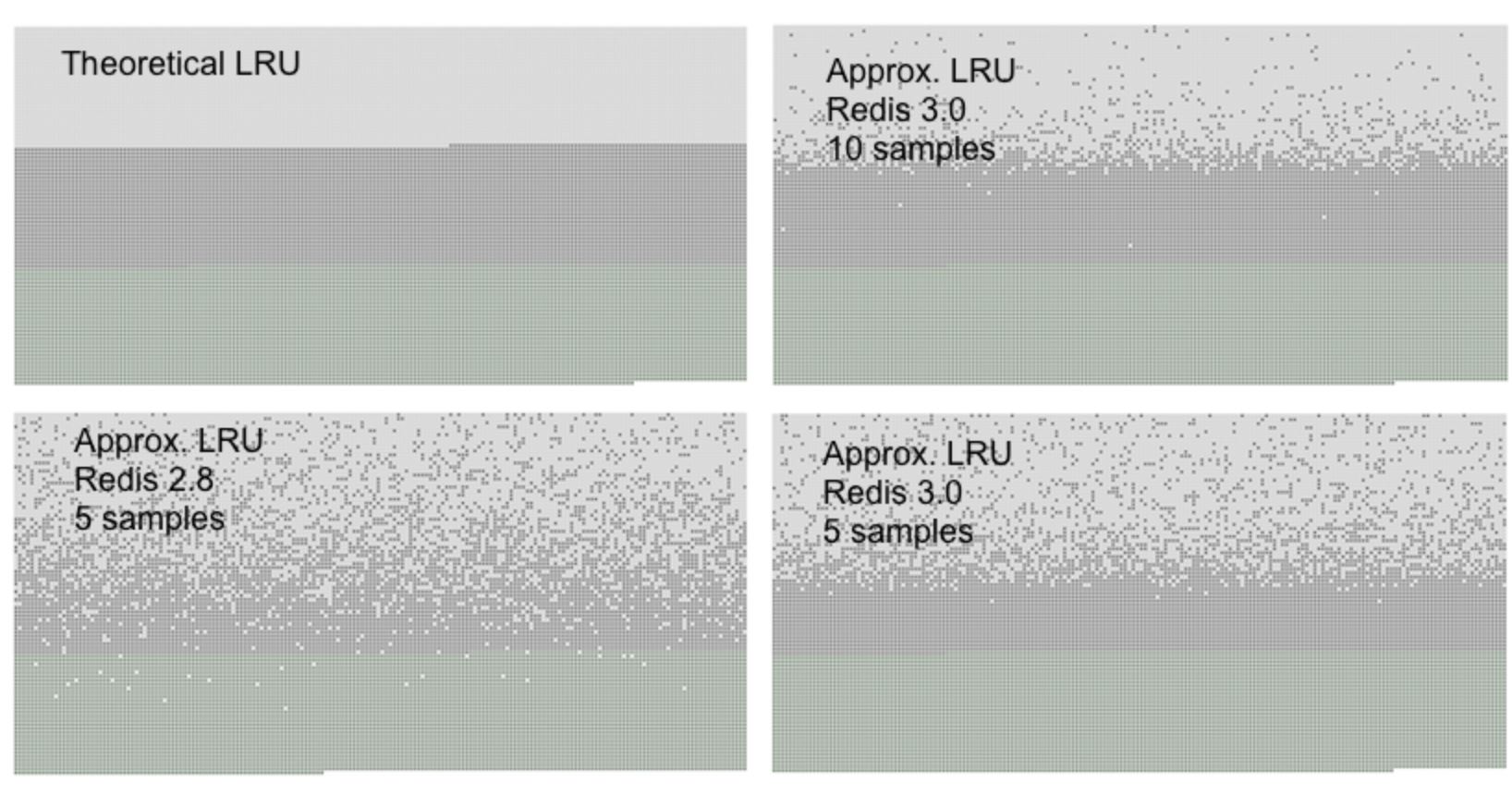
在 Redis 3.0 中,当取样数量设为 10 时,已经和传统的 LRU 算法效果很接近了
LFU 淘汰策略
LFU 算法复用 robj.lru 字段,将这个 24 bit 的字段拆分成了两部分:
- ldt(last decrement time,单位:分钟):lru 字段的前 16bit,表示数据的访问时间戳,最多只能存储 45 天。
- counter 值:lru 字段的后 8bit,表示数据的访问频率
递增策略
counter 能表示的最大值是 255,因此 counter 与访问次数不能是线性关系,这里采用的计算步骤如下:
- 随机取 0 到 1 之间的随机数 r
- 比较 r 与 1/((counter-LFU_INIT_VAL)*lfu_log_factor+1) 的大小,其中 LFU_INIT_VAL 是常量,默认为 5,lfu_log_factor 是可配置参数,默认为 10
- 如果 r 小则 counter 增加 1,否则 counter 不变
实现代码如下:
- uint8_t LFULogIncr(uint8_t counter) {
- // counter 值已经到达了 255,不能再增加,直接返回
- if (counter == 255) return 255;
- double r = (double)rand()/RAND_MAX;
- double baseval = counter - LFU_INIT_VAL; // LFU_INIT_VAL 值为 5
- if (baseval < 0) baseval = 0;
- double p = 1.0/(baseval*server.lfu_log_factor+1);
- if (r < p) counter++;
- return counter;
- }
访问次数与 counter 值之间大概是对数关系,counter 值越大,增速越低
- // https://redis.io/topics/lru-cache
- +--------+------------+------------+------------+------------+------------+
- | factor | 100 hits | 1000 hits | 100K hits | 1M hits | 10M hits |
- +--------+------------+------------+------------+------------+------------+
- | 0 | 104 | 255 | 255 | 255 | 255 |
- +--------+------------+------------+------------+------------+------------+
- | 1 | 18 | 49 | 255 | 255 | 255 |
- +--------+------------+------------+------------+------------+------------+
- | 10 | 10 | 18 | 142 | 255 | 255 |
- +--------+------------+------------+------------+------------+------------+
- | 100 | 8 | 11 | 49 | 143 | 255 |
- +--------+------------+------------+------------+------------+------------+
衰减策略
除了访问对象时 counter 需要增加,对于一段时间内没有访问的对象还要相应地减少 counter 值,递减的速率由 lfu-decay-time 参数控制。
counter 衰减步骤如下:
取当前时间戳(单位:分钟)的低 16 位记为 now ,计算与 ldt 的差值。这里与 LRU 算法中计算 lru_clock 和 robj.lru 时可能出现一样的问题,由于 ldt 最多只能表示 45 天,所以如果距离对象上次访问超过 45 天,则无法准确计算访问的时间间隔
- unsigned long LFUDecrAndReturn(robj *o) {
- // 取高 16 位
- unsigned long ldt = o->lru >> 8;
- // 取低 8 位
- unsigned long counter = o->lru & 255;
- // 如果 lfu_decay_time 为 0,则步修改 counter,否则将 counter 减少 LFUTimeElapsed(ldt)/lfu_decay_time
- unsigned long num_periods = server.lfu_decay_time ? LFUTimeElapsed(ldt) / server.lfu_decay_time : 0;
- if (num_periods)
- // 保证 counter 的最小值位 0
- counter = (num_periods > counter) ? 0 : counter - num_periods;
- return counter;
- }
- // 计算距离上次访问的间隔时间
- unsigned long LFUTimeElapsed(unsigned long ldt) {
- // 取当前时间戳(单位:分钟)
- unsigned long now = LFUGetTimeInMinutes();
- // 计算时间差
- if (now >= ldt) return now-ldt;
- return 65535-ldt+now;
- }
- // 获取当前时间戳,以分钟为单位,取低 8 位
- unsigned long LFUGetTimeInMinutes(void) {
- return (server.unixtime/60) & 65535;
- }
如果 lfu_decay_time 为 0,则步修改 counter,否则将 counter 减少 LFUTimeElapsed(ldt)/lfu_decay_time
例如,在 lfu_decay_time 为 1 的情况下,如果有 N 分钟没有访问这个对象,那么 counter 值减 N
每次访问一个对象时都会调用 updateLFU 更新 counter 的值:
- void updateLFU(robj *val) {
- unsigned long counter = LFUDecrAndReturn(val);
- counter = LFULogIncr(counter);
- val->lru = (LFUGetTimeInMinutes()<<8) | counter;
- }
执行淘汰
当 Redis 需要淘汰一批数据时,会调用 evictionPoolPopulate 获取一批待删除对象,根据设置的淘汰范围的不同,会决定传递给 evictionPoolPopulate 的 sampledict 参数是存有全部数据的 db->dict 还是只有设置了过期时间的数据的 db->expires
- void evictionPoolPopulate(int dbid, dict *sampledict, dict *keydict, struct evictionPoolEntry *pool) {
- int j, k, count;
- dictEntry *samples[server.maxmemory_samples];
- // 随机获取 server.maxmemory_samples 个对象,写入 samples 中
- count = dictGetSomeKeys(sampledict,samples,server.maxmemory_samples);
- // 遍历每个对象
- for (j = 0; j < count; j++) {
- // ...
- // 初始化
- // ...
- de = samples[j];
- key = dictGetKey(de);
- // 如果获取样本的字典不是 db->dict(还可能是 db->expires),并且不是按 volatile-ttl 淘汰
- // 那么还要将对象转化成数据字典中对应的对象,然后取其值
- if (server.maxmemory_policy != MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_TTL) {
- if (sampledict != keydict) de = dictFind(keydict, key);
- // #define dictGetVal(he) ((he)->v.val)
- // 这里还是利用 union 的特性,如果是 db->dict 中的元素,返回的是键的值
- // 如果是 db->expires 中的元素,返回的是过期时间
- o = dictGetVal(de);
- }
- // 按各算法计算 idle 分值,idle 越大的越应该被先淘汰
- //
- // 如果使用 LRU 淘汰算法,则计算对象的空闲时间
- if (server.maxmemory_policy & MAXMEMORY_FLAG_LRU) {
- idle = estimateObjectIdleTime(o);
- // 使用 LFU 淘汰算法,
- } else if (server.maxmemory_policy & MAXMEMORY_FLAG_LFU) {
- idle = 255-LFUDecrAndReturn(o);
- // 使用 volatile-ttl 算法,用 ULLONG_MAX 减去过期时间作为分值
- } else if (server.maxmemory_policy == MAXMEMORY_VOLATILE_TTL) {
- idle = ULLONG_MAX - (long)dictGetVal(de);
- } else {
- serverPanic("Unknown eviction policy in evictionPoolPopulate()");
- }
- k = 0;
- // 与原 pool 中的 idle 值进行比较,找出应该比当前对象先淘汰出去的对象
- while (k < EVPOOL_SIZE &&
- pool[k].key &&
- pool[k].idle < idle) k++;
- if (k == 0 && pool[EVPOOL_SIZE-1].key != NULL) {
- // 没有发现更需要被淘汰的对象,并且 pool 中也没有多余的位置
- // 那么当前对象仍然留在 samples 中
- continue;
- } else if (k < EVPOOL_SIZE && pool[k].key == NULL) {
- // 没有发现更需要被淘汰的对象,但 pool 中有多余的位置
- // 于是将这个对象插入 pool 中
- } else {
- // 当前对象
- // |
- // V
- // Pool: [ 0 1 2 3 ...k-1 k ... EVPOOL_SIZE-1]
- // 为了保证 pool 中的数据按 idle 从小到大排列,这里将当前对象插入第 k 个对象后面的位置
- if (pool[EVPOOL_SIZE-1].key == NULL) {
- // pool 的右边还有空余的位置,因此将从第 k 个开始后面的元素整体后移
- memmove(pool+k+1,pool+k,
- sizeof(pool[0])*(EVPOOL_SIZE-k-1));
- } else {
- // pool 的右边没有空余的位置了,那么将 pool 中前 k 个元素整体左移
- sds cached = pool[0].cached;
- memmove(pool,pool+1,sizeof(pool[0])*k);
- }
- }
- // ...
- // 将当前对象的属性赋值到下标为 k 的元素
- // ...
- }
- }
完成上述操作后,pool 中剩下的就是新筛选出来的最需要淘汰的对象了。
在 freeMemoryIfNeeded 中会调用 evictionPoolPopulate 来筛选需要淘汰的对象,每次删除一个,直到释放了足够的内存。如果始终无法达到内存需求,则会报错。
到此这篇关于Redis 缓存删除机制(源码解析)的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Redis 缓存删除内容请搜索服务器之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持服务器之家!