在使用PG数据库的这段时间,总结了三种删除重复数据的方法,其中最容易想到的就是最常规的删除方法,但此方法性能较差,删数据耗时较久,虽容易实现,但性能太差,影响写数据的速率。
另外就是被使用的group by删除方法,效率较高。
还有一种是刚发现的,还没有验证,现在就总结下这三种删除方法,并验证各自的执行效率。
首先创建一张基础表,并插入一定量的重复数据。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
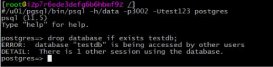
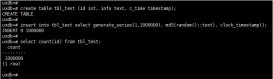
test=# create table deltest(id int, name varchar(255));CREATE TABLEtest=# create table deltest_bk (like deltest);CREATE TABLEtest=# insert into deltest select generate_series(1, 10000), 'ZhangSan';INSERT 0 10000test=# insert into deltest select generate_series(1, 10000), 'ZhangSan';INSERT 0 10000test=# insert into deltest_bk select * from deltest; |
常规删除方法
最容易想到的方法就是判断数据是否重复,对于重复的数据只保留ctid最小(或最大)的那条数据,删除其他的数据。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
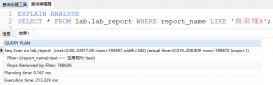
test=# explain analyse delete from deltest a where a.ctid <> (select min(t.ctid) from deltest t where a.id=t.id); QUERY PLAN ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Delete on deltest a (cost=0.00..195616.30 rows=1518 width=6) (actual time=67758.866..67758.866 rows=0 loops=1) -> Seq Scan on deltest a (cost=0.00..195616.30 rows=1518 width=6) (actual time=32896.517..67663.228 rows=10000 loops=1) Filter: (ctid <> (SubPlan 1)) Rows Removed by Filter: 10000 SubPlan 1 -> Aggregate (cost=128.10..128.10 rows=1 width=6) (actual time=3.374..3.374 rows=1 loops=20000) -> Seq Scan on deltest t (cost=0.00..128.07 rows=8 width=6) (actual time=0.831..3.344 rows=2 loops=20000) Filter: (a.id = id) Rows Removed by Filter: 19998 Total runtime: 67758.931 ms test=# select count(*) from deltest; count ------- 10000 (1 行记录) |
可以看到,id相同的数据,保留ctid最小的那条,其他的删除。相当于把deltest表中的数据删掉一半,耗时达到67s多。相当慢。
group by删除方法
第二种方法为group by方法,通过分组找到ctid最小的数据,然后删除其他数据。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
test=# truncate table deltest;TRUNCATE TABLEtest=# insert into deltest select * from deltest_bk;INSERT 0 20000test=# explain analyse delete from deltest a where a.ctid not in (select min(ctid) from deltest group by id); QUERY PLAN----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Delete on deltest a (cost=131.89..2930.46 rows=763 width=6) (actual time=30942.496..30942.496 rows=0 loops=1) -> Seq Scan on deltest a (cost=131.89..2930.46 rows=763 width=6) (actual time=10186.296..30814.366 rows=10000 loops=1) Filter: (NOT (SubPlan 1)) Rows Removed by Filter: 10000 SubPlan 1 -> Materialize (cost=131.89..134.89 rows=200 width=10) (actual time=0.001..0.471 rows=7500 loops=20000) -> HashAggregate (cost=131.89..133.89 rows=200 width=10) (actual time=10.568..13.584 rows=10000 loops=1) -> Seq Scan on deltest (cost=0.00..124.26 rows=1526 width=10) (actual time=0.006..3.829 rows=20000 loops=1) Total runtime: 30942.819 ms(9 行记录)test=# select count(*) from deltest; count-------10000(1 行记录) |
可以看到同样是删除一半的数据,使用group by的方式,时间节省了一半。但仍含需要30s,下面试一下第三种删除操作。
新的删除方法
在postgres修炼之道这本书中,作者提到一种效率较高的删除方法, 在这里验证一下,具体如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
test=# truncate table deltest;TRUNCATE TABLEtest=# insert into deltest select * from deltest_bk;INSERT 0 20000 test=# explain analyze delete from deltest a where a.ctid = any(array (select ctid from (select row_number() over (partition by id), ctid from deltest) t where t.row_number > 1)); QUERY PLAN----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Delete on deltest a (cost=250.74..270.84 rows=10 width=6) (actual time=98.363..98.363 rows=0 loops=1)InitPlan 1 (returns $0) -> Subquery Scan on t (cost=204.95..250.73 rows=509 width=6) (actual time=29.446..47.867 rows=10000 loops=1) Filter: (t.row_number > 1) Rows Removed by Filter: 10000 -> WindowAgg (cost=204.95..231.66 rows=1526 width=10) (actual time=29.436..44.790 rows=20000 loops=1) -> Sort (cost=204.95..208.77 rows=1526 width=10) (actual time=12.466..13.754 rows=20000 loops=1) Sort Key: deltest.id Sort Method: quicksort Memory: 1294kB -> Seq Scan on deltest (cost=0.00..124.26 rows=1526 width=10) (actual time=0.021..5.110 rows=20000 loops=1)-> Tid Scan on deltest a (cost=0.01..20.11 rows=10 width=6) (actual time=82.983..88.751 rows=10000 loops=1) TID Cond: (ctid = ANY ($0))Total runtime: 98.912 ms(13 行记录)test=# select count(*) from deltest;count-------10000(1 行记录) |
看到上述结果,真让我吃惊了一把,这么快的删除方法还是首次看到,自己真实孤陋寡闻,在这里要膜拜一下修炼之道这本书的大神作者了。
补充:pgsql 删除表中重复数据保留其中的一条
1.在表中(表名:table 主键:id)增加一个字段rownum,类型为serial
2.执行语句:
|
1
2
3
|
delete from table where rownum not in( select max(rownum) from table group by id ) |
3.最后删除rownum
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。如有错误或未考虑完全的地方,望不吝赐教。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/arcticJian/article/details/50042647