简介
使用spring时,达到同一目的通常有很多方法,对处理http响应也是一样。本文我们学习如何通过ResponseEntity设置http相应内容、状态以及头信息。
ResponseEntity
ResponseEntity标识整个http相应:状态码、头部信息以及相应体内容。因此我们可以使用其对http响应实现完整配置。
如果需要使用ResponseEntity,必须在请求点返回,通常在spring rest中实现。ResponseEntity是通用类型,因此可以使用任意类型作为响应体:
|
1
2
3
4
|
@GetMapping("/hello")ResponseEntity<String> hello() { return new ResponseEntity<>("Hello World!", HttpStatus.OK);} |
可以通过编程方式指明响应状态,所以根据不同场景返回不同状态:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
@GetMapping("/age")ResponseEntity<String> age( @RequestParam("yearOfBirth") int yearOfBirth) { if (isInFuture(yearOfBirth)) { return new ResponseEntity<>( "Year of birth cannot be in the future", HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST); } return new ResponseEntity<>( "Your age is " + calculateAge(yearOfBirth), HttpStatus.OK);} |
另外,还可以设置http响应头:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
@GetMapping("/customHeader")ResponseEntity<String> customHeader() { HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders(); headers.add("Custom-Header", "foo"); return new ResponseEntity<>( "Custom header set", headers, HttpStatus.OK);} |
而且, ResponseEntity提供了两个内嵌的构建器接口: HeadersBuilder 和其子接口 BodyBuilder。因此我们能通过ResponseEntity的静态方法直接访问。
最简单的情况是相应包括一个主体及http 200响应码:
|
1
2
3
4
|
@GetMapping("/hello")ResponseEntity<String> hello() { return ResponseEntity.ok("Hello World!");} |
大多数常用的http 响应码,可以通过下面static方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
BodyBuilder accepted();BodyBuilder badRequest();BodyBuilder created(java.net.URI location);HeadersBuilder<?> noContent();HeadersBuilder<?> notFound();BodyBuilder ok(); |
另外,可以能使用BodyBuilder status(HttpStatus status)和BodyBuilder status(int status) 方法设置http状态。使用ResponseEntity BodyBuilder.body(T body)设置http响应体:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
@GetMapping("/age")ResponseEntity<String> age(@RequestParam("yearOfBirth") int yearOfBirth) { if (isInFuture(yearOfBirth)) { return ResponseEntity.badRequest() .body("Year of birth cannot be in the future"); } return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.OK) .body("Your age is " + calculateAge(yearOfBirth));} |
也可以自定义头信息:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
@GetMapping("/customHeader")ResponseEntity<String> customHeader() { return ResponseEntity.ok() .header("Custom-Header", "foo") .body("Custom header set");} |
因为BodyBuilder.body()返回ResponseEntity 而不是 BodyBuilder,需要最后调用。注意使用HeaderBuilder 不能设置任何响应体属性。
尽管ResponseEntity非常强大,但不应该过度使用。在一些简单情况下,还有其他方法能满足我们的需求,使代码更整洁。
替代方法
@ResponseBody
典型spring mvc应用,请求点通常返回html页面。有时我们仅需要实际数据,如使用ajax请求。这时我们能通过@ResponseBody注解标记请求处理方法,审批人能够处理方法结果值作为http响应体。
@ResponseStatus
当请求点成功返回,spring提供http 200(ok)相应。如果请求点抛出异常,spring查找异常处理器,由其返回相应的http状态码。对这些方法增加@ResponseStatus注解,spring会返回自定义http状态码。
直接操作相应
Spring 也允许我们直接 javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse 对象;只需要申明其作为方法参数:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
@GetMapping("/manual")void manual(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException { response.setHeader("Custom-Header", "foo"); response.setStatus(200); response.getWriter().println("Hello World!");} |
但需要说明,既然spring已经提供底层实现的抽象和附件功能,我们不建议直接操作response。
总结:本文我们介绍了spring提供多种方式处理http响应,以及各自的优缺点,希望对你有帮助。
ResponseEntity的基本简介
1、ResponseEntity继承了HttpEntity
可以添加HttpStatus状态码的HttpEntity的扩展类。被用于RestTemplate和Controller层方法
2、ResponseEntity可以定义返回的HttpStatus(状态码)
和HttpHeaders(消息头:请求头和响应头)HttpStatus的状态码有以下几种
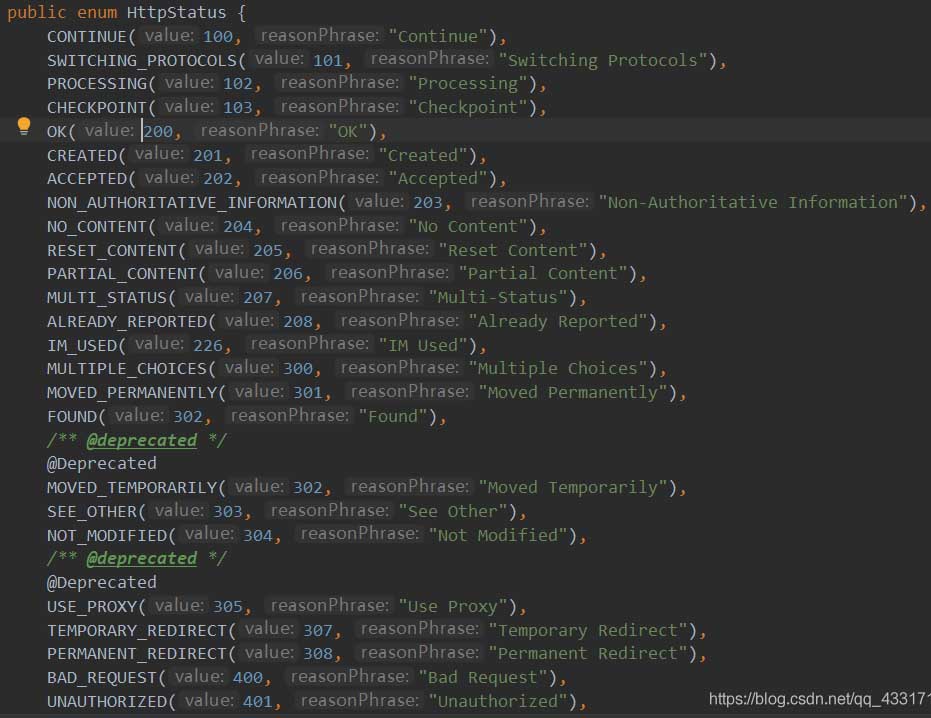
3、ResponseEntity的优先级高于@ResponseBody
在不是ResponseEntity的情况下才去检查有没有@ResponseBody注解。如果响应类型是ResponseEntity可以不写@ResponseBody注解,写了也没有关系。
简单的说@ResponseBody可以直接返回Json结果,@ResponseEntity不仅可以返回json结果,还可以定义返回的HttpHeaders和HttpStatus
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
public ResponseEntity<List<Category>> queryCategoriesByPid(@RequestParam(value = "pid",defaultValue = "0") Long pid){ if(pid == null || pid.longValue()<0){ // 响应400,相当于ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST).build(); return ResponseEntity.badRequest().build(); } //ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND).body(null); // ResponseEntity.notFound().build(); // ResponseEntity.ok(null); List<Category> categoryList = this.categoryService.queryCategoriesByPid(pid); if(CollectionUtils.isEmpty(categoryList)){ // 响应404 return ResponseEntity.notFound().build(); } return ResponseEntity.ok(categoryList); } |
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/neweastsun/article/details/81142870