自上学这么多年以来,得出了从一个例子入手来学习是最快最有效,并能培养出很强的实践能力,这是一种很好的学习方法。不访试试。比如看一本书的时候从各章节的例子入手,找出不了解的以及不懂的还是新知识,
进而有针对性的学习。看看下面的例子:
<?php
$ip = getenv("REMOTE_ADDR");
//echo "$ip";
$conn=mysql_connect('ip','root','****');
mysql_select_db('db',$conn);
$sql="select *from counter where ip="$ip";";
$result=mysql_query($sql,$conn);
$num=mysql_num_rows($result);
$count=mysql_query("select*from counter",$conn);
$count=mysql_num_rows($count);
//echo "$num";
//echo "$count";
if($num==0)
{
$sum=1;
$count++;
$sql="insert into counter(ip,sum,countdata)values('$ip','1','$count')";
mysql_query($sql,$conn);
mysql_close($conn);
//echo "$count";
}
else
{
$my="select sum from counter where ip='$ip'";
$bbbbbb=mysql_query($my) or die(mysql_error());
$row=mysql_fetch_Array($bbbbbb);
@$sum=$row[sum];
//echo "$sum";
$sum++;
$sql="update counter set sum='$sum' where ip='$ip'";
mysql_query($sql);
mysql_close($conn);
}
$str_count=strval($count);
$str_count=Chop($str_count);
$count_len=strlen($str_count);
$image_count="";
if($count_len<6)
{for($j=0;$j<6-$count_len;$j++)
{$image_count=$image_count."<ccid_file values="0" src=0.gif />";
}
}
for($i=0;$i<$count_len;$i++)
{
$nom=substr($str_count,$i,1);
$image_count = $image_count."<ccid_file values=";
$image_count = $image_count"
$image_count = $image_count.".gif />";
}
echo"$image_count<br>";
print"这是你的第".$sum."次访问";
?>
从上面的一个小小的计数器例子来看。已经包括了查询、插入、修改的知识。可以实现功能。记录每一个IP的访问量及总的访问次数。总量不支刷新
一、查询:
SELECT被用来检索从一个或多个表中精选的行。select_expression指出你想要检索的列。SELECT也可以用来检索不引用任何表的计算行
1、
select*from table1;
2、
select field1,field2 from table1;
3、
select count(*)from table2;
4、
select table1.filed1,table2.filed2 from table1,table2 where table1.field1='valed1';
5、
select *from table1 where field1='valed1' and fiels2='valed2' orded by field1;
6、
select*from table1 where filed1='valed1' order byfiled1 desc linit n;
7、
select *from table2 where name like '%$lin%';(模糊)
8、
sub_selects(高级)
select *from table1 where id In(select id from table2......);
9、
select ...into table...(高级)
(可用select...into outfile...;insert...selkect...替代)
10、SELECT MAX(field1) AS field1 FROM table1 列的最大值
其中:表:table 字段:field
二、修改
"update table1 set field1='value1',field2=value2'where fiels3='values3";
UPDATE用新值更新现存表中行的列,SET子句指出哪个列要修改和他们应该被给定的值,WHERE子句,如果给出,指定哪个行应该被更新,否则所有行被更新。
三、插入:
1、
insert into table1 values('field1',field2',...);
INSERT ... VALUES形式的语句基于明确指定的值插入行.
2、
replace into tbl_name(1,2,3)values('1','2','3');
REPLACE功能与INSERT完全一样,除了如果在表中的一个老记录具有在一个唯一索引上的新记录有相同的值,在新记录被插入之前,老记录被删除。
四、删除:
$a="delet from table1 where field1='$value1' and field2='$value2'";
DELETE从tbl_name表中删除满足由where_definition给出的条件的行,并且返回删除记录的个数。如果你执行一个没有WHERE子句的DELETE,所有行都被删除。
从一个MySQL的例子来学习查询语句
2019-10-16 13:16mysql教程网 Mysql
自上学这么多年以来,得出了从一个例子入手来学习是最快最有效,并能培养出很强的实践能力,这是一种很好的学习方法。不访试试。比如看一本书的时候从各章节的例子入手,找出不了解的以及不懂的还是新知识, 进而有针对
延伸 · 阅读
- 2022-06-24实战搭建MySQL高可用架构(手残党表示都会了!)
- 2022-06-24MySQL 数据库查询慢(除了索引问题还可能是什么原
- 2022-06-24面试官:线上MySQL的自增id用尽怎么办?
- 2022-04-29手残又删库了,binlog救了我的命……
- 2022-04-26MySQL优化的五个维度,你学会了吗?
- 2022-04-26MySQL到底支不支持哈希索引?
- Mysql

清理Mysql general_log的方法总结
在本篇文章里小编给大家分享的是一篇关于清理Mysql general_log的相关知识点,需要的朋友们学习下。...
- Mysql

MySQL启动报错问题InnoDB:Unable to lock/ibdata1 error
这篇文章主要介绍了MySQL启动报错问题InnoDB:Unable to lock/ibdata1 error,文中通过示例代码介绍的非常详细,对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,需要...
- Mysql
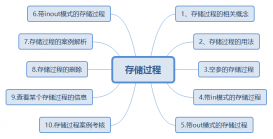
MySQL教程彻底学懂存储过程
这篇文章主要为大家介绍了MySQL系列的存储过程,文中详细的为大家解释存储过程的相关概念及用法语法,以及对存储过程的理解解析,有需要的朋友可以...
- Mysql
win10 64位 MySQL8.0下载和安装教程图解
这篇文章主要介绍了MySQL下载和安装 win10 64位 MySQL8.0的教程图解,本文图文并茂给大家介绍的非常详细,具有一定的参考借鉴价值,需要的朋友可以参考下...
- Mysql

幻读为什么会被 MySQL 单独拎出来解决?
所谓幻读,即一个事务在前后两次查询同一个范围的时候,后一次查询看到了前一次查询没有看到的行,这个回答估计大伙儿已经背烂了,但是它具体有什...
- Mysql

数据库管理,不能没有这5个MySQL GUI工具
MySQL的数据库管理工具非常多,有哪些优秀的GUI工具可以帮助提高工作效率?不妨看一看这5个MySQL GUI工具...
- Mysql

mysql数据库备份及恢复命令 mysqldump,source的用法
mysql数据库备份及恢复命令 mysqldump,source的用法,需要的朋友可以参考下。 ...
- Mysql
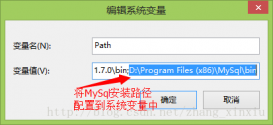
mysql 5.6.17 绿色版(免安装)安装配置教程
这篇文章主要为大家详细介绍了mysql 5.6.17 绿色版(免安装)安装配置教程,感兴趣的小伙伴们可以参考一下...










