无限循环控件是一个常常用到的一个控件,尤其是一些广告或者应用内容公告通知,或者新闻滚动的设计,都是必备的。这种控件网上也有很多,也有很多可以自定义的版本,功能非常强大。 但对于我们开发者来说,在具体的应用上风格和样式都是比较统一的,一般只需要自己特定的一种风格或样式即可,引入第三方显然有点大材小用。那么我们怎么能简单而且又快速的造一个无限循环的控件呢,只要我们知道无限循环的原理,那么我们就很自由的按照需求快速的完成。今天我们就讲讲这个‘造轮'过程。
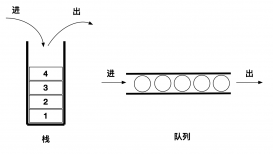
首先我们简单分析一下无限循环的原理。一个控件的自带滚动有UIScrollView、UICollectionView、UITableView。我们就选这个代表性的控件来讲------UICollectionView。他是一个横向和纵向都可以高度定制的一个控件,而且也遵循Cell重用机制。
第一步,数据倍数增加,一般为3倍,我们只显示中间那些数据即可,我们向左滑动的时候,滑到中间数据的最后一条数据的时候继续滑动的时候要瞬间换成中间的第一条数据。如果向右滑动的时候,如果当前是第一条数据那么就瞬间移到中间的最后一条数据上。这样看起来就是无限循环了。一图胜千言,有图为证。
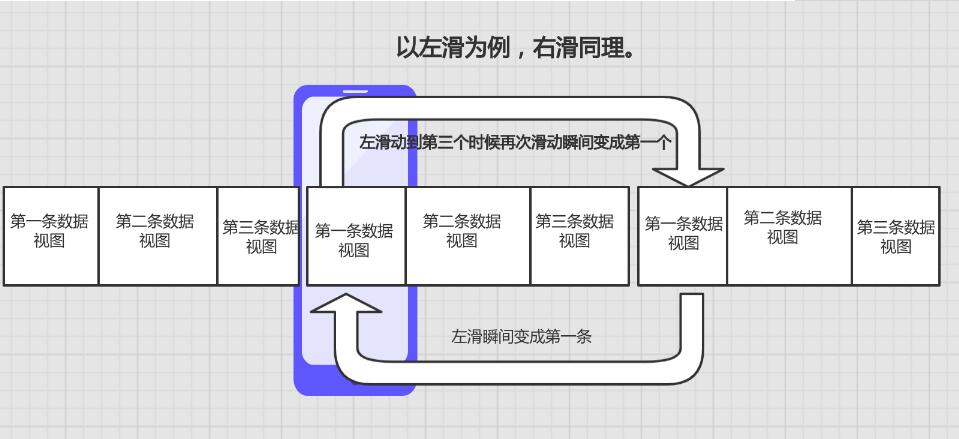
滑动原理很简单,那么我怎么来用代码实现呢。下面就使用代码来实现这个控件。
测试环境:Xcode版本: Version 11.5 (11E608c) Mac 系统:10.15.4 (19E266)
我们先创建一个工程命名为:InfiniteLoopDemo,然后我们在创建一个InfiniteLoopContentView视图。代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
|
import UIKit protocol InfiniteLoopContentViewDelegate: NSObjectProtocol { func infiniteLoopView(loopView: InfiniteLoopContentView,index: Int) -> UICollectionViewCell; func numberCountOfRows(loopView: InfiniteLoopContentView) -> Int; func infiniteLoopView(loopView: InfiniteLoopContentView,didSelectedIndexPath index: Int); func didEndScrollView(loopView: InfiniteLoopContentView) -> Void} extension InfiniteLoopContentViewDelegate { func didEndScrollView(loopView: InfiniteLoopContentView) { }} class InfiniteLoopContentView: UICollectionView { private var perContentSize: CGFloat { return contentSize.width / 3; } weak var infiniteDelegate: InfiniteLoopContentViewDelegate! private var perCount = 0; private var isAutoScroll = false; private let runDiration: Double = 3.2; weak fileprivate var pageControl: UIPageControl! var beginTimer = true { didSet{ runTimer(); } } private var width: CGFloat { frame.width } private var height: CGFloat { frame.height } private func runTimer() -> Void { if beginTimer { NSObject.cancelPreviousPerformRequests(withTarget: self); perform(#selector(runTimerAction), with: nil, afterDelay: runDiration); }else { NSObject.cancelPreviousPerformRequests(withTarget: self); isAutoScroll = false; } } @objc func runTimerAction() -> Void { if perCount <= 1 || contentSize.width < self.width { return; } let offsetx = contentOffset.x; guard let indexPath = indexPathForItem(at: .init(x: offsetx + width/2, y: height/2)) else{ return; } isAutoScroll = true; var next = indexPath.row + 1; if next >= (perCount * 3 - 1) { next = perCount * 3 - 1; UIView.animate(withDuration: 0.3, animations: { self.scrollToItem(at: .init(row: next, section: 0), at: .centeredHorizontally, animated: false); }) { (finished) in self.pageControl?.currentPage = self.perCount - 1; self.contentOffset = .init(x: (self.perCount - 1) * Int(self.width), y: 0); } }else{ scrollToItem(at: .init(row: next, section: 0), at: .centeredHorizontally, animated: true); pageControl?.currentPage = next % perCount; } perform(#selector(runTimerAction), with: nil, afterDelay: runDiration); } override init(frame: CGRect, collectionViewLayout layout: UICollectionViewLayout) { super.init(frame: frame, collectionViewLayout: layout); if let subLayout = layout as? UICollectionViewFlowLayout { subLayout.scrollDirection = .horizontal; subLayout.minimumLineSpacing = 0; subLayout.minimumInteritemSpacing = 0; subLayout.itemSize = .init(width: width, height: height); } showsHorizontalScrollIndicator = false; showsVerticalScrollIndicator = false; isPagingEnabled = true; delegate = self; dataSource = self; backgroundColor = UIColor.systemBackground; runTimer(); } deinit { infiniteDelegate = nil; beginTimer = false; } required init?(coder: NSCoder) { fatalError("init(coder:) has not been implemented") } override func layoutSubviews() { super.layoutSubviews(); if perCount <= 1 || isAutoScroll { return; } if contentSize.width < self.width { return; } let contentOffset = self.contentOffset; if contentOffset.x >= (perContentSize * 2) { let offset = contentOffset.x - (perContentSize * 2); self.contentOffset = .init(x: perContentSize + offset, y: 0); }else if contentOffset.x < perContentSize { let offset = Int(contentOffset.x) % Int(perContentSize); self.contentOffset = .init(x: perContentSize + CGFloat(offset), y: 0); } pageControl?.currentPage = Int((contentOffset.x + width/2) / width) % perCount; }} extension InfiniteLoopContentView: UICollectionViewDelegateFlowLayout,UICollectionViewDataSource{ // MARK: - collection view delegate and dataSource func collectionView(_ collectionView: UICollectionView, numberOfItemsInSection section: Int) -> Int { perCount = infiniteDelegate?.numberCountOfRows(loopView: self) ?? 0 if perCount == 1 { return perCount; } return perCount * 3; } func collectionView(_ collectionView: UICollectionView, layout collectionViewLayout: UICollectionViewLayout, sizeForItemAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> CGSize { return collectionView.bounds.size; } func collectionView(_ collectionView: UICollectionView, cellForItemAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> UICollectionViewCell { return infiniteDelegate.infiniteLoopView(loopView: self, index: indexPath.row % perCount); } func collectionView(_ collectionView: UICollectionView, didSelectItemAt indexPath: IndexPath) { infiniteDelegate.infiniteLoopView(loopView: self, didSelectedIndexPath: indexPath.row % perCount); } } extension InfiniteLoopContentView { func scrollViewWillBeginDragging(_ scrollView: UIScrollView) { beginTimer = false; } func scrollViewDidEndDecelerating(_ scrollView: UIScrollView) { beginTimer = true; infiniteDelegate?.didEndScrollView(loopView: self); } func scrollViewDidEndDragging(_ scrollView: UIScrollView, willDecelerate decelerate: Bool) { if !decelerate { scrollViewDidEndDecelerating(scrollView); } } func scrollViewDidEndScrollingAnimation(_ scrollView: UIScrollView) { scrollViewDidEndDecelerating(scrollView); }} |
这个是循环的主要代码,这里需要注意一下如果只有一条数据是禁止循环的。如果需要一张循环,自己可以实现以下。
使用的方法和UICollectionView一样,我们来看具体使用方式:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
|
import UIKit class MainViewController: UIViewController { var loopView: InfiniteLoopContentView! override func viewDidLoad() { super.viewDidLoad() // Do any additional setup after loading the view. let layout = UICollectionViewFlowLayout(); loopView = InfiniteLoopContentView(frame: .init(x: 0, y: 200, width: view.frame.width, height: 200), collectionViewLayout: layout); view.addSubview(loopView); loopView.infiniteDelegate = self; loopView.register(LoopViewCell.self, forCellWithReuseIdentifier: "cell"); loopView.reloadData(); } } extension MainViewController: InfiniteLoopContentViewDelegate{ func infiniteLoopView(loopView: InfiniteLoopContentView, index: Int) -> UICollectionViewCell { let cell = loopView.dequeueReusableCell(withReuseIdentifier: "cell", for: .init(row: index, section: 0)) as! LoopViewCell; cell.imageView.image = UIImage(named: (index + 1).description); return cell; } func numberCountOfRows(loopView: InfiniteLoopContentView) -> Int { return 3; } func infiniteLoopView(loopView: InfiniteLoopContentView, didSelectedIndexPath index: Int) { } } class LoopViewCell: UICollectionViewCell { var imageView: UIImageView! override init(frame: CGRect) { super.init(frame: frame); imageView = UIImageView(frame: bounds); imageView.contentMode = .scaleAspectFit; addSubview(imageView); backgroundColor = UIColor.black } required init?(coder: NSCoder) { fatalError("init(coder:) has not been implemented") }} |
这是SwiftUI创建的工程,所以我们可以只用使用最新的Canvars来预览效果就好。如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
struct ContentView: View { var body: some View { ViewController() }} struct ContentView_Previews: PreviewProvider { static var previews: some View { ContentView() }} struct ViewController: UIViewControllerRepresentable { func makeUIViewController(context: Context) -> MainViewController { MainViewController() } func updateUIViewController(_ uiViewController: MainViewController, context: Context) { } typealias UIViewControllerType = MainViewController } |
预览的效果如下:

最后上传上Demo,猛戳这里
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/yaojinhai06/article/details/107575194