数据结构算法复杂度
1、影响算法效率的主要因素
(1)算法采用的策略和方法;
(2)问题的输入规模;
(3)编译器所产生的代码;
(4)计算机执行速度。
2、时间复杂度
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
// 时间复杂度:2n + 5 long sum1(int n) { long ret = 0; \\1 int* array = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int)); \\1 int i = 0; \\1 for(i=0; i<n; i++) \\n { array[i] = i + 1; } for(i=0; i<n; i++) \\n { ret += array[i]; } free(array); \\1 return ret; \\1 } \\时间复杂度: n + 3 long sum2(int n) { long ret = 0; \\1 int i = 0; \\1 for(i=1; i<=n; i++) \\n { ret += i; } return ret; \\1 } \\时间复杂度: 3 long sum3(int n) { long ret = 0; \\1 if( n > 0 ) { ret = (1 + n) * n / 2; \\1 } return ret; \\1 } |
随着问题规模n的增大,它们操作数量的差异会越来越大,因此实际算法在时间效率上的差异也会变得非常明显!
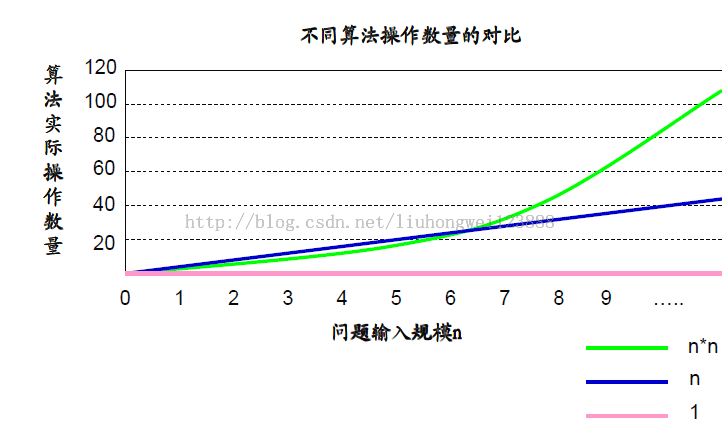
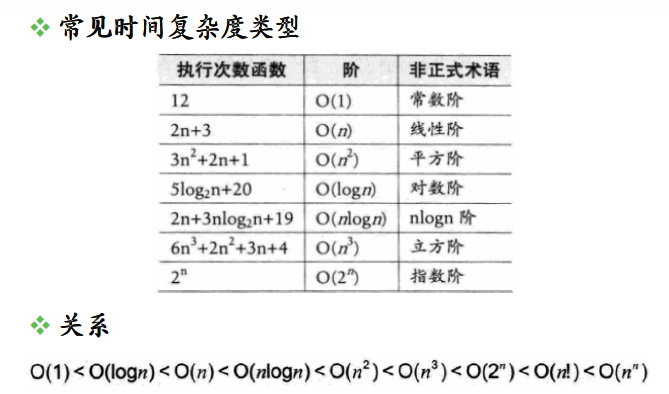
判断一个算法的效率时,往往只需要关注操作数量的最高次项,其它次要项和常数项可以忽略。

在没有特殊说明时,我们所分析的算法的时间复杂度都是指最坏时间复杂度。
3、空间复杂度
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
//空间复杂度:12 + n long sum1(int n) { long ret = 0; \\4 int* array = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int)); \\4 + 4 * n int i = 0; \\4 for(i=0; i<n; i++) { array[i] = i + 1; } for(i=0; i<n; i++) { ret += array[i]; } free(array); return ret; } \\空间复杂度: 8 long sum2(int n) { long ret = 0; \\4 int i = 0; \\4 for(i=1; i<=n; i++) { ret += i; } return ret; } \\空间复杂度: 4 long sum3(int n) { long ret = 0; \\4 if( n > 0 ) { ret = (1 + n) * n / 2; } return ret; } |
多数情况下,算法执行时所用的时间更令人关注,如果有必要,可以通过增加空间复杂度来降低时间复杂度,同理,也可以通过增加时间复杂度来降低空间复杂度,具体问题,具体分析。
数据结构顺序表
表是具有相同类型的n(n >= 0)个数据元素的有限序列,即:
- 线性表(List)是零个或多个数据元素的集合
- 线性表中的数据元素之间是有顺序的
- 线性表中的数据元素个数是有限的
- 线性表中的数据元素的类型必须相同
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
|
//seq_list.h #ifndef _SEQ_LIST_H_ #define _SEQ_LIST_H_ struct seq_list { int capacity; int length; unsigned int *node; }; struct seq_list* seq_list_create(int capacity); int seq_list_capacity(struct seq_list* list); int seq_list_length(struct seq_list* list); int seq_list_insert(struct seq_list* list, int position, void* data); void* seq_list_get(struct seq_list* list, int position); void* seq_list_remove(struct seq_list* list, int position); void seq_list_clear(); void seq_list_destroy(struct seq_list* list); #endif //seq_list.c #include "seq_list.h" #include <stddef.h> #include <malloc.h> struct seq_list* seq_list_create(int capacity) { int i = 0; struct seq_list* ret = NULL; if (capacity >= 0) { ret = (struct seq_list*) malloc(sizeof(struct seq_list) + sizeof(unsigned int) * capacity); if (ret != NULL) { ret->capacity = capacity; ret->length = 0; ret->node = (unsigned int*) (ret + 1); } } return ret; } int seq_list_insert(struct seq_list* list, int position, void* data) { int i = 0; int ret; ret = (list != NULL); ret = ret && position >= 0 && position < list->capacity; ret = ret && list->length < list->capacity; if (ret) { for (i = list->length; i > position; i--) { list->node[i] = (list->node[i - 1]); } list->node[i] = (unsigned int)data; double *p = (double *)data; list->length++; } return ret; } void* seq_list_get(struct seq_list* list, int position) { void* ret = NULL; if (list != NULL && position >= 0 && position < list->length) { ret = (void *)list->node[position]; } return ret; } void* seq_list_remove(struct seq_list* list, int position) { void* ret = NULL; int i = 0; if (list != NULL && position >= 0 && position < list->length) { int i = 0; ret = seq_list_get(list, position); for (i = position + 1; i < list->length; i++) { list->node[i - 1] = list->node[i]; } list->length--; } return ret; } int seq_list_capacity(struct seq_list* list) { int ret = -1; if (list != NULL) { ret = list->capacity; } return ret; } int seq_list_length(struct seq_list* list) { int ret = -1; if (list != NULL) { ret = list->length; } return ret; } void seq_list_clear(struct seq_list* list) { if (list != NULL) { list->length = 0; } } void seq_list_destroy(struct seq_list* list) { free(list); list = NULL; } //seq_list_main.c #include <stdio.h> #include "seq_list.h" int main(void) { struct seq_list* list = seq_list_create(100); double *p = NULL; int ret = 0; double a = 1.1; double b = 2.2; double c = 3.3; double d = 4.4; double e = 5.5; seq_list_insert(list, 0, &a); seq_list_insert(list, 1, &b); seq_list_insert(list, 2, &c); seq_list_insert(list, 3, &d); seq_list_insert(list, 4, &e); printf("list capacity = %d, length = %d\n", seq_list_capacity(list), seq_list_length(list)); p = (double *)seq_list_get(list, 0); if (p != NULL) { printf("%lf\n", *p); } p = (double *)seq_list_get(list, 3); if (p != NULL) { printf("%lf\n", *p); } p = (double *)seq_list_remove(list, 3); if (p != NULL) { printf("remove data %lf, index at 3 , after length: %d\n", *p, seq_list_length(list)); } p = (double *)seq_list_get(list, 3); if (p != NULL) { printf("after remove, index at 3: %lf\n", *p); } seq_list_clear(list); printf("after clear, list length is %d\n", seq_list_length(list)); seq_list_destroy(list); return 0; } |