目的
在刷算法题中经常遇到关于链表的操作,在使用go语言去操作链表时不熟悉其实现原理,目的是为了重温链表这一基础且关键的数据结构。
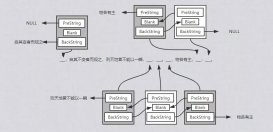
1、链表的特点和初始化
1.1、链表的特点
用一组任意的存储单元存储线性表的数据元素(这组存储单元可以是连续的,也可以是不连续的)
1.2、结点
结点(node)
- 数据域 => 存储元素信息
- 指针域 => 存储结点的直接后继,也称作指针或链
首元结点 是指链表中存储的第一个数据元素的结点
头结点 是在首元结点之前附设的一个结点,其指针域指向首元结点(非必须)
头指针 是指向链表中第一个结点的指针
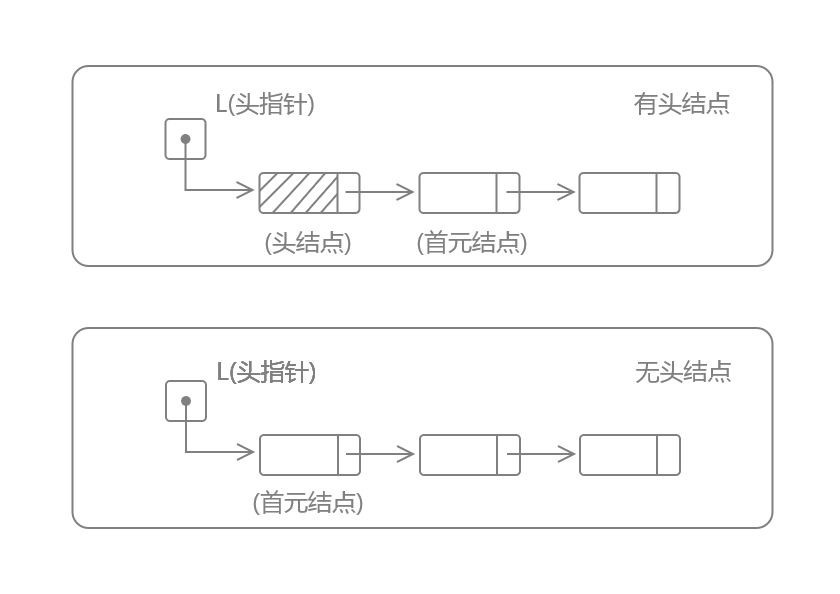
1.3、单链表
特点
- 每个结点中只包含一个指针域
- 单链表是非随机存取的存储结构,要取得第i个数据元素必须从头指针出发,顺链进行寻找,也称为顺序存取的存取结构
1.4、单链表的常用操作
本文主要实现了单链表的以下操作
- 判断是否为空
- 获取链表长度
- 在头部插入元素
- 在尾部插入元素
- 删除指定位置元素
- 删除指定值的元素
- 查找是否包含指定值
- 查找指定位置元素的值
- 遍历链表所有结点
1.5、单链表的初始化
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
//定义单链表结构体type Node struct { data interface{} //数据域 next *Node //指针域}type List struct { length int //储存链表的长度 headNode *Node}/*单链表的初始化1、生成新结点作为头结点,用头指针指向头结点2、头结点的指针域置空*/func InitList() *List { //即构造一个空的单链表L(包含头指针) node := new(Node) L := new(List) L.headNode = node return L} |
2、单链表的插入
先讲单链表的插入有利于后续相关操作的实现
2.1、在指定位置插入元素
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
/*单链表的插入=>将值为e的新结点插入到表的第i个结点的位置上,即插入到结点a(i-1)与a(i)之间1、查找结点a(i-1)并由指针p指向该结点2、生成一个新结点*s3、将新结点*s的数据域置为e4、将新结点*s的指针域指向结点a(i)5、将结点*p的指针域指向新结点*s*/func (list *List) InsertElem(index int, v interface{}) { if index <= 0 || index > list.length { fmt.Println("err") } else { pre := list.headNode node := &Node{data: v} if index == 1 { node.next = pre list.headNode = node } else { for count := 1; count < index-1; count++ { pre = pre.next } node.next = pre.next pre.next = node } list.length-- }} |
2.2、在头部插入元素
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
func (list *List) AddElem(v interface{}) { node := &Node{data: v} if list.IsNull() { //处理空表的插入,否则会导致一个空的头结点后移 list.headNode = node list.length++ return } node.next = list.headNode list.headNode = node list.length++ return} |
2.3、在尾部插入元素
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
func (list *List) AppendElem(v interface{}) { node := &Node{data: v} if list.IsNull() { list.headNode.next = node } else { cur := list.headNode for cur.next != nil { cur = cur.next } cur.next = node } list.length++ return} |
3、单链表的删除
3.1、删除指定值的元素
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
/*单链表的删除1、查找结点a(i-1)并由指针p指向该结点2、临时保存待删除结点a(i)的地址在q中,以备释放3、将结点*p的指针域指向a(i)的直接后继结点4、释放结点a(i)的空间*/func (list *List) DeleteElem(index int) { if index <= 0 || index > list.length { fmt.Println("删除位置不合理") return } else { pre := list.headNode if index == 1 { list.headNode = pre.next } else { pre := list.headNode for count := 1; count < index-1; count++ { pre = pre.next } pre.next = pre.next.next } list.length-- }} |
3.2、删除指定位置的元素
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
func (list *List) RemoveElem(v interface{}) { pre := list.headNode if pre.data == v { list.headNode = pre.next fmt.Println("ok") } else { for pre.next != nil { if pre.next.data == v { pre.next = pre.next.next fmt.Println("ok") return } else { pre = pre.next } } fmt.Println("fail") return }} |
4、单链表的查询
4.1、查找是否包含指定值
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
/*单链表的按值查找1、用指针p指向首元结点2、从首元结点开始以此顺着链域next向下查找,只要指向当前结点的指针p不为空,并且p所指结点的数据域不等于给定值e,则执行以下操作:p指向下一个结点3、返回p。若查找成功,p此时即为结点的地址值,若查找失败,p的值即为NULL。*/func (list *List) LocateElem(v interface{}) bool { if IsNull() { fmt.Println("err") } else { pre := list.headNode for pre != nil { if pre.data == v { return true } pre = pre.next } return false }} |
4.2、查找指定位置的值
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
/*单链表的取值1、用指针P指向首元结点,用j做计数器初值赋为12、从首元结点开始依次顺着链域(指针域)next向下访问,只要指向当前结点的指针P不为空,并且没有达到序号为i的结点,则循环执行以下操作: 2.1、P指向下一个结点 2.2、计数器j相应加13、退出循环时,如果指针P为空,或者计数器j大于i,说明指定的序号i值不合法(i大于表长n或i小于等于0),取值失败返回ERROR;否则取值成功,此时j==i时,P所指的结点就是要找的第i个结点,用参数e保存当前结点的数据域,返回OK*/func (list *List) GetElem(index int) int { if index <= 0 || index > list.length { fmt.Println("err") return } else { pre := list.headNode for j := 0; j < index; j++ { if pre != nil { pre = pre.next } } return pre.data }} |
4.3、遍历单链表
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
func (list *List) ShowList() { if !list.IsNull() { cur := list.headNode for { fmt.Printf("\t%v", cur.data) if cur.next != nil { cur = cur.next } else { break } } }} |
5、完整代码及结果展示
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
|
package mainimport "fmt"//定义单链表结构体type Node struct { data interface{} //数据域 next *Node //指针域}type List struct { length int //储存链表的长度 headNode *Node}/*type Method interface { IsNull() bool //1、判断是否为空 GetLength() int //2、获取链表长度 InsertElem(i int, v interface{}) //3、在指定位置添加元素 AddElem(v interface{}) //4、在头部插入元素 AppendElem(v interface{}) //5、在尾部插入元素 DeleteElem(i int) //6、删除指定位置元素 RemoveElem(v interface{}) //7、删除指定值的元素 ContaineElem(v interface{}) bool //8、是否包含指定值的元素 LocateElem(i int) interface{} //9、查找指定位置元素的值 ShowList() //10、遍历链表所有结点}*//*单链表的初始化1、生成新结点作为头结点,用头指针指向头结点2、头结点的指针域置空*/func InitList() *List { //即构造一个空的单链表L(包含头指针) node := new(Node) L := new(List) L.headNode = node return L}/*单链表的取值1、用指针P指向首元结点,用j做计数器初值赋为12、从首元结点开始依次顺着链域(指针域)next向下访问,只要指向当前结点的指针P不为空,并且没有达到序号为i的结点,则循环执行以下操作: 2.1、P指向下一个结点 2.2、计数器j相应加13、退出循环时,如果指针P为空,或者计数器j大于i,说明指定的序号i值不合法(i大于表长n或i小于等于0),取值失败返回ERROR;否则取值成功,此时j==i时,P所指的结点就是要找的第i个结点,用参数e保存当前结点的数据域,返回OK*/func (list *List) GetElem(index int) int { if index <= 0 || index > list.length { return 0 } else { pre := list.headNode for j := 0; j < index-1; j++ { if pre != nil { pre = pre.next } } return pre.data.(int) }}/*单链表的按值查找1、用指针p指向首元结点2、从首元结点开始以此顺着链域next向下查找,只要指向当前结点的指针p不为空,并且p所指结点的数据域不等于给定值e,则执行以下操作: 2.1、p指向下一个结点3、返回p。若查找成功,p此时即为结点的地址值,若查找失败,p的值即为NULL。*/func (list *List) LocateElem(v interface{}) bool { if list.IsNull() { fmt.Println("err") return false } else { pre := list.headNode for pre != nil { if pre.data == v { return true } pre = pre.next } return false }}/*单链表的插入=>将值为e的新结点插入到表的第i个结点的位置上,即插入到结点a(i-1)与a(i)之间1、查找结点a(i-1)并由指针p指向该结点2、生成一个新结点*s3、将新结点*s的数据域置为e4、将新结点*s的指针域指向结点a(i)5、将结点*p的指针域指向新结点*s*/func (list *List) InsertElem(index int, v interface{}) { if index <= 0 || index > list.length { fmt.Println("err") } else { pre := list.headNode node := &Node{data: v} if index == 1 { node.next = pre list.headNode = node } else { for count := 1; count < index-1; count++ { pre = pre.next } node.next = pre.next pre.next = node } list.length-- }}/*单链表的删除1、查找结点a(i-1)并由指针p指向该结点2、临时保存待删除结点a(i)的地址在q中,以备释放3、将结点*p的指针域指向a(i)的直接后继结点4、释放结点a(i)的空间*/func (list *List) DeleteElem(index int) { if index <= 0 || index > list.length { fmt.Println("删除位置不合理") return } else { pre := list.headNode if index == 1 { list.headNode = pre.next } else { pre := list.headNode for count := 1; count < index-1; count++ { pre = pre.next } pre.next = pre.next.next } list.length-- }}func (list *List) RemoveElem(v interface{}) { pre := list.headNode if pre.data == v { list.headNode = pre.next } else { for pre.next != nil { if pre.next.data == v { pre.next = pre.next.next return } else { pre = pre.next } } fmt.Println("fail") return }}func (list *List) IsNull() bool { if list.length == 0 { return true } else { return false }}func (list *List) AddElem(v interface{}) { node := &Node{data: v} if list.IsNull() { //处理空表的插入,否则会导致一个空的头结点后移 list.headNode = node list.length++ return } node.next = list.headNode list.headNode = node list.length++ return}func (list *List) AppendElem(v interface{}) { node := &Node{data: v} if list.IsNull() { list.headNode.next = node } else { cur := list.headNode for cur.next != nil { cur = cur.next } cur.next = node } list.length++ return}func (list *List) ShowList() { if !list.IsNull() { cur := list.headNode for { fmt.Printf("\t%v", cur.data) if cur.next != nil { cur = cur.next } else { break } } fmt.Printf("\n") }}func main() { L := InitList() msg := []int{12, 5, 3, 8, 55, 13} for i := range msg { L.AddElem(msg[i]) } fmt.Println("---- 添加元素 ----") L.AppendElem(66) L.ShowList() fmt.Println("---- 按位删除元素 ----") L.DeleteElem(3) L.ShowList() fmt.Println("---- 按值删除元素 ----") L.RemoveElem(13) L.ShowList() fmt.Println("---- 插入元素 ----") L.InsertElem(1, 88) L.ShowList() fmt.Println("---- 按值寻找元素 ----") fmt.Println(L.LocateElem(88)) fmt.Println("---- 按位寻找元素 ----") fmt.Println(L.GetElem(4))} |
结果
---- 添加元素 ----
13 55 8 3 5 12 66
---- 按位删除元素 ----
13 55 3 5 12 66
---- 按值删除元素 ----
55 3 5 12 66
---- 插入元素 ----
88 55 3 5 12 66
---- 按值寻找元素 ----
true
---- 按位寻找元素 ----
5
6、总结
本文中除了初始化时为链表添加了一个空的头结点,其他情况下均无头结点,正如书中所说,为单链表添加头结点会方便很多,对链表进行相关操作时,不需要对首元结点做额外的处理,也便于对空表和非空表做统一处理
关于删除时释放结点空间及指针回收,我们交由go强大的垃圾回收来完成
参考博客
Golang之单链表实现
go语言实现单链表
到此这篇关于详解go语言单链表及其常用方法的实现的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关go语言单链表内容请搜索服务器之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持服务器之家!
原文链接:https://studygolang.com/articles/31855